Dixie

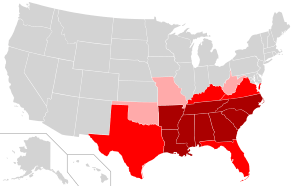
Dixie (otherwise known as Dixieland) is a nickname for the Southern United States, especially those states that composed the Confederate States of America.[5] The term originally referred simply to the states south of the Mason–Dixon line, but now is more of a cultural reference, referring to parts of the United States that "feel" southern.
Region

As a definite geographic location within the United States, "Dixie" is usually defined as the eleven Southern states that seceded in late 1860 and early 1861 to form the new Confederate States of America. They are (in order of secession): South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee. Maryland never seceded from the Union, but many of their citizens favored the Confederacy. Whilst many of Maryland’s representatives were arrested[6] to prevent secession,[7] both the states of Missouri and Kentucky produced Ordinances of Secession and were admitted into the Confederacy.[8] Note that West Virginia was part of Virginia until 1863; counties that chose not to secede from the Union became part of West Virginia.
Although Maryland is not included in Dixie today, Maryland is on the Dixie side of the Mason–Dixon line; if the origin of the term Dixie is accepted as referring to the region south (and west) of that line, Maryland was in Dixie in 1760. It can also be argued that Maryland was, in 1860, part of Dixie, especially culturally.[9] In this sense, it would remain so into the 1970s, when an influx of people from the Northeast made the state and its culture significantly less Southern (especially Baltimore and the suburbs of Washington DC).[10]
However, the location and boundaries of "Dixie" have, over time, become increasingly subjective and mercurial. Today, it is most often associated with those parts of the Southern United States where traditions and legacies of the Confederate era and the antebellum South live most strongly.[11] The concept of "Dixie" as the location of a certain set of cultural assumptions, mind-sets and traditions (along with those of other regions in North America) was explored in the 1981 book The Nine Nations of North America.[12]
In terms of self-identification and appeal the popularity of the word “Dixie” seems declining. A 1976 study revealed that on some 350,000 sq. miles “Dixie” reached 25% popularity of “American” in names of commercial business entities.[13] Though a 1999 analysis provided a confusing evidence,[14] a 2010 study conclusively demonstrated that in course of 40 years the area in question shrunk to just 40,000 sq. miles, to the territory at the confluence of Louisiana, Mississipi, Alabama and Florida.[15] In 1976 at some 600,000 sq. miles[16] “Dixie” reached at least 6% popularity of “American”; in 2010 the corresponding area was some 500,000 sq. miles.[17]
Origin of the name

According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the origin of this nickname remains obscure. The most common theories according to A Dictionary of Americanisms on Historical Principles (1951) by Mitford M. Mathews:
- "Dixie" is derived from Jeremiah Dixon, a surveyor of the Mason–Dixon line, which defined the border between Maryland and Pennsylvania, separating free and slave states subsequent to the Missouri Compromise.[18]
- The word "Dixie" refers to currency issued first by the Citizens State Bank in the French Quarter of New Orleans and then by other banks in Louisiana.[19] These banks issued ten-dollar notes[20] labeled Dix on the reverse side, French for "ten". The notes were known as "Dixies" by southerners, and the area around New Orleans and the French-speaking parts of Louisiana came to be known as "Dixieland".[5] Eventually, usage of the term broadened to refer to the Southern states in general.
- The word preserves the name of a Mr. Johan Dixie (sometimes spelled Dixy), a slave owner on Manhattan Island where slavery was legal until 1827. An apocryphal tale claims that following their posting to the South, the slaves who formerly worked "Dixie's Land" told of the relatively less harsh treatment they faced while in the North.[21]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Oh, Soo. "Which states do you think belong in the South?". Vox. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- ↑ Wilson, Charles & William Ferris Encyclopedia of Southern Culture ISBN 978-0-8078-1823-7; Univ. of Pennsylvania Telsur Project Telsur Map of Southern Dialect
- ↑ Vance, Rupert Bayless, Regionalism and the South, Univ. of North Carolina Press, 1982, p. 166 "West Virginia is found to have its closest attachment to the Southeast on the basis of agriculture and population."
- ↑ David Williamson (June 2, 1999). "UNC-CH surveys reveal where the 'real' South lies". Retrieved 22 Feb 2007.
- 1 2 "Dixie". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- ↑ Banks, Union General (September 20, 1861). "The war of the rebellion: a compilation of the official records of the Union and Confederate armies. ; Series 2 - Volume 1". cdl.library.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2018-01-01.
all members of the Maryland Legislature assembled at Frederick City on the 17th instant known or suspected to be disloyal in their relations to the Government have been arrested.
- ↑ Cameron, Secretary of War (September 11, 1861). "The war of the rebellion: a compilation of the official records of the Union and Confederate armies. ; Series 2 - Volume 1". cdl.library.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2018-01-01.
The passage of any act of secession by the Legislature of Maryland must be prevented. If necessary all, or any part of the members, must be arrested. Exercise your own judgment as to the time and manner, but do the work effectively.
- ↑ "Ordinances of Secession". Historical Text Archive. Retrieved July 19, 2017.
- ↑ "The General Assembly Moves to Frederick, 1861". Retrieved 25 Oct 2017.
- ↑ Rasmussen, Frederick (March 28, 2010). "Are we Northern? Southern? Yes". The Baltimore Sun. Retrieved February 23, 2018.
- ↑ ""Where Does the South Begin?"". The Atlantic. 28 Jan 2011.
- ↑ Joel Garreau. "Dixie". Retrieved November 24, 2017.
- ↑ the territory in question was all Mississipi and Alabama, almost all of Georgia, Tennessee and South Carolina, and around a half of Louisiana, Arkansas, Kentucky, North Carolina and Florida. The study in question was John Shelton Reed, "The Heart of Dixie: An Essay in Folk Geography", [in:] "Social Forces" 54/4 (1976), pp. 925-939
- ↑ the research demonstrated that between 1976 and 1999 in some 19% of US cities sampled there was an increase of relative use of “Dixie”, in 48% of cities sampled there was a decline and there was no change recorded in 32% of cities, Derek H. Alderman, Robert Maxwell Beavers, "Heart of Dixie Revisited: an Update on the Geography of Naming in the American South", [in:] "Southeastern Geographer" XXXlX/2 (1999), p. 196
- ↑ Christopher A. Cooper, H. Gibbs Knotts, "Declining Dixie: Regional Identification in the Modern American South", [in:] "Social Forces" 88/3 (2010), pp. 1083-1101
- ↑ from Eastern areas of Texas and Oklahoma to Southern areas of Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, West Virginia and Virginia
- ↑ compare a map at Cooper, Gibbs Knotts 2010, p. 1090
- ↑ John Mackenzie, "A brief history of the Mason-Dixon Line", APEC/CANR, University of Delaware; accessed 2017.01.05.
- ↑ "Dixie" Originated From Name "Dix" An Old Currency - New Orleans American May 29 1916, Vol. 2 No. 150, Page 3 Col. 1 Louisiana Works Progress Administration (WPA), Louisiana Digital Library
- ↑ Ten Dollar Note George Francois Mugnier Collection, Louisiana Digital Library
- ↑ Wilton, David (2008). Word Myths: Debunking Linguistic Urban Legends. Oxford University Press. p. 147.
References
- John Shelton Reed (with J. Kohl and C. Hanchette) (1990). The Shrinking South and the Dissolution of Dixie. Social Forces. pp. 69 (September 1990): 221–233.
- Sacks, Howard L. and Judith Rose. Way Up North In Dixie. (Smithsonian Institution Press, 1993)