Divisional general
Divisional general is a rank of general in command of a division. Examples would include the Spanish general de división, the French général de division and the Polish generał dywizji. For convenience such ranks are often translated into English as "major-general", the equivalent rank used by most English-speaking nations. The corresponding NATO code is OF-7, or a "two-star rank". Some countries of Latin America such as Brazil and Chile use divisional general as the equivalent of "lieutenant-general". This corresponding NATO code is OF-8, or a "three-star rank" for these countries. In Japan and Taiwan the rank of lieutenant-general is equivalent to divisional general.
Description
The rank is mostly used in countries where it is used as a modern alternative to a previous older rank of major-general. The rank is almost always above a rank corresponding to command of a brigade, and normally below a rank corresponding to command of a corps.
Bosnia
Division General was a military rank in the Bosnian army from 1992 to 1998.
Brazil
 General-de-Divisão |
The Brazilian rank general-de-divisão translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is major-brigadeiro (literally "major-brigadier").
France
Général de division |
 Général de division aérienne |
A French Army général de division translates as a "general of division". The French Air Force equivalent is général de division aérienne (literally "general of air division"). Rank insignia is that of 3 white stars on the epaulette, sleeve mark or shoulder board.
As well as commanding a division, a général de division may be appointed as général de corps d'armée (a "corps general") commanding an army corps, or as a général d'armée (a "general of an army"), commanding a field army. These are not ranks, but appointments of the same rank. The insignia of a général de corps d'armée is four stars in a diamond formation, and that of a général d'armée is five stars in a cross-shaped arrangement. The arrangement for the air force is the same, but the ranks are called général de corps d'armée aérien ("general of an air corps") and général d'armée aérienne ("general of an air army") respectively.
Italy
.svg.png)
The Italian army and Carabineer rank of generale di divisione translates as "divisional general". The air force equivalent is generale di divisione aerea (literally "general of air division").
Mexico

Poland
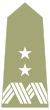
The Polish equivalent is generał dywizji (literally, "general of division"). The symbols of this rank are the general's wavy line and two stars, featured both on the rogatywka (the Polish peaked, four-pointed cap), on the sleeves of the uniform and above the breast pocket of a field uniform.
Spain
 Army general de división |
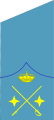 Air force general de división |
 Guardia Civil general de división |
The Spanish rank general de división translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army, the air force and the Guardia Civil ("Civil Guard").
Switzerland

The Swiss military use 4 languages, German, French, Romansh and Italian. The names of the OF-7 rank are divisionär (German); divisionnaire (French); divisiunari (Romansh); divisionario (Italian). In all cases, these are abbreviated as "Div", and in all cases represent the head of a division, and hence can be translated as "divisional general".
Serbia and Yugoslavia
In the Royal Serbian Army there was a proposition in 1898 by HM King Alexander I to introduce the rank of divisional general (Дивизијски ђенерал) along with Brigadier general and Corps general, but this was ultimately refused and only Army general was introduced. This rank was later replaced with Voyvoda.
The newly created Royal Yugoslav Army introduced the rank of Divisional general in 1923, as the second general rank, higher than Brigadier general but lower than Army general.[1] This rank was also used during WWII by the Yugoslav Home Army known as Chetniks. Most notable holders are div. gen. Miroslav Trifunović and Ivan Prezelj. These ranks were replaced in 1945 by Tito's partisans with the introduction of soviet style ranks.
References
- ↑ "Ranks of Royal Yugoslav Army". niehorster.org. Retrieved 15 October 2017.