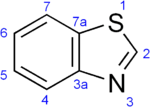
Benzothiazole
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3-Benzothiazole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.179 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5NS | |||
| Molar mass | 135.1863 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.238 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | 2 °C (36 °F; 275 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 227 to 228 °C (441 to 442 °F; 500 to 501 K) | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |||
Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas | ||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Benzothiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C
7H
5NS. It is colorless, slightly viscous liquid. Although the parent compound, benzothiazole is not widely used, many of its derivatives are found in commercial products or in nature. Firefly luciferin can be considered a derivative of benzothiazole.
Structure and preparation
Benzothiazoles consist of a 5-membered 1,3-thiazole ring fused to a benzene ring. The nine atoms of the bicycle and the attached substituents are coplanar.
Benzothiazole are prepared by treatment of 2-mercaptoaniline with acid chlorides:[1]
- C6H4(NH2)SH + RC(O)Cl → C6H4(NH)SCR + HCl + H2O
Uses
This heterocyclic scaffold is readily substituted at the unique methyne centre in the thiazole ring. It is a thermally stable electron-withdrawing moiety with numerous applications in dyes such as thioflavin. Some drugs contain this group, examples being riluzole and pramipexole. The heterocycle is found in nature.[2] Accelerators for the vulcanization of rubber are based on 2-mercaptobenzothiazole.[3] This ring is a potential component in nonlinear optics (NLO).[4] The compound is used also used as an insecticide and food flavoring agent.
See also
- Benzothiazoles are related to thiazoles, which lack the fused benzene ring.
- Benzoxazoles, which substitute an oxygen for the sulfur atom.
References
- ↑ T. E. Gilchrist "Heterocyclic Chemistry" 3rd Edition, Longman, 1992.
- ↑ Lucille Le Bozec, Christopher J. Moody "Naturally Occurring Nitrogen–Sulfur Compounds. The Benzothiazole Alkaloids" Australian Journal of Chemistry 62(7) 639–647.doi:10.1071/CH09126
- ↑ Hans-Wilhelm Engels, Herrmann-Josef Weidenhaupt, Manfred Pieroth, Werner Hofmann, Karl-Hans Menting, Thomas Mergenhagen, Ralf Schmoll, Stefan Uhrlandt "Rubber, 4. Chemicals and Additives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2004, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_365.pub2
- ↑ Hrobarik, P.; Sigmundova, I.; Zahradnik, P.; Kasak, P.; Arion, V.; Franz, E.; Clays, K. (2010). "Molecular Engineering of Benzothiazolium Salts with Large Quadratic Hyperpolarizabilities: Can Auxiliary Electron-Withdrawing Groups Enhance Nonlinear Optical Responses?". Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 114 (50): 22289–22302. doi:10.1021/jp108623d.