Europe India Gateway
| Europe India Gateway (EIG) | |
|---|---|
|
Owners: 18 companies | |
| Landing points | |
| Total length | 15,000 km |
| Design capacity | 3.84 terabits per second |
| Date of first use | February 2011 |
Europe India Gateway (EIG) is a submarine communications cable system to connect the U.K., Portugal, Gibraltar, Monaco, France, Libya, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Djibouti, Oman, United Arab Emirates, and India.[1]
Organization and owners
It is about 15,000 kilometres long.[1] It is capable of delivering up to 3.84 terabits per second.[2] The cable system is built by both Alcatel-Lucent[2] and TE Subcom (Formerly known as Tyco) and was scheduled to be completed in the second quarter of 2010.[2] The EIG is the first direct high-bandwidth optical fibre system from Britain to India.
The cable system was invested in by 18 companies,[3] including: AT&T; Bharti Airtel; BT Group; Cable & Wireless Worldwide; Djibouti Telecom; Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Co. (du); Gibtelecom; IAM; Libyan Post Telecommunications & Information Technology Company; Mauritius Telecom; Monaco Telecom; MTN Group; Omantel, PT Comunicações, S.A.; Saudi Telecom Company; Telecom Egypt; Telkom SA, and Verizon Business. The construction of the cable will cost $700 million.[4]
Outage
In March 2013, the EIG cable was cut near Egypt.[5] A few days later the I-ME-WE and SEA-ME-WE 4 cable was also cut near Egypt, supposedly by divers.[6]
Cable landing points
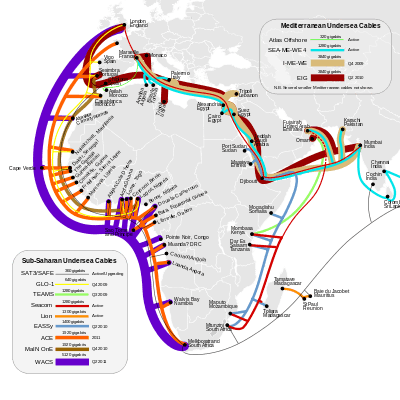
EIG has cable landing points at:[7][8]
Security breach
In February 2018, The Sunday Times reported that the infrastructure for the UK landing site of the Apollo, GLO-1 and Europe India Gateway cables had been found almost entirely unprotected. Their reporter was able to reach the premises without being challenged, and found the door to the generator room unlocked and left ajar. Vodafone, who manage the facility, said that he had not reached critical equipment and "would not have been able to interrupt the operation of the facility."[12]
See also
Other cable systems following a substantially similar route are:
External links
References
- 1 2 "Sixteen Telcos Invest $700M In EIG Cable System" (Press release). Lloyd's / Dow Jones Newswires. 2008-05-07. Archived from the original on 2009-10-01. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- 1 2 3 "Alcatel-Lucent to Help Build Underwater EIG Cable". Technology Marketing Corporation. 2008-07-31. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ "du invests in $700m Europe India Gateway undersea cable system" (Press release). du. 2008-05-08. Archived from the original on 2011-06-06. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ↑ Europe-India Gateway submarine cable launched Deccan Herald, Feb 24, 2011
- ↑ Cable snap off Egypt coast to slow down internet traffic ENS Economic Bureau : New Delhi, Sat Mar 30 2013
- ↑ Kirk, Jeremy (2013-03-27). Sabotage suspected in Egypt submarine cable cut. ComputerWorld, 27 March 2013
- ↑ Europe India Gateway main web page
- ↑ EIG on Greg's Cable Map
- ↑ "India to get first direct cable link to the UK". iTWire. 2008-05-07. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ "Du joins submarine cable consortium". Egypt.com. 2008-05-09. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ "Seamless Interconnection". Telecom and Networking Communications Today/ADI Media Pvt. Ltd. 2008-10-23. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ Gabriel Pogrund (4 February 2018). "Data-cable security scandal: It's easier to enter than a public library". The Sunday Times. p. 9.