CAESAR self-propelled howitzer
| CAESAR | |
|---|---|
|
CAESAR howitzer on a Unimog U2450L 6x6 chassis | |
| Type | Self-propelled howitzer |
| Place of origin | France |
| Service history | |
| Wars | War in Afghanistan, Cambodian–Thai border stand-off, Operation Serval, Battle of Mosul |
| Production history | |
| Designer | GIAT Industries |
| Specifications | |
| Weight |
17.7 tonnes (6×6) 28.7-30.2 tonnes (8×8)[1] |
| Length |
10 m (32 ft 10 in) 12.3 m (40 ft 4 in) (8x8)[1] |
| Width |
2.55 m (8 ft 4 in) 2.8 m (9 ft 2 in) (8x8)[1] |
| Height |
3.7 m (12 ft 2 in) 3.1 m (10 ft 2 in) (8x8)[1] |
| Crew | 5-6 (3, emergency) |
|
| |
Main armament | 155 mm/52-calibre |
Secondary armament | none |
| Engine | diesel |
| Suspension | 6x6 wheel |
Operational range | 600 km (370 mi) |
| Speed |
On-road: 100 km/h (62 mph) Off-road: 50 km/h (31 mph) |
The CAESAR (CAmion Equipé d'un Système d'ARtillerie; French: Truck equipped with an artillery system)[2] is a French self-propelled 155 mm/52-calibre gun-howitzer, installed on a 6X6 truck chassis. Examples built for the French Army use a Renault Sherpa 10 chassis, examples built for export utilize the 6x6 Unimog U2450L chassis. The CAESAR platform was developed by the former GIAT Industries (now known as Nexter) and is operated by the French, Indonesian, Saudi Arabian, and Thai militaries.
Development
Caesar was developed in the 1990s as a technology demonstrator by the French state-owned company GIAT Industries; in cooperation with Lohr Industrie. It was first shown in public in 1994. Four years later a pre-production model underwent trials with the French Army.[3]
The Caesar artillery system evolved from the earlier 155 AM F3 automotive gun, which used the chassis of the AMX-13 light tank.
Design
The CAESAR is a wheeled, 155mm 52-caliber self-propelled howitzer. It holds 18 rounds and is typically operated by a crew of five, though if necessary, the CAESAR can be operated by as few as three persons. It can be transported by C-130 or A400M, and has a firing range of approximately 42 km using an Extended Range, Full Bore (ERFB) shell, and more than 50 km using rocket assisted shells. The system is integrated with a fully computerized system, providing an automatic control. During Eurosatory 2006, CAESAR was exhibited with an automated laying system based on the SIGMA 30 inertial navigation system.
Nexter is developing an armored cab for the CAESAR in response to demand for more protection for the crew. The additional armor will protect against IEDs and roadside bombs, anti-vehicle mines, and 155 mm shells landing as close as five meters (16 feet) away from the vehicle. It can be added to the cabs of existing CAESARs. Heavier armor will increase its weight by 400 kg (880 pounds) and raise the price by 4-5 percent.[4]
Caesar 8x8
In 16 September 2015, Nexter has unveiled the Caesar 8x8 at DSEI 2015 with high level of mobility ensured by a modified Tatra T-815 8x8 chassis.[5] The 8x8 Caesar being shown is fitted with a standard unarmoured forward control four-person cab, but one of the options is a fully armour protected cab. Gross vehicle weight would depend on the level of armour protection, but is about 30 tonnes. It is powered by a 410 hp diesel engine.[6]
Operators
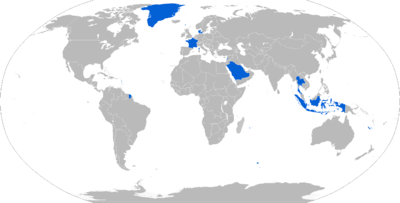
Current operators


 Indonesian CAESAR self-propelled howitzer
Indonesian CAESAR self-propelled howitzer

Future operators
Operational deployment
In June 2009, the French Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff confirmed that eight CAESAR would be sent to Afghanistan to support French operations. They were deployed during the summer.[19]
Three were deployed 1 August 2009[20] by the 3rd Marine Artillery Regiment (3è RAMa), followed by five others, deployed as a firebase in FOB Tora, Tagab and Nijrab. They are fitted with cabin armor add-ons, with fireport.
The French army deployed this system in southern Lebanon as part as the UNIFIL peace keeping force.
