GOC Army Headquarters
| General Officer Commanding Army Headquarters | |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1998 |
| Country |
|
| Allegiance |
|
| Size |
133,000 active 380,000 reserve |
| Nickname(s) | Mazi |
| Engagements |
South Lebanon conflict (1985–2000) First Intifada (1987–1993) Second Intifada (2000–2005) Second Lebanon War (2006) Operation Cast Lead (2008–2009) Pillar of Defense (2012) Protective Edge (2014) |
| Commanders | |
| Major general | Kobi Barak |
The Israeli GOC Army headquarters (Hebrew: זרוע היבשה, Zro'a ha-Yabasha, "Ground Arm"), known unofficially as Mazi, is a multi-corps command headquarters created in 1998, which amalgamates the ground forces of the Israel Defense Forces. The current size of the Israeli Ground Forces is estimated at roughly 133,000 active soldiers and 380,000 soldiers in reserve.
Name
The GOC Army Headquarters is known unofficially as Mazi, the Hebrew pronunciation for an acronym for "Ground Arm Command" (מז"י, (מפקדת זרוע היבשה, Mifkedet Zro'a ha-Yabasha), which was the GOC Army Headquarters' previous name before being renamed to the current "Ground Arm" (זרוע היבשה). After this renaming, the acronym MAZI officially refers nowadays to "Commander of the Ground Arm" (מפקד זרוע היבשה, Mefaked Zro'a Ha-Yabasha). However the old acronym MAZI still remains the popular name for the GOC Army Headquarters.
Units and structure
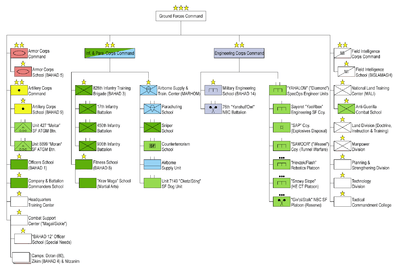
MAZI includes the five ground-warfare corps of specific military functions:
- The maneuvering corps:
- Infantry Corps (חיל הרגלים)
- Armor Corps (חיל השריון)
- The combat support corps:
- Artillery Corps (חיל התותחנים)
- Combat Engineering Corps (חיל ההנדסה הקרבית)
- Combat Intelligence Corps (חיל האיסוף הקרבי)
In addition, MAZI includes four "staff divisions":
- Planning Division (Budget and Organization Planning) (חטיבת התכנון)
- "Ground" Division (Training and Doctrine) (חטיבת יבשה)
- Personnel Division (חטיבת כוח-אדם)
- Technological Division (Materiel R&D and Acquisition) (חטיבת הטכנולוגיה)
The IDF's third arm
Under the IDF 2000 reforms, MAZI was set to become the IDF's third Arm, alongside the Air and Space Arm and the Sea Arm. Until the creation of MAZI, IDF ground forces were directly subordinated to the Chief of Staff through the Regional Commands (North, South, and Central). The intention of the reform was to subordinate the ground forces to one ground commander, who is a part of the Joint Staff, by the example of the Israeli Air Force and Navy; and unlike most of the other armed forces, where operational Army, Air Force, and Navy plus other auxiliary support units, are all subordinated to unified commands.
The proposed reform for the Ground Arm was rejected and the ground forces remain subordinated to the three regional commands. Likewise with combat support and rear-line corps, which are partly subordinated to the respective Directorates. In times of war, the Ground Arm Commander acts as an advisor to the IDF Chief of Staff on ground warfare.
As an IDF arm, the Ground Arm is meant to build of the ground forces' strength and working toward balance, combination, and coordination between the ground corps. It does so by instruction and training of individual units, planning and publishing the relevant doctrine, organizing the forces respectively for their missions, and R&D and acquisition of materiel. Its authority ranges up to the corps level. Above it, meaning the regional commands themselves, the authority is of the IDF Joint Staff.
Ranks
- Officers
| Equivalent NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) & Student officer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Unknown | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
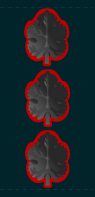
| Rav aluf Chief General |
Aluf General |
Tat aluf Subordinate General |
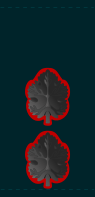
Aluf mishne Junior General |
Sgan aluf Deputy General |
Rav seren Chief Commander |
Seren Captain |
Segen Deputy |
Segen mishne Junior Deputy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Enlisted
| Equivalent NATO Code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | No insignia | No equivalent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief warrant officer (רב-נגד (רנ"ג |
Warrant officer (רב-נגד משנה (רנ"מ |
Command Sergeant Major (רב-סמל בכיר (רס"ב |
Sergeant Major (רב-סמל מתקדם (רס"מ |
Master Sergeant (רב-סמל ראשון (רס"ר |
Sergeant First Class (רב-סמל (רס"ל |
Staff Sergeant (סמל ראשון (סמ"ר |
Sergeant סמל |
Corporal (רב טוראי (רב"ט |
Private טוראי | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heads of Mafchash and MAZI
- Dan Shomron (1983–1985)
- Amir Drori (1985–1986)
- Uri Sagi (1986–1991)
- Emanuel Sakel (1991–1994)
- Ze'ev Livne (1994–1996)
- Amos Malka (1996–1998)
- Moshe Soknik (1998–2001)
- Yiftah Ron-Tal (2001–2005)
- Benjamin Gantz (2005 – December 20, 2007)
- Avi Mizrahi (December 20, 2007 – 2009)
- Sami Turgeman (2009–2013)[1]
- Guy Tzur (2013-2016)
- Kobi Barak (since 2016)
IDF Ground Forces equipment
Future
The IDF is currently planning major structural reform. Due to the poor training and equipment among army reservists, large numbers will be dismissed.[2]