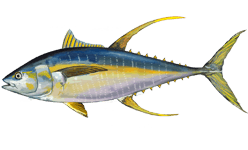
Blackfin tuna
| Blackfin tuna | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Scombriformes |
| Family: | Scombridae |
| Tribe: | Thunnini |
| Genus: | Thunnus |
| Subgenus: | Neothunnus |
| Species: | T. atlanticus |
| Binomial name | |
| Thunnus atlanticus (Lesson, 1831) | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
The blackfin tuna (Thunnus atlanticus) is the smallest tuna species in the genus Thunnus, generally growing to a maximum of 100 cm (39 in) in length and weighing 21 kg (46 lb).
Blackfin tuna have oval-shaped bodies, black backs with a slight yellow on the finlets, and yellow on the sides of their bodies. They are found in the western Atlantic from Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts, to Brazil, including the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico.[2]
Blackfin tuna hunt both epipelagic (surface) and mesopelagic (deeper water) fish and squid. They also eat crustaceans such as shrimp, crabs, amphipods, stomatopods, and the larvae of decapods.[2] They are a short-lived, fast-growing species; a 5-yr-old fish would be considered old. They reach sexual maturity at the age of 2 years, and spawn in the open sea during the summer. Blackfin tuna are a warmer-water fish, preferring water temperatures over 20 °C (68 °F).
Sustainable consumption
In 2010, Greenpeace International did not add the blackfin tuna, unlike other tuna species, to its seafood red list. [3]
References
- ↑ Collette, B.; Amorim, A.F.; Boustany, A.; et al. (2011). "Thunnus atlanticus". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2011: e.T155276A4764002. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2011-2.RLTS.T155276A4764002.en. Retrieved 26 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2018). "Thunnus atlanticus" in FishBase. February 2018 version.
- ↑ Greenpeace International Seafood Red list Archived February 5, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
External links


- FishBase info for black tuna
- Blackfin Tuna Identification
- Encyclopedia of Life Info for Thunnus atlanticus