Cereulide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
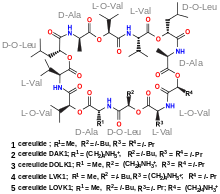
1,7,13,19,25,31-Hexaoxa-4,10,16,22,28,34-hexaazacyclohexatriacontane,cyclic peptide derivate; Cyclo(D-alanyl-3-methyl-L-2-hydroxybutanoyl-L-valyl-4-methyl-D-2-hydroxypentanoyl-D-alanyl-3-methyl-L-2-hydroxybutanoyl-L-valyl-4-methyl-D-2-hydroxypentanoyl-D-alanyl-3-methyl-L-2-hydroxybutanoyl-L-valyl-4-methyl-D-2-hydroxypentanoyl) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C57 H96 N6 O18 (D-Ala-D-O-Leu-L-Val)3 | |
| Molar mass | 1152 |
| extremely low | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Neurotoxicant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cereulide is a toxin produced by Bacillus cereus. A cyclic dodecadepsipeptide resembling valinomycin, it contains three repeats of four amino acids: D-Oxy-Leu—D-Ala—L-Oxy-Val—L-Val. It is a potent cytotoxin that destroys mitochondria. Cereulide acts as ionophore with a high affinity to potassium cations. Exposure to cereulide causes loss of the membrane potential and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.[1] [2] The spores of cereulide-producing strains of B. cereus are manyfold more heat resistant than spores of cereulide non-producers. It has no loss of activity upon autoclaving, cooking, or baking.[1] Cereulide is produced by a dedicated non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (NRPS) system in B. cereus.[3]
In addition to its cytotoxicity, cereulide causes nausea and vomiting. This effect is believed to be caused by its binding and activation of 5-HT3 receptors, leading to increased afferent vagus nerve stimulation.[4]
References
- 1 2 News on cereulide, the emetic toxin of Bacillus Cereus
- ↑ M. A. Andersson; R. Mikkola; J. Helin; M. C. Andersson; M. Salkinoja-Salonen (April 1998). "A Novel Sensitive Bioassay for Detection of Bacillus cereus Emetic Toxin and Related Depsipeptide Ionophores". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 64 (4): 1338–1343.
- ↑ http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0128569
- ↑ Agata N, Ohta M, Mori M, Isobe M (1995). "A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, is an emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus". FEMS Microbiol Lett. 129 (1): 17–20. doi:10.1016/0378-1097(95)00119-P. PMID 7781985.
External links
- Peltola; et al. (2004). "News on cereulide, the emetic toxin of Bacillus Cereus".
- S. Pitchayawasin; M. Isobe; M. Kuse; T. Franz; N. Agata; M. Ohta (May 19, 2004). "Molecular diversity of cereulide" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 13, 2005. Archive.org