Biosatellite 2
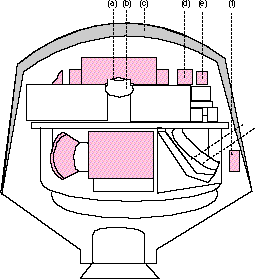 Drawing of Biosatellite 2. | |
| Mission type | Bioscience |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA / ARC |
| COSPAR ID | 1967-083B |
| SATCAT no. | 9236[1] |
| Mission duration | 27 days |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | General Electric |
| Launch mass | 955 kilograms (2,105 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 7 September 1967, 22:04:26 UTC[2] |
| Rocket | Delta G 475/D51 |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral LC-17B[3]rp |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | 4 October 1967 |
| Landing site | Hawaii, USA |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.00202[4] |
| Perigee | 286 kilometres (178 mi)[4] |
| Apogee | 313 kilometres (194 mi)[4] |
| Inclination | 33.5º[4] |
| Period | 90.8 minutes[4] |
| Epoch | 7 September 1967[4] |
Biosatellite 2, also known as abbreviated as Biosat 2 and as Biosatellite B, was a second artificial satellite unmanned U.S. belonging to Biosatellite program for biological research. It was released on September 7, 1967 by a rocket Delta G from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, USA.[5]
Biosatellite 2 carried 13 Biological experiments involving insects, frog eggs, plants and microorganisms. The capsule returned ahead of time because of the tropical storm threat in the recovery area and communication problems between the capsule and ground stations. The main objective of the mission was to determine if the level of radiation sensitivity of living organisms in space is greater, or less than on land, for which disposed of a radiation source in front of the capsule.
Experiments
- Effects of Weightlessness on Wheat Seedling Morphogenesis and Histochemistry
- Growth Physiology of the Wheat Seedling in Space
- Biochemical Changes in the Developing Wheat Seedling in a Weightless State
- Effect of Weightlessness on the Dividing Egg of Rana Pipiens
- Mutational Response of Habrobracon
- Liminal Angle of a Plagiogeotropic Organ
- Effects of Radiation and Weightlessness on Tribolium Pupae
- Effects of Weightlessness on Radiation Induced Somatic Dam. in Drosophila Larvae
- Effects of Space on Radiation-Induced Damage to Reproductive Cells of Pupae
- Genetic and Cytologic Studies of Tradescantia Irradiated During Flight
- Combined Effects of Weightlessness and Radiation on Inact.+Mutation in Neurospra
- Space Flight Effects + Gamma Radiation Interaction on Growth +Induc.of Bacteria
- Effect of Weightlessness on Amoeba, Pelomyxa Carolinensis[4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1967-083A - Bios 2. lib.cas.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 2018-06-14.
- ↑ Jonathan McDowell Launch Log. Jonathan's Space Page. Retrieved 2018-06-14.
- ↑ Mark Wade Biosatellite. Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2018-06-14.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 NASA GSFC. Biosatellite 2. NSSDCA. Retrieved 2018-06-14.
- ↑ Gunter Dirk Krebs. Biosat 1, 2, 3 (Bios 1, 2, 3). Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2016-16-05.
External links
- NASA Facts Biosatellite II. Scribd