DEPTOR
DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR) also known as DEP domain-containing protein 6 (DEPDC6) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DEPTOR gene.[5]
Structure
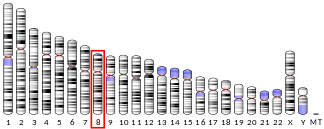
The gene DEPTOR can be found only in vertebrates. In human, DEPTOR gene locates at chromosome 8, 8q24.12 with protein size 409 a.a.[6] Human DEPTOR contains two N-terminal DEP domains and a C-terminal PDZ domain.[7]
Function
DEPTOR is involved in mTOR signaling pathway as an endogenous regulator. A direct interaction between DEPTOR and mTOR has been shown.[7] Overexpression of DEPTOR downregulates the activity of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in vitro. mTORC1 and mTORC2 can both inhibit DEPTOR through phosphorylation.[7]
Metabolism
DEPTOR cell-autonomously regulates adipogenesis.[8] In the muscle, Baf60c promotes a switch from oxidative to glycolytic myofiber type through DEPTOR-mediated Akt/PKB activation.[9] Within the brain, DEPTOR is highly expressed in the hippocampus, the medio-basal hypothalamus and the circumventricular organs.[10] Overexpression of DEPTOR in the medio-basal hypothalamus protects mice against high-fat diet-induced obesity by modulating Akt/PKB signaling.[11]
Clinical cancer
Although in most cancer, mTOR pathway is constitutively activated and the expression of DEPTOR is low, one study has found that DEPTOR is overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and is necessary for their survival.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000155792 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022419 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: DEPDC6 DEP domain containing 6".
- ↑ "Homo sapiens - Ensembl protein families - Gene: DEPTOR (ENSG00000155792)". Ensembl genome browser 78.
- 1 2 3 4 Peterson TR, Laplante M, Thoreen CC, Sancak Y, Kang SA, Kuehl WM, Gray NS, Sabatini DM (May 2009). "DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival". Cell. 137 (5): 873–86. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.046. PMC 2758791. PMID 19446321.
- ↑ Laplante M, Horvat S, Festuccia WT, Birsoy K, Prevorsek Z, Efeyan A, Sabatini DM (Aug 2012). "DEPTOR cell-autonomously promotes adipogenesis, and its expression is associated with obesity". Cell Metabolism. 16 (2): 202–12. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.008. PMC 3463374. PMID 22883231.
- ↑ Meng ZX, Li S, Wang L, Ko HJ, Lee Y, Jung DY, Okutsu M, Yan Z, Kim JK, Lin JD (May 2013). "Baf60c drives glycolytic metabolism in the muscle and improves systemic glucose homeostasis through Deptor-mediated Akt activation". Nature Medicine. 19 (5): 640–5. doi:10.1038/nm.3144. PMC 3650110. PMID 23563706.
- ↑ Caron A, Baraboi ED, Laplante M, Richard D (Jan 2015). "DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein in the rat brain: distribution of expression and potential implication". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 523 (1): 93–107. doi:10.1002/cne.23668. PMID 25159114.
- ↑ Caron, Alexandre; Labbé, Sébastien M.; Lanfray, Damien; Blanchard, Pierre-Gilles; Villot, Romain; Roy, Christian; Sabatini, David M.; Richard, Denis; Laplante, Mathieu. "Mediobasal Hypothalamic Overexpression of Deptor Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity". Molecular Metabolism. 5: 102–112. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2015.11.005.
Further reading
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (Jan 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (Oct 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (Nov 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (Mar 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, Pepperkok R, Wiemann S (Sep 2000). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Reports. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, Wellenreuther R, Schleeger S, Mehrle A, Bechtel S, Sauermann M, Korf U, Pepperkok R, Sültmann H, Poustka A (Oct 2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Research. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, del Val C, Arlt D, Hahne F, Bechtel S, Simpson J, Hofmann O, Hide W, Glatting KH, Huber W, Pepperkok R, Poustka A, Wiemann S (Jan 2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.