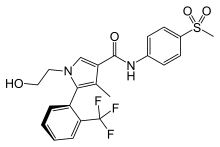
Esaxerenone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Drug class | Antimineralocorticoid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H21F3N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 466.475 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Esaxerenone (INN) (developmental code names CS-3150, XL-550) is a nonsteroidal antimineralocorticoid which was discovered by Exelixis and is now under development by Daiichi Sankyo Company for the treatment of hypertension, essential hypertension, hyperaldosteronism, and diabetic nephropathies.[1][2][3] It acts as a highly selective silent antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), the receptor for aldosterone, with greater than 1,000-fold selectivity for this receptor over other steroid hormone receptors, and 4-fold and 76-fold higher affinity for the MR relative to the existing antimineralocorticoids spironolactone and eplerenone.[1][2][3] As of 2017, esaxerenone is in phase III clinical trials for hypertension, essential hypertension, and hyperaldosteronism and is in phase II clinical trials for diabetic nephropathies.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800021527
- 1 2 Yang J, Young MJ (2016). "Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists-pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic differences". Curr Opin Pharmacol. 27: 78–85. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2016.02.005. PMID 26939027.
- 1 2 Kolkhof P, Nowack C, Eitner F (2015). "Nonsteroidal antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor". Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 24 (5): 417–24. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000147. PMID 26083526.
External links