First United States Army
| First Army | |
|---|---|
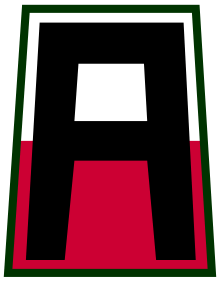 Shoulder sleeve insignia and combat service identification badge of the First United States Army. | |
| Active |
August 10, 1918 – April 20, 1919 September 8, 1932 – present |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Type | Security operations |
| Role | Training support |
| Size | Field army |
| Part of | United States Army Forces Command |
| Garrison/HQ |
Rock Island Arsenal Rock Island County, Illinois, U.S. |
| Nickname(s) | Doughboys |
| Motto(s) | First In Deed |
| Anniversaries | 10 August 1918 |
| Engagements |
World War I World War II |
| Website | Official website |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | MG Erik Peterson, Acting |
| Notable commanders |
John J. Pershing Omar Bradley Courtney Hodges Russel L. Honoré |
| Insignia | |
| Distinctive unit insignia |
 |
| Flag |
 |
The First Army is the oldest and longest established field army of the United States Army, having seen service in both World War I and World War II, under some of the most famous and distinguished officers of the U.S. Army. It now serves as a mobilization, readiness and training command.
History
Establishment and World War I
First Army was established on 10 August 1918 as a field army when sufficient American military manpower had arrived in France during World War I. As an element of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) in the latter stages of World War I it was the first of three field armies established under the AEF. Serving in its ranks were many figures who later played important roles in World War II. First Army was inactivated in April 1919.
Inter-war years
As part of an army reorganization and final realization of the 1920 amendment to the National Defense Act of 1916, Army Chief of Staff, General Douglas MacArthur directed the establishment of four field armies that each commanded three corps areas that were geographically located. The field armies were established to provide organizational structure for large military organizations that might be mobilized in time of national need.
First Army was located in the northeast United States and was activated on 11 September 1933 at Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York. Initially activated as a paper army, it was commanded by General Dennis E. Nolan. Until 1942, First Army's commander was always the senior commander of one of its three corps areas. The First Corps Area was headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts, Second Corps Area was headquartered at Fort Jay, Governors Island, in New York, New York, and Third Corps Area was located at Fort Howard (Maryland) near Baltimore, Maryland. Since First Army was only a paper organization in its early days, its staff was the existing staff of the corps areas. The overall mission of the First Army was commanding and training regular army, army reserve and national guard units in the three corps areas.
Nolan, the American Expeditionary Force's (AEF) chief of intelligence during World War I was followed by Major General Fox Conner, First Corps Area commander and another AEF veteran and its Chief of Operations. In the years after World War I, Conner was a crucial mentor in the careers of Dwight Eisenhower and George C. Marshall. Passed over as a candidate for Army Chief of Staff for Douglas MacArthur, Conner retired.
In 1938 First Army came under command of General Hugh A. Drum. Drum, who along with a buildup of the Army in 1939 and through the early 1940s, began to develop First Army into a bona fide field army. It began to establish and develop its own staff and participated in the large scale Army maneuvers in Louisiana and North Carolina between 1939 and 1941. As the United States entered World War II, Drum was assigned command of the newly established Eastern Defense Command, responsible for coastal and domestic defense, which relieved First Army of this responsibility on 24 December 1942. Drum retired in 1943 when he reached mandatory retirement age. General George Grunert, commander of Second Service Command, assumed command of First Army until Headquarters, First Army was activated in Bristol, England in January 1944 under command of General Omar Bradley.
World War II
First Army's entry into World War II began in October 1943 as Bradley returned to Washington, D.C. to receive his command and began to assemble a staff and headquarters to prepare for Operation Overlord, the codename assigned to the establishment of a large-scale lodgement on the European Continent following Operation Neptune, which was the invasion of Normandy. The headquarters were activated in January 1944 at Bristol, England.
