Ciraparantag
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
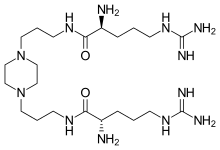
PER977 N1,N1′-[Piperazine-1,4-diylbis(propane-1,3-diyl)]bis-L-argininamide |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Onset of action | 10 min |
| Duration of action | 24 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H48N12O2 |
| Molar mass | 512.71 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ciraparantag (INN/USAN, or aripazine) is a drug under investigation as an antidote for a number of anticoagulant (anti-blood clotting) drugs, including factor Xa inhibitors (rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban), dabigatran, low molecular weight heparins and unfractionated heparin.[1][2]
Mechanism of action
According to in vitro studies, the substance binds directly to anticoagulants via hydrogen bonds from or to various parts of the molecule:[1]
| Hydrogen bonds | Rivaroxaban | Apixaban | Edoxaban | Dabigatran | Heparins |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guanidine part | |||||
| α-Amino group | |||||
| Amide nitrogen | |||||
| Amide oxygen |
Chemical properties
Ciraparantag consists of two L-arginine units connected with a piperazine containing linker chain.[1]
See also
Other anticoagulant antidotes
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.