Carbylamine reaction
The carbylamine reaction, also known as Hofmann's isocyanide test is a chemical test for detection of primary amines.[1] In this reaction, the analyte is heated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide and chloroform. If a primary amine is present, the isocyanide (carbylamine) is formed which are foul smelling substances.
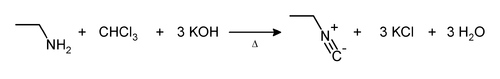
For example, the reaction with ethylamine:
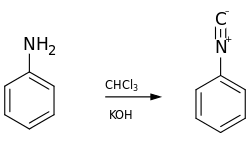
The reaction with aniline:
The carbylamine test does not give a positive reaction with secondary and tertiary amines.
This test is useful for identify the primary amine.
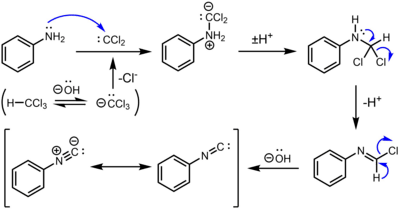
The mechanism involves the addition of aniline and dichlorocarbene, a reactive intermediate generated by the action of base on chloroform. Two successive base-mediated dehydrochlorination steps result in formation of the isocyanide.