Upon going ashore on 6 June 1944, D-Day, First Army came under General Bernard Montgomery's 21st Army Group (alongside the British Second Army) which commanded all American ground forces during the invasion. Three American divisions were landed by sea at the western end of the beaches, and two more were landed by air. On Utah Beach, the assault troops made good progress, but Omaha Beach came nearest of all of the five landing areas to disaster. The two American airborne divisions that landed were scattered all over the landscape, and caused considerable confusion among the German soldiers, as well as largely securing their objectives, albeit with units completely mixed up with each other. First Army captured much of the early gains of the Allied forces in Normandy. Once the beachheads were linked together, its troops struck west and isolated the Cotentin Peninsula, and then captured Cherbourg. When the American Mulberry harbour was wrecked by a storm, Cherbourg became even more vital.
After the capture of Cherbourg, First Army struck south. In Operation Cobra, its forces finally managed to break through the German lines. The newly established Third Army was then fed through the gap and raced across France.
With the arrival of more US troops in France, the Army then passed from the control of 21st Army Group to the newly arrived 12th Army Group which commanded the First Army and the newly formed Third Army under Lieutenant General George S. Patton. General Bradley assumed command of the 12th Army Group and Lieutenant General Courtney Hodges was placed in command of the First Army. First Army followed Third Army, the American armies forming the southern part of the encirclement of Germans at the Falaise pocket.
After capturing Paris (the Wehrmachtbefehlshaber von Groß-Paris, Dietrich von Choltitz, capitulated 25 August, ignoring Hitler's Trümmerfeldbefehl),[1][2] First Army headed towards the south of the Netherlands.
When the Germans attacked during the Battle of the Bulge, First Army found itself on the north side of the salient, and thus isolated from 12th Army Group, its commanding authority. It was, therefore, temporarily transferred, along with Ninth Army, back to 21st Army Group under Montgomery on 20 December.[3] The salient was reduced by early February 1945. Following the Battle of the Bulge, the Rhineland Campaign began, and First Army was transferred back to 12th Army Group. In Operation Lumberjack, First Army closed up to the lower Rhine by 5 March, and the higher parts of the river five days later.
On 7 March, in a stroke of luck, Company A, 27th Armored Infantry Battalion, part of Combat Command B, found the Ludendorff Bridge across the Rhine at Remagen still standing. It quickly captured the bridge and established a secure bridgehead. in the next 15 days, over 25,000 troops and their equipment crossed the river. By 4 April, an enormous pocket had been created by First Army and Ninth Army, which contained the German Army Group B under Field Marshal Model, the last significant combat force in the northwest of Germany. While some elements of First Army concentrated on reducing the Ruhr pocket, others headed further east, creating another pocket containing the German Eleventh Army. First Army reached the Elbe by 18 April. There the advance halted, as that was the agreed demarcation zone between the American and Soviet forces. First Army and Soviet forces met on 25 April.
In May 1945, advance elements of First Army headquarters had returned to New York City and were preparing to redeploy to the Pacific theater of the war to prepare for Operation Coronet, the planned second phase of Operation Downfall the proposed invasion of Honshū, the main island of Japan in the spring of 1946, but the Japanese surrender in August 1945 thanks to the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki terminated that effort.
Post-war and peacetime missions
First Army returned to the United States in late 1945; first to Fort Jackson (South Carolina), then to Fort Bragg, North Carolina, returning to Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York, in the spring of 1946. Twenty years later, in 1966, First Army relocated to Fort Meade, Maryland, and took over the responsibilities of Second Army, which was deactivated. In 1973, First Army's mission changed from training and preparation of active units to Army Reserve units. In a 1993 reorganization, five divisions carried out that training and support mission:
- 75th Division, Houston, Texas
- 78th "Lightning" Division, Edison, New Jersey
- 85th "Custer" Division, Arlington Heights, Illinois
- 87th "Golden Acorn" Division, Birmingham, Alabama
- 91st "Wild West" Division, Dublin, California
In 1993, Headquarters First Army relocated to Fort Gillem, near Atlanta, Georgia, and became responsible for the training and mobilization of all Army Reserve and National Guard units in the United States and providing assistance to the civilian sector during national emergencies and natural disasters. In the latter role, First Army's contributions during the 2005 Hurricane Katrina disaster was a rare bright spot in leading federal relief efforts in the aftermath of the storm. Its commander, Russel L. Honoré, a Louisiana native, became a nationally recognized figure in his direct, no-nonsense approach to disaster relief which earned First Army a Joint Meritorious Unit Award.
