Maratha Peshwa and Generals from Bhat Family
| Peshwa Family (Bhat family) | |
|---|---|
| Current region | Pune, India |
| Place of origin | Konkan, India |
| Members |
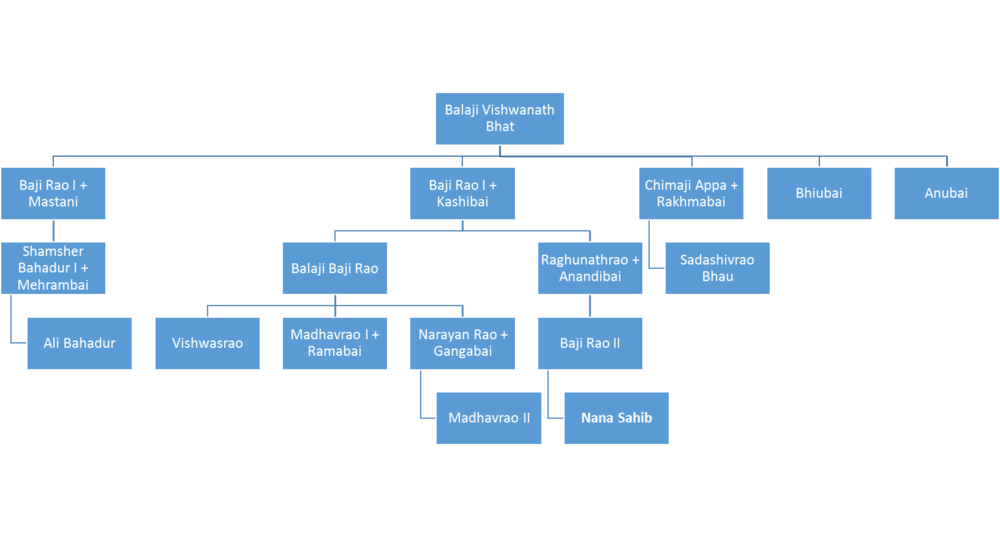
Vishwanathpant (Visaji) Bhat Balaji Vishwanath Bajirao I Balaji Bajirao Madhavrao Peshwa Narayanrao Peshwa Raghunathrao Sawai Madhava Rao II Narayan Baji Rao II |
The Peshwa family earlier known as Bhat family is a prominent Indian family who dominated India for around 100 years in the 18th century. Most of the members in this family were the Prime Ministers in Peshwa Era and that later became their surname. During their regime, most of India was under their control. The last Peshwa, Baji Rao II, was defeated by the British East India Company in the Third Anglo-Maratha War in 1818. The territory was annexed to the British East India Company's Bombay Presidency, and he was pensioned off.
Family tree
First generation
- Balaji Vishwanath (1662–1720) was the first of a series of hereditary Peshwas (Marathi for Prime Minister) hailing from the Marathi Chitpavan Brahmin family[1][2][3] who gained effective control of the Maratha Empire during the 18th century. Balaji Vishwanath assisted a young Maratha Emperor Chhatrapati Shahu, grandson of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, to consolidate his grip on a kingdom that had been racked by civil war and persistent attack by the Mughals under Aurangzeb. He was called "the second founder of the Maratha State."[4]
Second generation
Balaji married Radhabai Barve (16??–1752) and had two sons & two daughters.
- Baji Rao I (18 August 1700 – 28 April 1740), also known as Bajirao I, was a noted general who was appointed as the Peshwa by Chhatrapati Shahu of the Maratha Empire in 1720 as the successor to Balaji Vishwanath[4][5], He is also known as Thorale Bajirao (Bajirao the elder) in (Marathi to distinguish him from his grandson and namesake, Bajirao II, the last Peshwa.
- Chimaji Appa (1707–1741) was the son of Balaji Vishwanath Bhat and the younger brother of Bajirao Peshwa.He was an able military commander who liberated Vasai fort from the Portuguese in a hard fought battle in 1739[6],[7].
- Bhiubai – She married Abaji Joshi of Baramati, brother of the banker Balaji Naik famed as Bajirao I's "most tormenting creditor",who belongs to Deshastha Brahmin community.[8]
- Anubai - She married Venkatrao Ghorpade of Ichalkaranji[9]. Their heirs ruled the state of Ichalkaranji till 1947.
Third generation
Bajirao was married to Kashibai (née Barve), and had two sons together: Balaji Bajirao Peshwa (Nanasaheb) who was later appointed Peshwa by Shahu in 1740. Their second son was named Raghunathrao. Bajirao also took Mastani as the second wife who was the daughter of Maharaja Chhatrasal of Panna by a Persian Muslim wife. Chimajiappa was married to Rakhmabai (Pethe family). He had only son, Sadashivrao known popularly as Sadashivrao Bhau who led the Maratha forces in the Third Battle of Panipat against Ahmad Shah Abdali. Rakhmabai died shortly after Sadashivrao's birth, which led to Chimajiappa's second marriage to Annapuurnabai. Bajirao and Mastani had a son named Shamsher Bahadur
- Balaji Baji Rao (Nanasaheb) (8 December 1720 – 23 June 1761), also known as Nana Saheb Peshwa was son of Bajirao[4] and Kashibai. Chattrapati Shahu, at time of his death, appointed Balaji Baji Rao Peshwa of Maratha Empire. He contributed to development of Pune, India. Under his reign, borders of Maratha Empire crossed Peshawar (presently in Pakistan) by 1760 AD . However, he is also held responsible for defeat of Marathas at the Battle of Panipat (1761).
