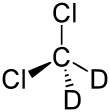
Deuterated dichloromethane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 1733318 | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.252 | ||
| EC Number | 216-776-0 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UN number | 1593 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2Cl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 86.945 g mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.362 g cm−3 | ||
| Boiling point | 40 °C (104 °F; 313 K) | ||
| Vapor pressure | 52.6 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R40 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | S23, S24/25, S36/37 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Deuterated chloroform | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Deuterated dichloromethane (CD2Cl2) is a form (called an isotopologue) of dichloromethane (DCM, CH2Cl2) in which the hydrogen atoms ("H") are replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D").[1] Deuterated DCM is not a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy as it is expensive compared to deuterated chloroform.
References
- ↑ Bertolini, Alessandro; Carelli, Giorgio; Moretti, Augusto; Moruzzi, Giovanni (2001). "Assignment of Fir Laser Lines of Fully Deuterated Dichloromethane". International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves. 22 (10): 1421–1431. doi:10.1023/A:1015082422018.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.