In the 21st century, First Army was subjected to more changes as base closures and force structures were instituted to modernize, economize and change its mission. In 2005, a BRAC decision called for the relocation of First Army headquarters to Rock Island Arsenal, Illinois, in 2011. Its former quarters at Fort Gillem was to transition to a single national location for the mobilization and demobilization of Army National Guard and Reserve units.
In a second change, as part of the 2006 reorganization of the United States Army program, First Army exchanged its civilian assistance mission for the training and support missions for military units in the western United States formerly held by US Fifth Army. Fifth Army then became U.S. Army, North with responsibilities for homeland defense and domestic emergency assistance.
First Army deactivated its training divisions and reactivated them as separate training brigades under two commands. First Army Division East, headquartered at Fort George G. Meade, Maryland, has responsibilities in all states east of the Mississippi River; and First Army Division West assuming Fifth Army's role and relocating from Fort Carson to its new headquarters at Fort Hood, Texas, oversees units in all states west of the Mississippi River.
First United States Army was redesignated as First Army on 3 October 2006.
Heraldic items
Shoulder sleeve insignia
- Description: On a background equally divided horizontally white and red, 3¼ inches high and 2½ inches wide at base and 2⅛ inches wide at top, a black block letter "A", 2¾ inches high, 2 inches wide at base and 1⅝ inches wide at top, all members 7/16 inch wide, all enclosed within a 1/8 inch Army Green border.
- Symbolism:
- The red and white of the background are the colors used in flags for Armies.
- The letter "A" represents "Army" and is also the first letter of the alphabet suggesting "First Army."
- Background:
- A black letter "A" was approved as the authorized insignia by the Commanding General, American Expedition Force, on 16 November 1918 and approved by the War Department on 5 May 1922.
- The background was added on 17 November 1950.
Insignia
- Description:
- A gold color metal and enamel device 1¼ inches high overall consisting of a black enamel capital letter "A" bearing three gold stars on the top cross bar and five gold on the center cross bar, in front of and interlaced with a gold fleur-de-lis.
- The vertical petal is charged in base with a red enamel arrowhead behind and extending above the letter "A" and the tops of the two outside or flanking petals above the cross bar extending over the vertical legs of the letter "A".
- The lower ends of the outside petals curve under and over the lower ends of the vertical legs of the letter "A" and are joined together by a gold arched scroll inscribed "First In Deed" in black enamel letters.
- The areas within the letter "A" above the center cross bar are white enamel and the areas below the cross bar are red enamel.
- Symbolism:
- The basic design was suggested by the authorized shoulder sleeve insignia of the First Army.
- The Interlaced fleur-de-lis represent wartime service in France and alludes to the initial organization of the Headquarters Company as the Headquarters Troop, First Army at La Ferte-sous-Jouarre, France 10 August 1918.
- The three stars at the top of the letter "A" are for Lorraine 1918, St. Mihiel and Meuse-Argonne campaigns in which the First Army participated in World War I.
- The five stars on the center cross bar are for the Normandy, Northern France, Rhineland, Ardennes-Alsace and Central Europe campaigns in which the First Army participated in World War II, the red arrowhead referring to the assault landing on the Normandy beaches.
- The motto "First In Deed" is based on the numerical designation, purpose and achievements of the First United States Army.
- Background: The insignia was approved on 27 January 1969.
Lineage
- The First United States Army was organized on 10 August 1918 in the Regular Army in France as Headquarters and Headquarters Troop, First Army.
- Headquarters Troop was reorganized and redesignated in September 1918 as Troop A, Headquarters Battalion, First Army. It saw action in the American Expeditionary Force in the latter stages of World War I and included many figures who were later to become very famous, such as Douglas MacArthur.
- Troop A, Headquarters Battalion, First Army was redesignated on 1 March 1919, as Headquarters Troop, First Army, and Headquarters and Headquarters Troop, First Army, demobilized on 20 April 1919 in France.
