Bhuj (weapon)
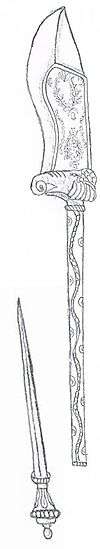
The bhuj (Devanāgarī: भुज) is a type of knife or dagger from western India. It is commonly called an axe-knife, because the blade is fixed onto an axe-like haft. The weapon takes its name from the city of Bhuj in the Kachchh district of the state of Gujarat, where it originated.[1] The Bhuj is short, broad, stout, and heavy, with a mild curve. It often sports an engraved and gilded mount, inlaid haft and decorated knob. This knob is typically a stylized elephant head, giving the weapon the nickname elephant knife. The short re-curved blade measures 7-10 inches long, and its copper sheath makes the weapon 20 inches long in total. It is mostly single-edged, except for a slight rear edge at the tip. The blade is mounted at a right angle to a metal haft in a manner similar to a parashu or axe. The haft is sometimes hollow, concealing another small stiletto-like dagger.
References
- ↑ "Partitioned: the other face of freedom: Volume 1". Google.co.in. Retrieved 2012-03-05.
Sources
- The complete encyclopedia of arms and weapons, Edited by Leonid Tarassuk and Claude Blair, Bonanza books (Crown)
- Dr Tobias Capwell (2009). The World Encyclopedia Of Knives, Daggers And Bayonets. Anness Publishing.