Dois Paus redoubt
| Dois Paus redoubt (Reduto dos Dois Paus) | |
| Redoubt of Two Sticks/Clubs | |
| Fort (Forto) | |
| Official name: Reduto dos Dois Paus | |
| Name origin: two sticks/clubs | |
| Country | |
|---|---|
| Region | |
| Group | Central |
| Island | Terceira |
| Municipality | Angra do Heroísmo |
| Location | Sé |
| - coordinates | 38°38′55″N 27°13′14″W / 38.648518°N 27.220453°WCoordinates: 38°38′55″N 27°13′14″W / 38.648518°N 27.220453°W |
| Architects | Tommaso Benedetto |
| Styles | Medieval, Fortification |
| Materials | Basalt, Tuff |
| Origin | 1543 |
| - Initiated | 15th-16th century |
| For public | Private |
| Management | Direção Regional da Cultura |
| Operator | Portuguese Army |
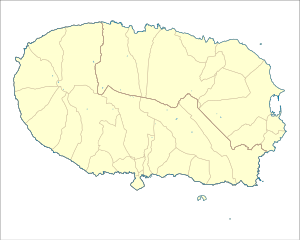 Location of the fortification within the municipality of Angra do Heroísmo, island of Terceira | |
The Dois Paus redoubt (Portuguese: Reduto dos Dois Paus) is a redoubt fortification situated on the peninsula of Monte Brasil, in the civil parish of Sé, in the municipality of Angra do Heroísmo, in the Porutguese archipelago of the Azores. It was part of the fortified defenses of the Fortress of São João Baptista.
History
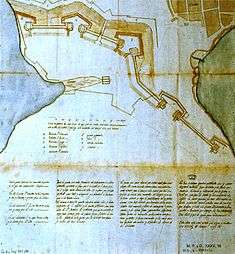
Bartolomeu Ferraz first presented his recommendations to John III of Portugal in 1543 for the fortification of the Azores, then an important waypoint in trans-Atlantic commerce between the Indies and America.[1] On 5 March 1567, in his proposal to the Crown, Engineer Tommaso Benedetto elaborated a plan to protect the island's coastal defence, that included the construction of a fort on Monte Brasil.[1] Shortly following this proposal, the Portuguese Crown began the construction of the Fort of Dois Paus, in order to protect the port of Dois Paus-Portinho Novo.[1] It is unclear from where its name originated; the name "dois paus" is a literally translated as "the redoubt of the two sticks/clubs".
In the context of the Captaincy-General of the Azores, there was a reference to the structure, stating in 1767:
- "...In the redoubt of Dois Paus there are three canon emplacements and two pieces...it needs one more with its support."[2]
Its remains continue to lie on the volcanic cone of Monte Brasil to this day, in ruins.
References
Notes
- 1 2 3 Dias, Sofia (2015). SIPA, ed. "Igreja de São João Baptista do Castelo, Fortaleza e Muralhas" (in Portuguese). Lisbon, Portugal: SIPA – Sistema de Informação para o Património Arquitectónico. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ↑ Júdice (1981), p.416
Sources
- Júdice, João António, "Revistas feitas no Castello de S. João Baptista, Forte de S. Sebastião e de todos os mais fortes que tem esta Ilha Terceira", Arquivo dos Açores (in Portuguese), V (facsimile 1883), Ponta Delgada (Azores), Portugal: Arquivo Nacional da Torre do Tombo/Papéis do Ministério do Reino (Maço 611); Universidade dos Açores (1981), pp. 407–418
- Mota, Valdemar (1994), "Fortificação da Ilha Terceira", Boletim do Instituto Histórico da Ilha Terceira (in Portuguese), LI-LII, Angra do Heroísmo (Azores), Portugal
