Blaise ketone synthesis
The Blaise ketone synthesis (named after Edmond Blaise) is the chemical reaction of acid chlorides with organozinc compounds to give ketones.
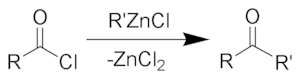
The reaction also works with organocuprates.
Variations
Blaise-Maire reaction
The Blaise-Maire reaction is the Blaise ketone synthesis using β-hydroxy acid chlorides to give β-hydroxyketones, which are converted into α,β-unsaturated ketones using sulfuric acid.
See also
References
- ^ Blaise, E. E.; Koehler, A. (1910). "Synthèse au moyen des dérivés organo-métalliques mixtes du zinc (II)". Bull. Soc. Chim. Paris. 7: 215–227.
- ^ Blaise, E. E. (1911). Bull. Soc. Chim. 9: 1. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ Posner, G. H.; Whitten, C. E. (1976). "Secondary and Tertiary Alkyl Ketones from Carboxylic Acid Chlorides and Lithium Phenylthio(Alkyl)Cuprate Reagents: tert-Butyl Phenyl Ketone". Organic Syntheses. 55: 122. ; Collective Volume, 6, p. 248
- ^ Fujisawa, T.; Sato, T. (1988). "Ketones from Carboxylic Acids and Grignard Reagents: Methyl 6-Oxodecanoate". Organic Syntheses. 66: 116. ; Collective Volume, 8, p. 441
- ^ Cason, J. (1947). "The Use of Organocadmium Reagents for the Preparation of Ketones". Chem. Rev. 40 (1): 17. doi:10.1021/cr60125a002. PMID 20287882.
- ^ Shirley, D. A. (1954). "The Synthesis of Ketones from Acid Halides and Organometallic Compounds of Magnesium, Zinc, and Cadmium". Org. React. 8: 29. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or008.02. ISBN 0471264180.
- ^ Blaise, E. E.; Maire, M. (1907). Compt. Rend. 145: 73. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.