Fallopia
| Fallopia | |
|---|---|
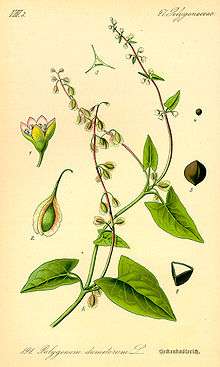 | |
| 1885 illustration[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Polygonaceae |
| Subfamily: | Polygonoideae |
| Genus: | Fallopia Adans. 1763 not Lour. 1790 |
| Type species | |
| Polygonum scandens | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Bilderdykia Dumortier | |
Fallopia is a genus of about 12–15 species of flowering plants in the buckwheat family,[3] often included in a wider treatment of the related genus Polygonum in the past. The genus is native to temperate and subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The genus includes herbaceous perennial plants, herbaceous vines, and woody vines.[2][4][5][6]
Several species are serious invasive weeds, notably Japanese knotweed in Europe and North America.[7][8][9][10]
The genus is named after Italian botanist Gabriello Fallopio, or Fallopius, who was the superintendent of the botanical garden at Padua. He was also an acclaimed anatomist, being considered a founder of modern anatomy along with Vesalius and Eustachius.
Fallopia species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including Coleophora therinella (recorded on F. convolvulus).
- Accepted species[3]
- Fallopia aubertii (L.Henry) Holub – silver lace vine, China
- Fallopia baldschuanica (Polygonum baldschuanicum is a synonym) – Russian vine; mile-a-minute vine; China fleece vine; fleece flower, Eastern Asia.
- Fallopia cilinodis (syn. Polygonum cilinode and Bilderdykia cilinodis are synonyms) – fringed black bindweed, North America.
- Fallopia convolvulus (Polygonum convolvulus and Bilderdykia convolvulus are synonyms) – black-bindweed, Europe, Asia, northern Africa.
- Fallopia cristata (Engelm. ex A.Gray) Holub – eastern + central United States
- Fallopia cynanchoides (Polygonum cynanchoides is a synonym) – Western China.
- Fallopia dentatoalata (Polygonum dentatoalatum is a synonym) – Eastern Asia.
- Fallopia denticulata (Polygonum denticulatum is a synonym) – Southern China.
- Fallopia dumetorum (Polygonum dumetorum and Bilderdykia dumetorum are synonyms) – copse bindweed, small-flower knotweed[11] – Europe, Asia, northern Africa.
- Fallopia filipes (Hara) Holub – Nepal
- Fallopia koreana B.U.Oh & J.G.Kim – Korean knotweed[11] – Korea
- Fallopia multiflora (Polygonum multiflorum is a synonym) – Eastern Asia.
- Fallopia pterocarpa (Polygonum pterocarpum is a synonym) – Southern Asia.
- Fallopia scandens (Polygonum scandens and Reynoutria scandens are synonyms) – climbing false buckwheat, North America.
- Fallopia schischkinii Tzvelev – Russian Far East
- Renamed species[3]
- Fallopia forbesii is a synonym of Reynoutria forbesii (Hance) T.Yamaz - Northern China, Korea.
- Fallopia japonica Houtt. is a synonym of *Reynoutria japonica Houtt. Japanese knotweed - Eastern Asia.
- Fallopia multiflora (Thunb.) Haraldson is a synonym of Reynoutria multiflora (Thunb.) Moldenke - Eastern Asia
- Unresolved species[3]
- Fallopia sachalinensis is an unresolved species name that may be synonymous with Reynoutria sachalinensis (F.Schmidt) Nakai giant knotweed - Eastern Siberia.
Hybrids
Crosses between Japanese knotweed and giant knotweed have occurred where the two species grow in close proximity. The hybrid, Fallopia × bohemica (syn. Polygonum × bohemicum) is known as Bohemian knotweed.
Fallopia × conollyana (F. baldschuanica × F. japonica) is called railway-yard knotweed.
Invasive species

Many knotweed species, particularly Japanese knotweed, giant knotweed and Himalayan knotweed are considered noxious, invasive pests. Like many such weeds, Japanese knotweed was introduced from Japan first into the U.K., then into North America in the 19th century as an ornamental plant.
Some knotweeds grow extremely quickly during the spring; giant knotweed can reach 4.5 m by summer, Japanese knotweed 3 m, and "dwarf" Himalayan knotweed 1.5–2 m. In Japan, Japanese knotweed is known as itadori, or "strong plant". Some species can spread rapidly from an extensive network of rhizomes (roots that can sprout) spreading from 7–20 m from the parent plant and at least 2 m deep. Root and stem fragments as small as 1 cm can form new plant colonies. Floods and high water events wash whole or partial plants into rivers and creeks, dispersing pieces of knotweed throughout the flooded area and banks, which give rise to new plants. As with other invasive species of plants, freshly disturbed soil allows the rapidly growing young knotweed plants to outgrow other plants and take over the area, suppressing other species. Cutting, mowing, digging and some herbicide treatments, especially in early to mid growing season, fail to curb knotweed growth and in fact often stimulate the production of shoots from latent buds dispersed on the root crown or rhizomes.
Medicinal properties
Recently, Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica, syn. Polygonum japonicum, Polygonum cuspidatum, Reynoutria japonica) and others have been used to exploit their high concentrations of trans-resveratrol in the plants' stalks. Previously associated with and identified mainly in the skins of red grapes, resveratrol is currently under study in a number of research projects investigating its possible antiaging properties.
References
- ↑ illustration from Thomé, Flora von Deutschland, Österreich und der Schweiz, 1885
- 1 2 Flora of North America, Fallopia Adanson, 1763. False-buckwheat
- 1 2 3 4 "The Plant List, Fallopia". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic Garden.
- ↑ Flora of China, Fallopia Adanson, 1763. 首乌属 shou wu shu
- ↑ Altervista Flora Italiana, genere Fallopia
- ↑ Online database of the Royal Horticultural Society
- ↑ Species Profile - Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia japonica), National Invasive Species Information Center, National Agricultural Library. Lists general information and resources for Japanese knotweed.
- ↑ Japanese Knotweed (Polygonum cuspidatum) - A Noxious Weed in Washington (US State)
- ↑ Control advice from the Royal Horticultural Society
- ↑ Ecocontrol, Advice on the Eradication of Japanese Knotweed
- 1 2 English Names for Korean Native Plants (PDF). Pocheon: Korea National Arboretum. 2015. p. 467. ISBN 978-89-97450-98-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 22 December 2016 – via Korea Forest Service.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fallopia. |