Focal cloud
| Part of a series on |
| Antennas |
|---|
 |
|
Common types |
|
Radiation sources / regions |
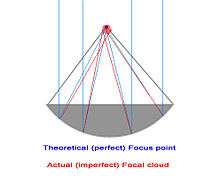
A focal cloud is the collection of focal points of an imperfect lens or parabolic reflector whether optical, electrostatic or electromagnetic. This includes parabolic antennas and lens-type reflective antennas of all kinds. The effect is analogous to the circle of confusion in photography.
In a perfect lens or parabolic reflector, rays parallel to the device's axis striking the lens or reflector all pass through a single point, the focal point. In an imperfectly constructed lens or reflector, rays passing through different parts of the element do not converge to a single point but have different focal points. The set of these focal points forms a region called the focal cloud. The diameter of the focal cloud determines the maximum resolution of the optical system. Lens-reflector artifacts, geometry and other imperfections determine the actual diameter of the focal cloud.
Satellite dish effects
A focal cloud can render a satellite dish rather inefficient in relation to its size in specific frequencies. If the imperfections are formed in a way that the phase shifts of reflected waves, at a large portion of the dish, are near 180 degrees between them and the feed horn, this results in self-cancellation of the specific frequency.
For countering the effect, there are several techniques, either in construction of the reflectors or lenses, or in the way signal beams are concentrated. In satellite antennas, scalar rings are used to push the spread signal into the feed horn.
Satellite-based dish antennas may be deformed intentionally to distribute radiated power over a desired "footprint," typically shaped like a continent. Tidal action tends to move a satellite in a figure-8 pattern. Ground-based antennas should be aligned when the satellite is at the center of this pattern, or when the "bird is in the box" (slang used by satellite operators). Ground based dish antennas might benefit from minor deformation, producing a footprint encompassing satellite tidal motion.