- First Army was Constituted 15 August 1927 in the Regular Army as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, Seventh Army, but was Redesignated 13 October 1927 as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, First Army.
- Headquarters, First Army activated 1 October 1933 at Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York. It had the mission of training Army formations at the time, as did all the other field armies.
- Headquarters Company activated 18 November 1940 at Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York.
- October 1943, Headquarters First Army relocated from Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York to Bristol, England in anticipation of Normandy invasion.
- A separate First Army was Reconstituted on 27 June 1944 in the Regular Army as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, First Army; concurrently consolidated with the original Headquarters and Headquarters Company, First Army. The consolidated unit designated as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, First Army.
- First Army Headquarters returns to Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York in 1946.
- First Army was Redesignated 1 January 1957 as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, First United States Army.
- Merger of First and Second Army, relocation of headquarters to Fort Meade and closure of Fort Jay, Governors Island, New York announced 20 November 1964.
- 1 January 1966, the First and Second U.S. Armies merged and First Army headquarters moved to Fort Meade, Maryland.
- Headquarters Company inactivated 5 June 1970 at Fort George G. Meade, Maryland, while Headquarters, First U.S. Army continued to function.
- In 1973 the First Army again changed its orientation to improving the readiness of the Reserve Components.
- In 1993, First Army headquarters was moved to Fort Gillem, Georgia (the former Atlanta Army Depot).
- 2005, First Army is awarded a Joint Meritorious Unit Award for leading federal response to Hurricane Katrina.[4]
- In 2006, it was announced that subject to Base Realignment and Closure Act, Fort Gillem will eventually be closed and First Army headquarters relocated to Rock Island Arsenal Illinois.
- 1 December 2006, First Army reorganizes and reflags its five Reserve Component Training Support Divisions into 16 training brigades and establishes two sub-commands, First Army Division East and First Army Division West. First Army East at Fort Meade, Maryland administers eight brigades east of the Mississippi River and First Army West at Fort Hood, Texas, assumes the training responsibilities with eight brigades formerly held by U.S. Fifth Army. Fifth Army becomes U.S. Army, North, and assumes First Army's domestic assistance duties.
First U.S. Army honors
Campaign participation credit
| Conflict | Streamer | Year(s) |
|---|---|---|
| World War I |
St. Mihiel | 1918 |
| Meuse-Argonne | 1918 | |
| Lorraine 1918 | 1918 | |
| World War II |
Normandy (with arrowhead) | 1944 |
| Northern France | 1944 | |
| Rhineland | 1945 | |
| Ardennes-Alsace | 1944–1945 | |
| Central Europe | 1945 | |
Decorations
| Ribbon | Award | Year | Orders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Meritorious Unit Award | 2005 | For leading the federal response to Hurricane Katrina 2005.[5] | |
| Army Superior Unit Award | 2001-2004 | Lineage & Honors Statement 30 April 2012[6] | |
| Army Superior Unit Award | 2004-2008 | Permanent Orders 120-10 30 April 2009[7] | |
| Army Superior Unit Award | 2008-2011 |  Permanent Orders 332-07 announcing award of the Army Superior Unit award | |
Organization
Current
![]()
- 4th "Saber" Cavalry Brigade – Fort Knox, Kentucky. Formerly the 85th Division's 4th Brigade.
- 157th "Spartan" Infantry Brigade – Fort Jackson, South Carolina. Formerly the 87th Division's 5th Brigade.
- 174th "Patriot" Infantry Brigade – Fort Dix, New Jersey. Formerly the 78th Division's 2nd Brigade.
- 177th "Mudcats" Armored Brigade – Camp Shelby, Mississippi. Formerly the 87th Division's 3rd Brigade.
- 188th "Battle Ready" Infantry Brigade – Fort Stewart, Georgia. Formerly the 87th Division's 4th Brigade.
![]()
- 5th Armored Brigade – Fort Bliss, Texas. Formerly the 91st Division's 2d Brigade.
- 120th Infantry Brigade – Fort Hood, Texas. Formerly the 75th Division's 2d Brigade.
