Canvas fingerprinting
Canvas fingerprinting is one of a number of browser fingerprinting techniques for tracking online users that allow websites to identify and track visitors using the HTML5 canvas element instead of browser cookies or other similar means. The technique received wide media coverage in 2014[1][2][3][4] after researchers from Princeton University and KU Leuven University described it in their paper The Web never forgets.[5]
Description
Canvas fingerprinting works by exploiting the HTML5 canvas element. As described by Acar et. al. in [5]:
When a user visits a page, the fingerprinting script first draws text with the font and size of its choice and adds background colors (1). Next, the script calls Canvas API’s ToDataURL method to get the canvas pixel data in dataURL format (2), which is basically a Base64 encoded representation of the binary pixel data. Finally, the script takes the hash of the text-encoded pixel data (3), which serves as the fingerprint ...
Variations in which graphics processing unit (GPU) is installed or the graphics driver cause the variations in the fingerprint. The fingerprint can be stored and shared with advertising partners to identify users when they visit affiliated websites. A profile can be created from the user's browsing activity allowing advertisers to target advertising to the user's inferred demographics and preferences.[3][6]
Uniqueness
Since the fingerprint is primarily based on the browser, operating system, and installed graphics hardware it does not uniquely identify users. In a small-scale study with 294 participants from Amazon's Mechanical Turk, an experimental entropy of 5.7 bits was observed, but the authors of the study suggest more entropy could likely be observed in the wild and with more patterns used in the fingerprint. While not sufficient to uniquely identify users by itself, this fingerprint could be combined with other sources of entropy to provide a unique identifier. It is claimed that because the technique is effectively fingerprinting the GPU, the entropy is "orthogonal" to the entropy of previous browser fingerprint techniques such as screen resolution and browser JavaScript capabilities.[7]
Mitigation
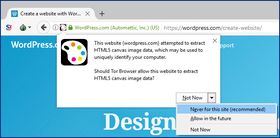
Tor Project reference documentation states, "After plugins and plugin-provided information, we believe that the HTML5 Canvas is the single largest fingerprinting threat browsers face today."[8] Tor Browser notifies the user of canvas read attempts and provides the option to return blank image data to prevent fingerprinting[5]. However, Tor Browser is currently unable to distinguish between legitimate uses of the canvas element and fingerprinting efforts, so its warning cannot be taken as proof of a website's intent to identify and track its visitors. Browser add-ons like Privacy Badger,[9] DoNotTrackMe[10] or Adblock Plus[11] manually enhanced with EasyPrivacy list are able to block third-party ad network trackers and will block canvas fingerprinting provided that the tracker is served by a third party server (as opposed to being implemented by the visited website itself).
History
In May 2012, Keaton Mowery and Hovav Shacham, researchers at University of California, San Diego, wrote a paper Pixel Perfect: Fingerprinting Canvas in HTML5 describing how the HTML5 canvas could be used to create digital fingerprints of web users.[3][7]
Social bookmarking technology company AddThis began experimenting with canvas fingerprinting early in 2014 as a potential replacement for cookies. 5% of the top 100,000 websites used canvas fingerprinting while it was deployed.[9] According to AddThis CEO Richard Harris, the company has only used data collected from these tests to conduct internal research. Users will be able to install an opt-out cookie on any computer to prevent being tracked by AddThis with canvas fingerprinting.[3]
A software developer writing in Forbes stated that device fingerprinting has been utilized for the purpose of preventing unauthorized access to systems long before it was used for tracking users without their consent.[2]
As of 2014 the technique is widespread in all sorts of websites with at least a dozen of high-profile web ads and user tracking suppliers using it.[12]
See also
- Evercookie – a type of browser cookie that is intentionally difficult to delete
- Local shared object – a persistent browser cookie also known as a Flash cookie
- Web storage – web application software methods and protocols used for storing data in a web browser
References
- ↑ Knibbs, Kate (July 21, 2014). "What You Need to Know About the Sneakiest New Online Tracking Tool". Gizmodo. Retrieved July 21, 2014.
- 1 2 Joseph Steinberg (July 23, 2014). "You Are Being Tracked Online By A Sneaky New Technology -- Here's What You Need To Know". Forbes. Retrieved November 15, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Angwin, Julia (July 21, 2014). "Meet the Online Tracking Device That is Virtually Impossible to Block". ProPublica. Retrieved July 21, 2014.
- ↑ Kirk, Jeremy (July 21, 2014). "Stealthy Web tracking tools pose increasing privacy risks to users". PC World. Retrieved July 21, 2014.
- 1 2 3 Acar, Gunes; Eubank, Christian; Englehardt, Steven; Juarez, Marc; Narayanan, Arvind; Diaz, Claudia (July 24, 2014). "The Web never forgets: Persistent tracking mechanisms in the wild". Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ Nikiforakis, Nick; Acar, Günes (2014-07-25). "Browser Fingerprinting and the Online-Tracking Arms Race". ieee.org. IEEE. Retrieved October 31, 2014.
- 1 2 Mowery, Keaton; Shacham, Hovav. "Pixel Perfect: Fingerprinting Canvas in HTML5" (PDF). Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- ↑ "The Design and Implementation of the Tor Browser [DRAFT]". www.torproject.org. Retrieved 2018-05-25.
- 1 2 Davis, Wendy (July 21, 2014). "EFF Says Its Anti-Tracking Tool Blocks New Form Of Digital Fingerprinting". MediaPost. Retrieved July 21, 2014.
- ↑ Kirk, Jeremy (July 25, 2014). "'Canvas fingerprinting' online tracking is sneaky but easy to halt". PC World. Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ Smith, Chris. "Adblock Plus: We can stop canvas fingerprinting, the 'unstoppable' new browser tracking technique". BGR. PMC. Archived from the original on July 28, 2014.
- ↑ "Websites using HTML5 canvas fingerprinting". WebCookies.org. Archived from the original on 2014-12-28. Retrieved 2014-12-28.