- Raghunathrao (b. 18 Aug.1734 – d. 11 Dec.1783) was Peshwa of the Maratha Empire from 1773 to 1774. Earlier in his career as a commander of Maratha forces, he is credited with expanding the Maratha Kingdom to include far-flung areas such as Attock in present-day Pakistan[10]. However, he is also blamed sowing the seeds for the downfall of the Peshwa Dynasty. He is nicknamed as Ragho Bharari since he is instrumental in planting the triumphant Hindu Maratha flag till Attock in present-day Pakistan.[11]
- Janardan Rao who died young
- Sadashivrao Bhau (4 August 1730 – 14 January 1761) was the son of Chimaji Appa and Rakhmabai and the nephew of Peshwa Baji Rao I. He served as the Sarsenapati (commander-in-chief) of the Maratha army at the third battle of Panipat. He died fighting at the third battle of Panipat.[12]
- Shamsher Bahadur I (Krishna Rao) (1734 - 1761) also spelled as Samsher Bahadur, a.k.a. Krishnasinh, was a Maratha ruler of the dominion of Banda in northern India. He was the son of Shreemant Peshwa Bajirao I and Mastani.[13][14][15].
Fourth generation
Sadashivrao Bhau’s first wife's name was Umabai. She gave birth to two sons who died as soon. Umabai died in 1750. His second wife was Parvatibai. She accompanied Sadashivrao bhau during the battle of Panipat.
- Vishwasrao (7 March 1741 – 14 January 1761) was the eldest son of Balaji Baji Rao, Peshwa of Pune (Poona) (the prime minister and de facto ruler/administrator) of the Maratha Empire and also was the heir to the title of Peshwa of Maratha Empire. He was killed during the period of the most intense fighting (Approx. between 01pm and 02:30pm) at Third Battle of Panipat, fighting on the front lines. It is generally accepted that the third battle of Panipat, which hung in balance till his death, moved decisively in favour of the Afghans and ended up in victory of Durrani Empire.
- Madhavrao I (or Pradhanpant Shrimant Madhavrao (Ballal) Peshwa I a.k.a. Thorle Madhav Rao Peshwa ) (14 February 1745 – 18 November 1772) was the fourth Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. During his tenure, Maratha power recovered from the losses suffered during the Panipat Campaign, a phenomenon known as "Maratha Resurrection". He is considered as one of the greatest personalities of the Maratha history.
- Narayan Rao (10 August 1755 – 30 August 1773) was the fifth Peshwa or ruler of the Maratha Empire from November 1772 until his murder by his palace guards in August 1773[16] [17]
.His widow Gangabai (nee Sathe) who was pregnant at the time of murder gave birth to their son Sawai Madhavrao Peshwa.
- Baji Rao II (10 January 1775 – 28 January 1851), also Rao Pandit Pandham, was the son of Peshwa Raghunathrao and Anandibai was Peshwa of the Maratha Empire, and governed from 1796 to 1818.
- Ali Bahadur (Krishna Sinh) (1758-1802), was a Nawab of the dominion of Banda (present day Uttar Pradesh) in northern India, a vassal of Mahratta polity. He was the son of Shamsher Bahadur I (Krishna Rao) and the grandson of Shreemant Peshwa Bajirao I[18] Under the auspices of the powerful Maratha nobles, Ali Bahadur established his authority over large parts of Bundelkhand and became the Nawab of Banda. His son and successor Shamsher Bahadur II held allegiance towards the Maratha polity and fought the English in the Anglo-Maratha War of 1803[18][19]
Fifth generation
Madhavrao was the son of Peshwa Narayanrao and his wife, Gangabail Gangabai (Nee, Sathe) was pregnant at the time of Narayanrao's murder. After Narayanrao's murder, Raghunathrao became Peshwa but was soon deposed by the courtiers and knights of the Maratha Empire. They instead installed Gangabai's new born son, Sawai Madhavrao as the Peshwa with the courtiers themselves, led by Nana Fadnavis, as the Regents.His time in power was dominated by the political intrigues of Nana. He was made Peshawa when his age was barely 40 days. He is the youngest Peshawa/King ever seen in the history.[20]
- Madhavrao II (b. 18 Apr. 1774 – d. 27 Oct. 1795), (a.k.a. ' Sawai Madhavrao Peshwa or Madhav Rao II Narayan), was Peshwa of the Maratha Empire in India, from his infancy. He was known as Sawai Madhav Rao or Madhav Rao Narayan. He was the posthumous son of Narayanrao Peshwa, murdered in 1773 on the orders of Raghunathrao Madhavrao was considered the legal heir, and was installed as Peshwa by the treaty of Salbai[21] in 1782. He was made Peshawa when he was barely 40 days. He is the youngest Peshawa/King ever seen in history.[20]
- Nana Sahib (born 19 May 1824 – disappeared 1857), Nana Sahib was born as Nana Govind Dhondu Pant, to Narayan Bhatt and Ganga Bai.[22] who led the during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He was adopted son by the exiled Maratha Peshwa Baji Rao II.The Company's refusal to continue the pension after his father's death, as well as what he perceived as high-handed policies, compelled him to lead the First Indian Revolution against the British and seek freedom from company rule in India. He forced the British garrison in Kanpur to surrender, and thus gained control of Kanpur for a few days. He later disappeared, after his forces were defeated by a British force that recaptured the city. He also led the battle at Gwalior with Rani Laxmibai of Jhansi; but was unsuccessful as many Indian rulers sided with the British including the Afghans, Sikhs & Gorkhas. He disappeared after the war but there were many rumors that he was seen alive at a number of places in a period after 1857.
