''cis''-3-Hexenal
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3Z)-Hex-3-enal | |
| Other names
(Z)-Hex-3-enal cis-3-Hexenal Leaf aldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.141 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O | |
| Molar mass | 98.15 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.851 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 126 °C (259 °F; 399 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkenals |
Acrolein |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
cis-3-Hexenal, also known as (Z)-3-hexenal and leaf aldehyde, is colorless liquid and an aroma compound with an intense odor of freshly cut grass and leaves.[1][2] It is one of the major volatile compounds in ripe tomatoes. It is produced in small amounts by most plants and it acts as an attractant to many predatory insects. It is also a pheromone in many insect species.[3]
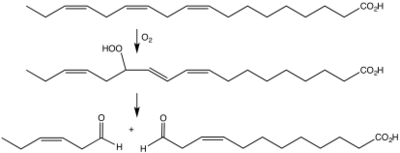
Biosynthesis of cis-3-hexenal from linolenic acid via the hydroperoxide by the action of a lipoxygenase followed by a hydroperoxide lyase.[4]
cis-3-Hexenal is an aldehyde. It is relatively unstable and isomerizes into the conjugated trans-2-hexenal. The related alcohol cis-3-hexen-1-ol is much more stable. It has a similar but weaker odor and is widely used in flavors and perfumes.
See also
- 1-Hexanol, another volatile organic compound, also considered responsible for the freshly mowed grass odor
External links
References
- ↑ "Molecule of the Month: Hexenal". Chm.bris.ac.uk. doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.5245834. Retrieved 2018-07-26.
- ↑ Hexenal / Chemistry World, Royal Society of Chemistry, 27 November 2013
- ↑ Ashraf El-Sayed. "Pheromone database". Pherobase.com. Retrieved 2018-07-26.
- ↑ KenjiMatsui (2006). "Green leaf volatiles: hydroperoxide lyase pathway of oxylipin metabolism". Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 9: 274–280. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2006.03.002.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.