Chondrocalcinosis
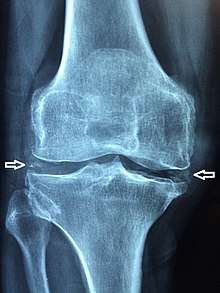
Chondrocalcinosis is calcification in hyaline and/or fibrocartilage.[1] It can be seen on radiography.
Causes
A common cause of chondrocalcinosis is calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD).[2]
Hypomagnesemia may cause chondrocalcinosis, and magnesium supplementation may reduce or alleviate symptoms.[3] In some cases, arthritis from injury can cause chondrocalcinosis.[4]
Other causes of chondrocalcinosis include:[2]
Diagnosis
Chondrocalcinosis can be visualized on projectional radiography, CT scan, MRI, US, and nuclear medicine.[1] CT scans and MRIs show calcific masses (usually within the ligamentum flavum or joint capsule), however radiography is more successful.[1] At ultrasound, chondrocalcinosis may be depicted as echogenic foci with no acoustic shadow within the hyaline cartilage.[5] As with most conditions, chondrocalcinosis can present with similarity to other diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis and gout.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Rothschild, Bruce M Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (radiology)
- 1 2 Matt A. Morgan and Frank Gaillard; et al. "Chondrocalcinosis". Radiopedia. Retrieved 2017-08-11.
- ↑ de Filippi JP, Diderich PP, Wouters JM (1992). "Hypomagnesemia and chondrocalcinosis". Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 136 (20): 139–41. PMID 1732847.
- ↑ Wright GD, Doherty M (1997). "Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition is not always 'wear and tear' or aging". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 56 (10): 586–8. doi:10.1136/ard.56.10.586. PMC 1752269. PMID 9389218.
- ↑ Arend CF. Ultrasound of the Shoulder. Master Medical Books, 2013. Free chapter on acromioclavicular chondrocalcinosis is available at ShoulderUS.com