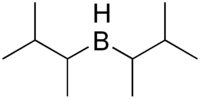
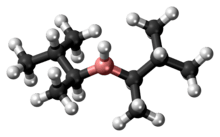
Disiamylborane
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bis(1,2-dimethylpropyl)borane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H23B | |
| Molar mass | 154.09 g/mol |
| Melting point | 35-40 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Disiamylborane (bis(1,2-dimethylpropyl)borane, Sia2BH) is an organoborane used in organic synthesis. It is used to add water to a terminal alkyne, forming an aldehyde via anti-Markovnikov addition. Disiamylborane is relatively selective for terminal alkynes. It also is used for the selective functionalization of terminal alkenes.[1] 9-Borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane (9-BBN) is another reagent that can be used for these purposes. Disiamylborane can be selectively prepared from hydroboration trimethylethylene; the reaction stops at the secondary borane due to steric hindrance.
Naming
"Siamyl" is an abbreviation for sec-isoamyl. More modern conventions replace amyl with the pentyl group,[2] and dispense with the sec and iso naming of pentyl isomers in favor of systematic naming as a substituted alkyl chain.[3] A related reagent named thexylborane ((1,1,2-trimethylpropyl)borane, ThxBH2) is a primary borane obtained from hydroboration of the even more hindered tetramethylethylene. In this compound, "thexyl" is an abbreviation for tert-hexyl.
References
- ↑ Eric J. Leopold (1990). "Selective Hydroboration of a 1,3,7-Triene: Homogeraniol". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 7, p. 258
- ↑ "Friday Dec 4 Lecture" (PDF). Amherst University.
- ↑ "Disiamylborane". PubChem.