GNGT1
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(T) subunit gamma-T1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNGT1 gene.[5][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000127928 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029663 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
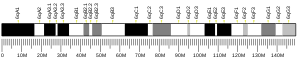
- ↑ Scherer SW, Feinstein DS, Oliveira L, Tsui LC, Pittler SJ (Sep 1996). "Gene structure and chromosome localization to 7q21.3 of the human rod photoreceptor transducin gamma-subunit gene (GNGT1)". Genomics. 35 (1): 241–3. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0346. PMID 8661128.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: GNGT1 guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma transducing activity polypeptide 1".
Further reading
- Simonds WF, Butrynski JE, Gautam N, et al. (1991). "G-protein beta gamma dimers. Membrane targeting requires subunit coexpression and intact gamma C-A-A-X domain". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (9): 5363–6. PMID 1706334.
- Ray K, Kunsch C, Bonner LM, Robishaw JD (1995). "Isolation of cDNA clones encoding eight different human G protein gamma subunits, including three novel forms designated the gamma 4, gamma 10, and gamma 11 subunits". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (37): 21765–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.37.21765. PMID 7665596.
- Tao L, Pandey S, Simon MI, Fong HK (1993). "Structure of the bovine transducin gamma subunit gene and analysis of promoter function in transgenic mice". Exp. Eye Res. 56 (4): 497–507. doi:10.1006/exer.1993.1063. PMID 8500562.
- Yan K, Kalyanaraman V, Gautam N (1996). "Differential ability to form the G protein betagamma complex among members of the beta and gamma subunit families". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (12): 7141–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.12.7141. PMID 8636150.
- Gaudet R, Savage JR, McLaughlin JN, et al. (1999). "A molecular mechanism for the phosphorylation-dependent regulation of heterotrimeric G proteins by phosducin". Mol. Cell. 3 (5): 649–60. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80358-5. PMID 10360181.
- Xu S, Ladak R, Swanson DA, et al. (2000). "PHR1 encodes an abundant, pleckstrin homology domain-containing integral membrane protein in the photoreceptor outer segments". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (50): 35676–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.50.35676. PMID 10585447.
- Marin EP, Krishna AG, Zvyaga TA, et al. (2000). "The amino terminus of the fourth cytoplasmic loop of rhodopsin modulates rhodopsin-transducin interaction". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (3): 1930–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.3.1930. PMID 10636894.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Cuello F, Schulze RA, Heemeyer F, et al. (2003). "Activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by a high energy phosphate transfer via nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) B and Gbeta subunits. Complex formation of NDPK B with Gbeta gamma dimers and phosphorylation of His-266 IN Gbeta". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (9): 7220–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210304200. PMID 12486123.
- Scherer SW, Cheung J, MacDonald JR, et al. (2003). "Human chromosome 7: DNA sequence and biology". Science. 300 (5620): 767–72. doi:10.1126/science.1083423. PMC 2882961. PMID 12690205.
- Hillier LW, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7". Nature. 424 (6945): 157–64. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948.
- Hinrichs MV, Montecino M, Bunster M, Olate J (2005). "Mutation of the highly conserved Arg165 and Glu168 residues of human Gsalpha disrupts the alphaD-alphaE loop and enhances basal GDP/GTP exchange rate". J. Cell. Biochem. 93 (2): 409–17. doi:10.1002/jcb.20193. PMID 15368366.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Gao X, Sadana R, Dessauer CW, Patel TB (2007). "Conditional stimulation of type V and VI adenylyl cyclases by G protein betagamma subunits". J. Biol. Chem. 282 (1): 294–302. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607522200. PMID 17110384.
- Seo M, Lee MJ, Heo JH, et al. (2007). "G Protein betagamma subunits augment UVB-induced apoptosis by stimulating the release of soluble heparin-binding epidermal growth factor from human keratinocytes". J. Biol. Chem. 282 (34): 24720–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702343200. PMID 17548351.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.