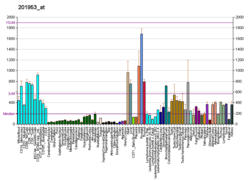
CIB1
Calcium and integrin-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CIB1 gene.[5][6][7]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the calcium-binding protein family. The specific function of this protein has not yet been determined; however this protein is known to interact with DNA-dependent protein kinase and may play a role in kinase-phosphatase regulation of DNA end-joining. This protein also interacts with integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3), which may implicate this protein as a regulatory molecule for alpha(IIb)beta(3).[7]
Interactions
CIB1 has been shown to interact with RAC3,[8] PSEN2,[9] DNA-PKcs,[10] UBR5[11] and CD61.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000185043 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030538 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 Naik UP, Patel PM, Parise LV (Apr 1997). "Identification of a novel calcium-binding protein that interacts with the integrin alphaIIb cytoplasmic domain". J Biol Chem. 272 (8): 4651–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.8.4651. PMID 9030514.
- ↑ Hattori A, Seki N, Hayashi A, Kozuma S, Saito T (Aug 2000). "Genomic structure of mouse and human genes for DNA-PKcs interacting protein (KIP)". DNA Seq. 10 (6): 415–8. doi:10.3109/10425170009015612. PMID 10826701.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: CIB1 calcium and integrin binding 1 (calmyrin)".
- ↑ Haataja, Leena; Kaartinen Vesa; Groffen John; Heisterkamp Nora (Mar 2002). "The small GTPase Rac3 interacts with the integrin-binding protein CIB and promotes integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3)-mediated adhesion and spreading". J. Biol. Chem. United States. 277 (10): 8321–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105363200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11756406.
- ↑ Stabler, S M; Ostrowski L L; Janicki S M; Monteiro M J (Jun 1999). "A myristoylated calcium-binding protein that preferentially interacts with the Alzheimer's disease presenilin 2 protein". J. Cell Biol. UNITED STATES. 145 (6): 1277–92. doi:10.1083/jcb.145.6.1277. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2133148. PMID 10366599.
- ↑ Wu, X; Lieber M R (Oct 1997). "Interaction between DNA-dependent protein kinase and a novel protein, KIP". Mutat. Res. NETHERLANDS. 385 (1): 13–20. doi:10.1016/s0921-8777(97)00035-9. ISSN 0027-5107. PMID 9372844.
- ↑ Henderson, Michelle J; Russell Amanda J; Hird Samantha; Muñoz Marcia; Clancy Jennifer L; Lehrbach Gillian M; Calanni Sophina T; Jans David A; Sutherland Robert L; Watts Colin K W (Jul 2002). "EDD, the human hyperplastic discs protein, has a role in progesterone receptor coactivation and potential involvement in DNA damage response". J. Biol. Chem. United States. 277 (29): 26468–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203527200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12011095.
External links
- Human CIB1 genome location and CIB1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Wu X, Lieber MR (1997). "Interaction between DNA-dependent protein kinase and a novel protein, KIP". Mutat. Res. 385 (1): 13–20. doi:10.1016/s0921-8777(97)00035-9. PMID 9372844.
- Seki N, Hayashi A, Abe M, et al. (1999). "Chromosomal assignment of the gene for human DNA-PKcs interacting protein (KIP) on chromosome 15q25.3-q26.1 by somatic hybrid analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization". J. Hum. Genet. 43 (4): 275–7. doi:10.1007/s100380050089. PMID 9852683.
- Stabler SM, Ostrowski LL, Janicki SM, Monteiro MJ (1999). "A myristoylated calcium-binding protein that preferentially interacts with the Alzheimer's disease presenilin 2 protein". J. Cell Biol. 145 (6): 1277–92. doi:10.1083/jcb.145.6.1277. PMC 2133148. PMID 10366599.
- Kauselmann G, Weiler M, Wulff P, et al. (1999). "The polo-like protein kinases Fnk and Snk associate with a Ca(2+)- and integrin-binding protein and are regulated dynamically with synaptic plasticity". EMBO J. 18 (20): 5528–39. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.20.5528. PMC 1171621. PMID 10523297.
- Hwang PM, Vogel HJ (2000). "Structures of the platelet calcium- and integrin-binding protein and the alphaIIb-integrin cytoplasmic domain suggest a mechanism for calcium-regulated recognition; homology modelling and NMR studies". J. Mol. Recognit. 13 (2): 83–92. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(200003/04)13:2<83::AID-JMR491>3.0.CO;2-A. PMID 10822252.
- Holtrich U, Wolf G, Yuan J, et al. (2000). "Adhesion induced expression of the serine/threonine kinase Fnk in human macrophages". Oncogene. 19 (42): 4832–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203845. PMID 11039900.
- Haataja L, Kaartinen V, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N (2002). "The small GTPase Rac3 interacts with the integrin-binding protein CIB and promotes integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3)-mediated adhesion and spreading". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (10): 8321–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105363200. PMID 11756406.
- Whitehouse C, Chambers J, Howe K, et al. (2002). "NBR1 interacts with fasciculation and elongation protein zeta-1 (FEZ1) and calcium and integrin binding protein (CIB) and shows developmentally restricted expression in the neural tube". Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (2): 538–45. doi:10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02681.x. PMID 11856312.
- Hollenbach AD, McPherson CJ, Lagutina I, Grosveld G (2002). "The EF-hand calcium-binding protein calmyrin inhibits the transcriptional and DNA-binding activity of Pax3". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1574 (3): 321–8. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00230-0. PMID 11997098.
- Henderson MJ, Russell AJ, Hird S, et al. (2002). "EDD, the human hyperplastic discs protein, has a role in progesterone receptor coactivation and potential involvement in DNA damage response" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 277 (29): 26468–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203527200. PMID 12011095.
- Barry WT, Boudignon-Proudhon C, Shock DD, et al. (2002). "Molecular basis of CIB binding to the integrin alpha IIb cytoplasmic domain". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (32): 28877–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202983200. PMID 12023286.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ma S, Liu MA, Yuan YL, Erikson RL (2003). "The serum-inducible protein kinase Snk is a G1 phase polo-like kinase that is inhibited by the calcium- and integrin-binding protein CIB". Mol. Cancer Res. 1 (5): 376–84. PMID 12651910.
- Naik UP, Naik MU (2003). "Association of CIB with GPIIb/IIIa during outside-in signaling is required for platelet spreading on fibrinogen". Blood. 102 (4): 1355–62. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-02-0591. PMID 12714504.
- Naik MU, Naik UP (2004). "Calcium-and integrin-binding protein regulates focal adhesion kinase activity during platelet spreading on immobilized fibrinogen". Blood. 102 (10): 3629–36. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-05-1703. PMID 12881299.
- Yamniuk AP, Nguyen LT, Hoang TT, Vogel HJ (2004). "Metal ion binding properties and conformational states of calcium- and integrin-binding protein". Biochemistry. 43 (9): 2558–68. doi:10.1021/bi035432b. PMID 14992593.
- Lee GE, Yu EY, Cho CH, et al. (2004). "DNA-protein kinase catalytic subunit-interacting protein KIP binds telomerase by interacting with human telomerase reverse transcriptase". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (33): 34750–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401843200. PMID 15190070.
- Lehner B, Sanderson CM (2004). "A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.