Dichloro(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane)nickel
New.png) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Dichloro[1,3-propanediylbis(diphenylphosphanuide-kappaP)]nickel | |
| Other names
1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propanenickel(II) chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.628 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H26Cl2NiP2 | |
| Molar mass | 542.05 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange to red-orange powder |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K) |
| immiscible in water | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External SDS |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS signal word | Danger[1] |
| H315, H317, H319, H334, H335, H350[1] | |
| P201, P261, P280, P305+351+338, P308+313[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dichloro[1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane]nickel a coordination complex with the formula NiCl2(dppp); where dppp is the diphosphine 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. The compound is a bright orange-red crystalline powder.
Structure and properties
The compound has idealized C2v symmetry, ignoring orientation of the phenyl groups. The Nickel has square planar geometry. The compound is soluble in non-polar organic solvents and is diamagnetic.
Preparation
NiCl2(dppp) is prepared by combining equal molar portions of nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate with 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane in 2-propanol.[2]
- Ni(H2O)6Cl2 + dppp → NiCl2(dppp) + 6 H2O
Reactions
NiCl2(dppp) in an effective catalyst for coupling reactions such as the Kumada coupling[2] and Suzuki reactions (example below).[3] It also catalyzes other reactions that convert enol ethers, dithioacetals, and vinyl sulfides to olefins.[4][5]
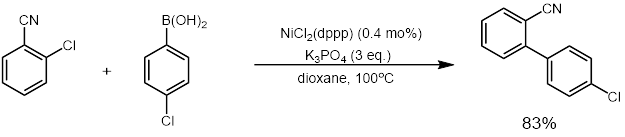
References
- 1 2 3 4 "1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane Nickel(II) Chloride". American Elements. Retrieved September 6, 2018.
- 1 2 Kumada, Makota; Tamao, Kohei; Sumitani, Koji (1988). "Phosphine-Nickel Complex Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Grignard Reagents with Aryl and Alkenyl Halides: 1,2-dibutylbenzene". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 6, p. 407
- ↑ Zhao, Yu-Long; Li, You; Li, Shui-Ming; Zhou, Yi-Guo; Sun, Feng-Yi; Gao, Lian-Xun; Han, Fu-She (1 June 2011). "A Highly Practical and Reliable Nickel Catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling of Aryl Halides". Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis. 353 (9): 1543–1550. doi:10.1002/adsc.201100101.
- ↑ Tien-Yau Luh; Tien-Min Yuan. "Cross-Coupling Reactions". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd100.pub2.
- ↑ Ljungdahl, Thomas; Bennur, Timmanna; Dallas, Andrea; Emtenaes, Hans; Maartensson, Jerker (2008). "Two Competing Mechanisms for the Copper-Free Sonogashira Cross-Coupling Reaction". Organometallics. 27 (11): 2490–2498. doi:10.1021/om800251s.