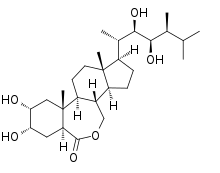
Brassinolide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(22R,23R)-2α,3α,22,23-tetrahydroxy-6,7-seco-5α-campestano-6,7-lactone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,5S,6R,7aR,7bS,9aS,10R,12aS,12bS)-10-[(2S,3R,4R,5S)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5,6-dimethyl-2-heptanyl]-5,6-dihydroxy-7a,9a-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-benzo[c]indeno[5,4-e]oxepin-3-one | |
| Other names
2,3,22,23-Tetrahydroxy-β-homo-7-oxaergostan-6-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H48O6 | |
| Molar mass | 480.69 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Brassinolide is a plant hormone. The first isolated brassinosteroid, it was discovered when it was shown that pollen from rapeseed (Brassica napus) could promote stem elongation and cell division.[1] The biologically active component was isolated and named brassinolide.[2]
References
- ↑ Mitchell JW, Mandava N, Worley JF, Plimmer JR, Smith MV (1970). "Brassins--a new family of plant hormones from rape pollen". Nature. 225 (5237): 1065–6. doi:10.1038/2251065a0. PMID 16056912.
- ↑ Grove, Michael D.; Spencer, Gayland F.; Rohwedder, William K.; Mandava, Nagabhushanam; Worley, Joseph F.; Warthen, J. David; Steffens, George L.; Flippen-Anderson, Judith L.; Cook, J. Carter (1979). "Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica napus pollen". Nature. 281 (5728): 216–217. Bibcode:1979Natur.281..216G. doi:10.1038/281216a0.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.