Compliant mechanism
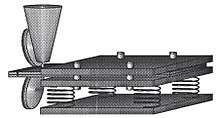
In mechanical engineering, compliant mechanisms are flexible mechanisms that transfer an input force and displacement at one port to an output force and displacement at another port through elastic body deformation. These may be monolithic (single-piece) or jointless structures.
Detail
Since many compliant mechanisms are single-piece structures, there is no need of assembly. With no joints, "rubbing" between two parts or friction as seen at the joints of rigid body mechanisms is absent. Compliant mechanisms are elastic.
Compliant mechanisms are usually designed using two techniques,[1] the first being a pseudo-rigid-body model and the second, the topology optimization. Other techniques are being conceived to design these mechanisms. Compliant mechanisms manufactured in a plane that have motion emerging from said plane are known as lamina emergent mechanisms (LEMs).
The flexible drive or resilient drive, often used to couple an electric motor to a machine (for example, a pump), is one example. The drive consists of a rubber "spider" sandwiched between two metal dogs. One dog is fixed to the motor shaft and the other to the pump shaft. The flexibility of the rubber part compensates for any slight misalignment between the motor and the pump. See rag joint and giubo.
The Second International Symposium on Compliant Mechanisms,[2] was held on May 19-20, 2011 at Delft, Netherlands.
Research laboratories and researchers
A number of labs and researchers are explicitly researching compliant mechanisms:
- Prof. Larry Howell, Brigham Young University Compliant Mechanisms research[3]
- Prof. Haijun Su at the Ohio State University[4][5]
- Prof. Kota at University of Michigan Compliant Systems Design Lab[6]
- Prof. Zentner at Ilmenau University of Technology[7]
- Prof. Martin Culpepper at MIT Precision Compliant Systems Laboratory[8]
- Prof. Just L. Herder at Delft University of Technology[9]
- Prof. Engin Tanık and Prof. Volkan Parlaktaş at Hacettepe University[10]
- Prof. Jonathan Hopkins at University of California, Los Angeles[11]
- Prof. Alexander Hasse at Chemnitz University of Technology[12]
In addition, the following researchers may be doing compliant mechanism research:
- The Multidisciplinary and Multiscale Device and Design Laboratory (M2D2) at the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore[13]
- Prof. Sridhar Kota[14]
- Prof. Shorya Awtar at University of Michigan[15]
- Prof. G. K. Ananthasuresh at IISc, Bangalore[16]
- Prof. Stephen L. Canfield at Tennessee Tech University[17]
- Prof. Charles Kim at Bucknell University[18]
- Prof. Anupam Saxena at IIT Kanpur, India[19]
- Prof. Mary Frecker at The Pennsylvania State University, University Park[20]
- Prof. Guimin Chen, Compliant Mechanisms & Precision Instruments Lab at Xidian University [21]
- Prof. Guangbo Hao, Compliant Mechanisms and Robotics Research Group at University College Cork, Ireland[22]
- Prof. W.J. Zhang, Soft Body Mechanisms and Robots Research Group at University of Saskatchewan, Canada[23]
See also
References
- ↑ Alejandro E. Albanesi, Victor D. Fachinotti and Martin A. Pucheta: [www.cimec.org.ar/ojs/index.php/mc/article/viewFile/3015/2946%7Cdate=October A review of design methods for compliant mechnasms.] In: Mecánica Computacional, Vol XXIX, pages 59-72. Eduardo Dvorkin, Marcela Goldschmit, Mario Storti (Eds.) Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15-18 November 2010.
- ↑ Archived January 12, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "CMR Awarded Research Grant from National Science Foundation". Cmr.byu.edu. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ↑ "Home Page - DAS 2D/3D". DAS 2D/3D. Retrieved 2015-11-11.
- ↑ "Design Innovation and Simulation Laboratory". Design Innovation and Simulation Laboratory. Retrieved 2015-11-11.
- ↑ "U of M - Compliant Systems Design Laboratory". Sitemaker.umich.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "FG Nachgiebige Systeme". www.tu-ilmenau.de (in German). Retrieved 2017-08-03.
- ↑ "MIT Precision Compliant Systems Laboratory Home". Pcsl.mit.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ Archived November 16, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "CRMR". Yunus.hacettepe.edu.tr. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Flexible Research Group". ucla.edu. Retrieved 2017-12-02.
- ↑ "Nachgiebige Systeme". www.tu-chemnitz.de/mb/mp/ (in German). Retrieved 2018-05-22.
- ↑ "M2D2 Index". Mecheng.iisc.ernet.in. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Sridhar Kota | me.engin.umich.edu". Personal.umich.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Precision Systems Design Lab". Personal.umich.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Ananthasuresh". Mecheng.iisc.ernet.in. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Stephen L Canfield, Ph.D., Professor of Mechanical Engineering". Archived from the original on November 20, 2012. Retrieved July 15, 2013.
- ↑ "Mechanical Engineering Department: Charles J. Kim". Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved May 9, 2008.
- ↑ "index_iitk_32". Home.iitk.ac.in. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Home". Edog.mne.psu.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ "Compliant Mechanisms & Precision Instruments". web.xidian.edu.cn. Retrieved 2015-05-06.
- ↑ https://sites.google.com/site/doctorghao/
- ↑ https://homepage.usask.ca/~wjz485/