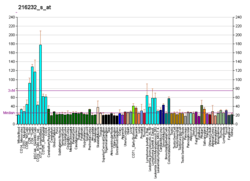
GCN1L1
Translational activator GCN1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GCN1L1 gene.[5][6]
Interactions
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000089154 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000041638 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Marton MJ, Vazquez de Aldana CR, Qiu H, Chakraburtty K, Hinnebusch AG (August 1997). "Evidence that GCN1 and GCN20, translational regulators of GCN4, function on elongating ribosomes in activation of eIF2alpha kinase GCN2". Mol Cell Biol. 17 (8): 4474–89. PMC 232301. PMID 9234705.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: GCN1L1 GCN1 general control of amino-acid synthesis 1-like 1 (yeast)".
- ↑ Ajuh, P; Kuster B; Panov K; Zomerdijk J C; Mann M; Lamond A I (December 2000). "Functional analysis of the human CDC5L complex and identification of its components by mass spectrometry". EMBO J. ENGLAND. 19 (23): 6569–81. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.23.6569. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 305846. PMID 11101529.
Further reading
- Nakajima D, Okazaki N, Yamakawa H, et al. (2003). "Construction of expression-ready cDNA clones for KIAA genes: manual curation of 330 KIAA cDNA clones". DNA Res. 9 (3): 99–106. doi:10.1093/dnares/9.3.99. PMID 12168954.
- Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, et al. (1997). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VI. The coding sequences of 80 new genes (KIAA0201-KIAA0280) deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from cell line KG-1 and brain". DNA Res. 3 (5): 321–9, 341–54. doi:10.1093/dnares/3.5.321. PMID 9039502.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Bouwmeester T, Bauch A, Ruffner H, et al. (2004). "A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (2): 97–105. doi:10.1038/ncb1086. PMID 14743216.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. Bibcode:2005Natur.433...77A. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Scherer SE, Muzny DM, Buhay CJ, et al. (2006). "The finished DNA sequence of human chromosome 12". Nature. 440 (7082): 346–51. Bibcode:2006Natur.440..346S. doi:10.1038/nature04569. PMID 16541075.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.