Plectranthus barbatus
| Indian coleus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Plectranthus |
| Species: | P. barbatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Plectranthus barbatus | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
List
| |
Plectranthus barbatus, also known by the synonym Coleus forskohlii and vernacular names forskohlii[2] and Indian coleus, is a tropical perennial plant related to the typical coleus species. It produces forskolin, an extract useful for pharmaceutical preparations and research in cell biology.[3]
Name
The Brazilian name is boldo brasileiro (Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈbowdu bɾɐziˈlejɾu], as opposed to the Chilean true boldo), boldo-da-terra ([ˈbowdu dɐ ˈtɛʁɐ]), boldo-de-jardim ([ˈbowdu dʒi ʒaʁˈdʒĩ]) or tapete-de-Oxalá ([tɐˈpetʃi dʒ oʃaˈla]) (Oxalá's carpet, because it's velvety texture).
Chemistry
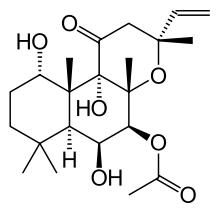
Herbal teas made from Plectranthus barbatus contains rosmarinic acid and also flavonoid glucuronides and diterpenoids.[4][5] The chemical constituents of Plectranthus barbatus showed activities in vitro, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibition.[3][4][5]
Forskolin, which derives its name from the former binomial name Coleus forskohlii, is a constituent of Plectranthus barbatus.[3][6]
Ayurveda
In Ayurvedic traditional medicine, Coleus has been used to treat various disorders,[7] although there is no evidence for its efficacy confirmed by high-quality clinical research in any of those conditions.
References
- ↑ "The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species".
- ↑ "Plectranthus barbatus". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- 1 2 3 Alasbahi, R. H.; Melzig, M. F. (2010). "Plectranthus barbatus: A review of phytochemistry, ethnobotanical uses and pharmacology - Part 1". Planta Medica. 76 (7): 653–61. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1240898. PMID 20178070.
- 1 2 Falé, P.L., Borges, C., Madeira, P.J.A., Ascensão, L.; et al. (2009). "Rosmarinic acid, scutellarein 4′-methyl ether 7-O-glucuronide and (16S)-coleon E are the main compounds responsible for the antiacetylcholinesterase and antioxidant activity in herbal tea of Plectranthus barbatus ("falso boldo")". Food Chem. 114 (3): 798–805. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.10.015.
- 1 2 Porfírio S, Falé PL, Madeira PJ, Florêncio MH, Ascensão L, Serralheiro ML (2010). "Antiacetylcholinesterase and antioxidant activities of Plectranthus barbatus tea, after in vitro gastrointestinal metabolism". Food Chem. 122: 179–187. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.044.
- ↑ Pizzorno, Joseph E.; Murray, Michael T. (2012). Textbook of Natural Medicine (4th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. p. 686. ISBN 9781437723335.
- ↑ Dubey MP, Srimal RC, Nityanand S, et al. (1981). "Pharmacological studies on coleonol, a hypotensive diterpene from Coleus forskohlii". J Ethnopharmacol. 3 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(81)90010-6. PMID 7193263.