During Operation Serval in Mali 4 CAESAR were deployed by the 68e régiment d'artillerie d'Afrique (68th Artillery Regiment of Africa).[21]
In April 2011, the Royal Thai Army used the CAESAR against Cambodia's BM-21, Thai Army claimed that they destroyed more than 2 BM-21 systems.[22]
Four CAESAR were deployed to Iraq for the Battle of Mosul, where French forces are supporting the Iraqi army and an international coalition forces to reclaim Mosul from ISIL in October 2016 and into the first half of 2017.[23]
Gallery
_2.jpg) On display, side profile of deployed howitzer.
On display, side profile of deployed howitzer._Strasbourg.jpg) On display, close up of system.
On display, close up of system. Live fire in Afghanistan, August 2009.
Live fire in Afghanistan, August 2009.- CAESAR gun line in Afghanistan, August 2009.
- Preparing to load the breech in Afghanistan, August 2009.
See also
References
- Citations
- 1 2 3 4 http://www.military-today.com/artillery/caesar_8x8.htm
- 1 2 Caesar self propelled gun-www.defense-update.com; retrieved 13 February 2007
- ↑ "Nexter Systems CAESAR 155 mm self-propelled gun (France), Self-propelled guns and howitzers (wheeled)". Jane's Armour and Artillery. February 10, 2010. Retrieved January 5, 2011.
- ↑ Caesar Gets Bulletproof, Just In Case - Strategypage.com, 15 June 2013
- ↑ http://www.janes.com/article/68983/denmark-orders-caesar-howitzers-on-8x8-tatra-trucks
- ↑ http://www.janes.com/article/54396/caesar-rolls-in-on-eight-wheels-dsei15-d2
- ↑ Daffix, Bruno. "La DGA livre le premier canon Caesar à l'armée de terre". DGA. Archived from the original on 2008-07-25. Retrieved 2008-07-26.
- ↑ Opex360; Artillerie : 32 CAESAR blindés remplaceront les derniers canons AUF1 en 2030 En savoir plus sur http://www.opex360.com/2015/10/24/artillerie-32-caesar-blindes-remplaceront-les-derniers-canons-auf1-en-2030/#xBBW5PRSGGXzg7iI.99; 24 October 2015(in French)
- 1 2 Libération; Des canons français pour l'Arabie saoudite; 20 July 2006(in French)
- ↑ "Janes.com; Déjà 163 "feuilles" de laurier à la couronne de Caesar". Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ↑ "Saudi Arabia takes delivery of first CAESARs",Jane's Information Group, 31 March 2010
- ↑ "Défense : quand le Danemark veut du "Made in France"". La Tribune. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ↑ NurW. "Indonesia Signs Contract for 37 Self-Propelled Artillery "Caesar"". Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ↑ Tomkins, Richard (20 February 2017). "Nexter providing CAESAR howitzer systems to Indonesia". United Press International. Archived from the original on 21 February 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ↑ http://www.armyrecognition.com/october_2014_global_defense_security_news_uk/lebanese_armed_forces_to_purchase_french_vbc_90_armoured_and_caesar_155mm_howitzers_2510142.html
- ↑ "Nyt materiel til Forsvaret". www.fmn.dk (in Danish). Retrieved 2017-03-14.
- ↑ "Denmark selects CAESAR self-propelled 155mm gun-howitzer installed on an 8X8 truck chassis". Defence Blog. 15 March 2017. Archived from the original on 15 March 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ↑ Felstead, Peter (23 May 2017). "Nexter announces Danish 8x8 CAESAR contract". IHS Jane's 360. Archived from the original on 24 May 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ↑ Libération; La France va envoyer des CAESAR en Afghanistan; 29 June 2009(in French)
- ↑ http://www.defense.gouv.fr/ema/operations_exterieures/afghanistan/breves_et_photos/afghanistan_arrivee_des_caesa
- ↑ "FOB – Forces Operations Blog » Mali: VBCI et Caesar engagés dans l'opération Serval". Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ↑ "Artillery : Caesar Gets Bulletproof, Just In Case - RP Defense". RP Defense. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ↑ "Mossoul : le Charles de Gaulle manque le début de l'offensive". Ouest-France.fr (in French). 17 October 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Camion équipé d'un système d'artillerie. |
- (in English) Caesar Renault Sherpa 5 Nexter wheeled self-propelled howitzer
- (in English) Caesar 155mm Artillery System, France
- (in English) CAESAR page at Janes.com
- (in French) CAESAR description by Nexter Systems