O'Shaughnessy's chameleon
| O'Shaughnessy's chameleon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Iguania |
| Family: | Chamaeleonidae |
| Genus: | Calumma |
| Species: | C. oshaughnessyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Calumma oshaughnessyi (Günther, 1881) | |
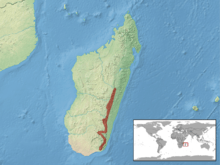 | |
| Range of O'Shaughnessy's chameleon | |
| Synonyms | |
O'Shaughnessy's chameleon (Calumma oshaughnessyi) is a species of chameleon endemic to Madagascar. It was named after the British poet and herpetologist Arthur O'Shaughnessy.[1][2]
Distribution
O'Shaughnessy's chameleon has a range of about 18,000 square kilometers throughout the southeastern portion of the central highlands of Madagascar. Its distribution extends from Tsinjoarivo, Ambatolampy in the north to Andohahela National Park in the south. The species is highly dependent on intact, humid forest as its habitat, living in lower densities on selectively logged territories.[3]
Description
O'Shaughnessy's chameleon, being closely related to Parson's chameleon, is similar in shape and color but slightly smaller.[4] Albert Günther, the first to scientifically describe the species, stated that the type specimen is a male measuring 15.5 inches (39.4 cm) in total length, including its tail which is 9 inches (22.9 cm) long. It is mostly brownish gray, with a darker throat and jaw.[5] Although lacking horns, males of the species have a short, bony structure on their snouts that females lack.[6]
Behavior
During a 1997 study, researchers discovered that adult O'Shaughnessy's chameleons are most active in the morning and the evening.[3]
Conservation and threats
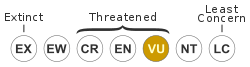
Although in some places common, O'Shaughnessy's chameleon is severely threatened. Its populations are declining and fragmented, and the species is ranked as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. Although reports of illegal trade in the species do exist, its primary threat is habitat loss, such as logging and deforestation. While significant populations do exist in protected areas, further loss of inhabitable terrain could fragment and isolate these communities.[3]
References
- 1 2 Calumma oshaughnessyi | The Reptile Database
- ↑ Beolens B, Watkins M, Grayson M. 2011. The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Calumma oshaughnessyi, p. 197).
- 1 2 3 Calumma oshaughnessyi (O'Shaughnessy's Chameleon) at The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- ↑ Mattison, Chris; Garbutt, Nick (2012). Chameleons. United States: Firefly Books Inc. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-77085-121-4.
- ↑ Günther A. 1881. Seventh Contribution to the Knowledge of the Fauna of Madagascar. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., Fifth Series, 7: 357-360. ("Chamæleon O'Shaughnessii ", new species, p. 358). (at Biodiversity Heritage Library).
- ↑ Mattison, Chris; Garbutt, Nick (2012). Chameleons. United States: Firefly Books Inc. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-77085-121-4.