- 166th Aviation Brigade – Fort Hood, Texas.
- 181st "Eagle" Infantry Brigade – Fort McCoy, Wisconsin. Formerly the 85th Division's 2d Brigade.
- 189th "Bayonet" Infantry Brigade – Fort Lewis, Washington. Formerly the 78th Division's 4th Brigade.
List of commanders
- GEN John J. Pershing 1918
- LTG Hunter Liggett 1918–1919
- MG Dennis E. Nolan 1932–1936
- MG Fox Conner 1936–1938
- MG Frank Ross McCoy 1938 (interim)
- MG James K. Parsons 1938 (interim)
- LTG Hugh A. Drum 1938–1943
- LTG George Grunert 1943–1944
- LTG Omar N. Bradley 1944
- GEN Courtney H. Hodges 1944–1949
- MG Roscoe B. Woodruff 1949 (interim)
- GEN Walter Bedell Smith 1949–1950
- MG Roscoe B. Woodruff 1950 (interim)
- LTG Willis D. Crittenberger 1950–1952
- LTG Withers A. Burress 1953–1954
- LTG Thomas W. Herren 1954–1957
- LTG Blackshear M. Bryan 1957–1960
- LTG Edward J. O'Neill 1960–1962
- LTG Garrison H. Davidson 1962–1964
- LTG Robert W. Porter Jr. 1964–1965
- LTG Thomas W. Dunn 1965
- LTG William F. Train 1966–1967
- LTG Jonathan O. Seaman 1967–1971
- LTG Claire E. Hutchin, Jr. 1971–1973
- LTG Glenn D. Walker 1973–1974
- LTG James G. Kalergis 1974–1975
- LTG Jeffrey G. Smith 1975–1979
- LTG John F. Forrest 1979–1981
- LTG Donald E. Rosenblum 1981–1984
- LTG Charles D. Franklin 1984–1987
- LTG James E. Thompson Jr. 1987–1991
- LTG James H. Johnson Jr. 1991-1993
- LTG John P. Otjen 1993–1995
- LTG Guy A. J. LaBoa 1995–1997
- LTG George A. Fisher Jr. 1997–1999
- LTG John M. Riggs 1999–2001
- LTG Joseph R. Inge 2001–2004
- LTG Russel L. Honoré 2004–2008
- LTG Thomas G. Miller 2008–2011
- LTG John Michael Bednarek 2011–2013
- MG Kevin R. Wendel 2013 (interim)
- LTG Michael S. Tucker 2013–2016
- LTG Stephen M. Twitty 2016–2018
- MG Erik Peterson, Acting 2018
Notes
![]()
- ↑ Foto des Befehls
- ↑ Dokument, Deutsches Historisches Museum
- ↑ Ardennes-Alsace, Sullivan, Gordon R.
- ↑ https://prhome.defense.gov/Portals/52/Documents/MRA_Docs/MPP/OEPM/Approved%20JMUAs%20-%20Updated%202018%2001%2004.pdf?ver=2018-01-30-214312-817 HQ, Joint Task Force Katrina, Fort Gillem, Georgia 31 Aug 05 – 13 Oct 05
- ↑ https://prhome.defense.gov/Portals/52/Documents/MRA_Docs/MPP/OEPM/Approved%20JMUAs%20-%20Updated%202018%2001%2004.pdf?ver=2018-01-30-214312-817 HQ, Joint Task Force Katrina, Fort Gillem, Georgia 31 Aug 05 – 13 Oct 05
- ↑ United States Army Center of Military History, Lineage and Honors, First United States Army, dated 30 April 2012. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ↑ US Army Human Resources Command, Permanent Orders 120-10, dated 30 April 2009. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ↑ First Army Division East
- ↑ First Army Division West Archived 11 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
References
- After Action Report First U.S. Army, 1–3 December 1944. Fort Jackson, 1945.
- American Battle Monuments Commission. American Armies and Battlefields in Europe. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1938. Reprint. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1992.
- Blumenson, Martin. Breakout and Pursuit. United States Army in World War II. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1961. OCLC 78605078
- Borovatz, Frank M. "First United States Army: A Working Army". Army Digest 25 (February 1970): 4–8.