- Shamsher Bahadur II, Nawab of Banda 1802/1825, died 1823/1825 son of Ali Bahadur I
- Nawab Zulfikar Ali, Nawab of Banda in 1802 and 1825/1850, son of Ali Bahadur I. He was married and had issue.
- Nawab Ali Bahadur II, Nawab of Banda 1850/1858, son of Ali Bahadur I. He was married and had issue, three sons. He died 1873.
- Jagat Bahadur fl.1833 son of Ali Bahadur I
Genealogy
References
- ↑ Burman, J. J. Roy (2002-01-01). Hindu-Muslim Syncretic Shrines and Communities. Mittal Publications. ISBN 9788170998396.
- ↑ Singer, Milton B.; Cohn, Bernard S. (1970-01-01). Structure and Change in Indian Society. Transaction Publishers. ISBN 9780202369334.
- ↑ Rao, Anupama (2009-01-01). The Caste Question: Dalits and the Politics of Modern India. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520255593.
- 1 2 3 Sen, Sailendra (2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Primus Books. pp. 202–205. ISBN 978-9-38060-734-4.
- ↑ Singer, Milton B.; Cohn, Bernard S. (1970-01-01). Structure and Change in Indian Society. Transaction Publishers. ISBN 9780202369334.
- ↑ Naravane, M.S (1998). The maritime and coastal forts of India. New Delhi: APH Pub. Corp. pp. 44–45. ISBN 9788170249108. Retrieved 21 June 2017.
- ↑ Kantak, M.R. (1993). The First Anglo-Maratha War, 1774-1783: A Military Study of Major Battles. South Asia Books. p. 127. ISBN 9788171546961. Retrieved 11 September 2017.
- ↑ The Struggle for Hindu supremacy. Shri Bhagavan Vedavyasa Itihasa Samshodhana Mandira (Bhishma). 1992. p. 194.
- ↑ Chitnis, K. N. (2006). Research methodology in history. New Delhi: Atlantic Publishers. p. 23. ISBN 9788171561216.
- ↑ A Comprehensive History of India: 1712-1772. Orient Longmans. 1978-01-01.
- ↑ Congress, Indian History (1966-01-01). Proceedings.
- ↑ Patil, Vishwas. Panipat.
- ↑ Rana, Bhawan Singh (2005-01-01). Rani of Jhansi. Diamond Pocket Books (P) Ltd. ISBN 9788128808753.
- ↑ bahadur), Chidambaram S. Srinivasachari (dewan (1951-01-01). The Inwardness of British Annexations in India. University of Madras.
- ↑ Crill, Rosemary; Jariwala, Kapil (2010-01-01). The Indian Portrait, 1560-1860. Mapin Publishing Pvt Ltd. ISBN 9788189995379.
- ↑ Gense, Banaji (1934). Third English Embassy to the Marathas: Mostyn's diary. Jal Taraporewalla.
- ↑ Kincaid, C.A.; Bahadur, Rao; Parasnis, D. B. (1925). A History of Maratha people. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- 1 2 "The Inwardness of British Annexations in India - Chidambaram S. Srinivasachari (dewan bahadur)". Books.google.co.in. 2009-02-12. Retrieved 2015-06-21.
- ↑ "Fall of the Mughal Empire: 1789-1803 - Jadunath Sarkar". Books.google.co.in. 1992-01-01. Retrieved 2015-06-21.
- 1 2 Madhavrao II Archived 14 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Thorpe, S.T.E. The Pearson General Studies Manual 2009, 1/e. Pearson Education. p. 96. ISBN 9788131721339. Retrieved 2014-10-12.
- ↑ Wolpert, Stanley. A New History of India (3rd ed., 1989), pp. 226–28. Oxford University Press.
Further reading
- Ranjit Desai. Swami (in Marathi), a historical novel