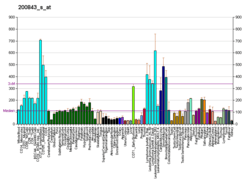
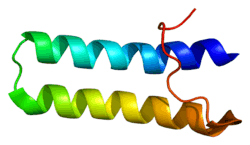EPRS
Bifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EPRS gene.[5][6]
Gene
Alternative splicing has been observed for this gene, but the full-length nature and biological validity of the variant have not been determined.[6]
Function
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are a class of enzymes that charge tRNAs with their cognate amino acids. The protein encoded by this gene is a multifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that catalyzes the aminoacylation of glutamic acid and proline tRNA species.[6]
Phosphorylation of EPRS is reported to be essential for the formation of GAIT (Gamma-interferon Activated Inhibitor of Translation) complex that regulates the translation of multiple genes in monocytes and macrophages.[7]
Interactions
EPRS has been shown to interact with POU2F1,[8] Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic), member A1[9] and IARS.[10]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000136628 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026615 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Fett R, Knippers R (February 1991). "The primary structure of human glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. A highly conserved core, amino acid repeat regions, and homologies with translation elongation factors". J Biol Chem. 266 (3): 1448–55. PMID 1988429.
- 1 2 3 "Entrez Gene: EPRS glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase".
- ↑ Arif A, Jia J, Mukhopadhyay R, Willard B, Kinter M, Fox PL (July 2009). "Two-site phosphorylation of EPRS coordinates multimodal regulation of noncanonical translational control activity". Mol. Cell. 35 (2): 164–80. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.05.028. PMC 2752289. PMID 19647514.
- ↑ Nie, J; Sakamoto S; Song D; Qu Z; Ota K; Taniguchi T (March 1998). "Interaction of Oct–1 and automodification domain of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase". FEBS Lett. 424 (1–2): 27–32. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00131-8. PMID 9537509.
- ↑ Kang, J; Kim T; Ko Y G; Rho S B; Park S G; Kim M J; Kwon H J; Kim S (October 2000). "Heat shock protein 90 mediates protein-protein interactions between human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases". J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 275 (41): 31682–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909965199. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10913161.
- ↑ Rho, S B; Lee J S; Jeong E J; Kim K S; Kim Y G; Kim S (May 1998). "A multifunctional repeated motif is present in human bifunctional tRNA synthetase". J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 273 (18): 11267–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.18.11267. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9556618.
Further reading
- Kaiser E, Eberhard D, Knippers R (1992). "Exons encoding the highly conserved part of human glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase". J. Mol. Evol. 34 (1): 45–53. Bibcode:1992JMolE..34...45K. doi:10.1007/BF00163851. PMID 1556743.
- Norcum MT (1991). "Structural analysis of the high molecular mass aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex. Effects of neutral salts and detergents". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (23): 15398–405. PMID 1651330.
- Cerini C, Kerjan P, Astier M, et al. (1992). "A component of the multisynthetase complex is a multifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase". EMBO J. 10 (13): 4267–77. PMC 453179. PMID 1756734.
- Kunze N, Bittler E, Fett R, et al. (1990). "The human QARS locus: assignment of the human gene for glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase to chromosome 1q32-42". Hum. Genet. 85 (5): 527–30. doi:10.1007/BF00194231. PMID 2227938.
- Thömmes P, Fett R, Schray B, et al. (1988). "The core region of human glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase homologies with the Escherichia coli and yeast enzymes". Nucleic Acids Res. 16 (12): 5391–406. doi:10.1093/nar/16.12.5391. PMC 336774. PMID 3290852.
- Kaiser E, Hu B, Becher S, et al. (1994). "The human EPRS locus (formerly the QARS locus): a gene encoding a class I and a class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase". Genomics. 19 (2): 280–90. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1059. PMID 8188258.
- Hillier LD, Lennon G, Becker M, et al. (1997). "Generation and analysis of 280,000 human expressed sequence tags". Genome Res. 6 (9): 807–28. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.807. PMID 8889549.
- Rho SB, Lee JS, Jeong EJ, et al. (1998). "A multifunctional repeated motif is present in human bifunctional tRNA synthetase". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (18): 11267–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.18.11267. PMID 9556618.
- Quevillon S, Robinson JC, Berthonneau E, et al. (1999). "Macromolecular assemblage of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: identification of protein-protein interactions and characterization of a core protein". J. Mol. Biol. 285 (1): 183–95. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2316. PMID 9878398.
- Kang J, Kim T, Ko YG, et al. (2000). "Heat shock protein 90 mediates protein-protein interactions between human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (41): 31682–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909965199. PMID 10913161.
- Jeong EJ, Hwang GS, Kim KH, et al. (2001). "Structural analysis of multifunctional peptide motifs in human bifunctional tRNA synthetase: identification of RNA-binding residues and functional implications for tandem repeats". Biochemistry. 39 (51): 15775–82. doi:10.1021/bi001393h. PMID 11123902.
- Sang Lee J, Gyu Park S, Park H, et al. (2002). "Interaction network of human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and subunits of elongation factor 1 complex". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 291 (1): 158–64. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6398. PMID 11829477.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Bouwmeester T, Bauch A, Ruffner H, et al. (2004). "A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (2): 97–105. doi:10.1038/ncb1086. PMID 14743216.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Sampath P, Mazumder B, Seshadri V, et al. (2004). "Noncanonical function of glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase: gene-specific silencing of translation". Cell. 119 (2): 195–208. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.030. PMID 15479637.
- Kato T, Daigo Y, Hayama S, et al. (2005). "A novel human tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase involved in pulmonary carcinogenesis". Cancer Res. 65 (13): 5638–46. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0600. PMID 15994936.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.