- A Brief History of the First United States Army From 1918 to 1946. Fayetteville, N. C.: Worth Publishing Co., 1947. OCLC 4985955
- Cole, Hugh M. The Ardennes: Battle of the Bulge. United States Army in World War II. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1965. OCLC 78624377
- Cole, Hugh M. The Lorraine Campaign. United States Army in World War II. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1950. OCLC 1253758
- Dalessandro, Robert J. & Knapp, Michael G. Organization and Insignia of the American Expeditionary Force, 1917–1923. Schiffer Publishing, 2008. ISBN 0764329375
- First Army, TI&E Section. History of the United States First Army. Fort Jay, 1953.
- First United States Army Combat Operations Data, Europe, 1944–45. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1948.
- First United States Army Report of Operations, 20 October 1943 – 1 August 1944. 7 vols. Paris, 1944.
- First United States Army Report of Operations, 1 August 1944 to 22 February 1945. 4 vols. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1946.
- First United States Army Report of Operations, 23 February–8 May 1945. 3 vols. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1946.
- Gabel, Christopher R. The U.S. Army GHQ Maneuvers of 1941. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1991. OCLC 23651527
- Hallas, James H. Squandered Victory: The American First Army at St. Mihiel. Westport, Conn.: Praeger Pubs., 1996. ISBN 0275950220
- Harbord, James G. The American Army in France, 1917–1919. Boston: Little, Brown, and Co., 1936.
- Harrison, Gordon A. Cross-Channel Attack. United States Army in World War II. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1951.
- Historical Section, Army War College. Order of Battle of the United States Land Forces in the World War; American Expeditionary Forces; General Headquarters, Armies, Army Corps, Services of Supply, and Separate Forces. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1937. Reprint. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1988.
- Historical Section, Army War College. The Genesis of the American First Army. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1929. 2d ed. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1938.
- Liggett, Hunter. Commanding an American Army, Recollections of the World War. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1925.
- MacDonald, Charles B. The Last Offensive. United States Army in World War II. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1973.
- MacDonald, Charles B. The Siegfried Line Campaign. United States Army in World War II. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1963.
- "Why Didn't They Let First Army Win the War?" Army 9 (April 1959):48–52.
- Pershing, John J. My Experiences in the World War. New York: Frederick A. Stokes Co., 1931.
- Pogue, Forrest C. The Supreme Command. United States Army in World War II. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1954.
- Report of the Commanding General, First Army, American Expeditionary Forces: Organizations and Operations, First Army, A.E.F. France, 1919.
- Report of the First Army, American Expeditionary Forces: Organization and Operations. Fort Leavenworth: General Service Schools Press, 1923.
- Report of the First Army, American Expeditionary Forces, Organization and Operations, General John J Pershing, 10 Aug. 1918; Lieutenant General Hunter Liggett, 16 Oct. 1918, 20 Apr. 1919. Fort Leavenworth, Kans.: General Service School Press, 1923.
- "Salute to the Numbered U.S. Armies". Army Information Digest 17 (October 1962):32–39.
- Walker, Glenn D. "First U.S. Army: A New Challenge". Army 23 (October 1973):72–76.
- Ziemke, Earl F. The U.S. Army in the Occupation of Germany 1944–1946. Army Historical Series. Washington, D.C.: United States Army Center of Military History, 1990 (1975). CMH Pub 30-6.
Further reading
- "First United States Army". Armies, Corps, Division and Separate Brigades. United States Army Center of Military History. 1999. CMH Pub 60-7-1. Archived from the original on 8 June 2010.
External links
- First Army official site
- First Army News
- The short film Big Picture: The Army's First is available for free download at the Internet Archive
- First United States Army Report of Operations - Volumes available for operations of the First United States Army during World War II (1943-1945) on Cleveland Public Library's Digital Gallery. The Federal Depository Library Program has cataloged the reports in three sections: Report of operations - October 20 1943- 1 August 1944, 1 August 1944-22 February 1945, 23 February-8 May 1945.