Bender Machine Works
The Bender Machine Works in Hayward, Wisconsin, is a dairy equipment manufacturer that played a major role in the history of the dairy farming business in the United States from the 1950s to the 1980s, producing milk pipeline and milk transfer cart components, and washing/vacuum-releasing equipment.
The company continues to be in business but now focuses its manufacturing on private label electromechanical milk pipeline washing systems.
Washer/Releaser and Step-Saver
 |
 |
 |
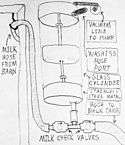 |
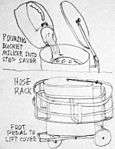
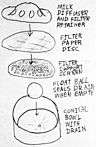
| Freehand paper drawings of how a Step Saver milk transfer cart was used in combination with a Washer/Releaser in a typical dairy barn, also including other common barn structures. | |||
The Bender Washer/Releaser was a vacuum-operated device first invented and patented by Lloyd Bender of Hayward, WI, USA in the 1950s, used to both wash dairy milking equipment and to transfer milk from piping containing a vacuum, into a storage tank at normal atmospheric pressure.
As a non-electric pneumatically operated device, the washer/releaser could be used on small dairy farms without electricity that used an engine to supply milking vacuum, and used well water to cool milk.
The Washer/Releaser could be used in association with both dairy pipelines and the Step-Saver, a milk transfer cart used with bucket milkers. The Step-Saver and the Washer/Releaser were once extremely common in the 1960s to 1980s on small family dairy farms in the United States, to reduce the labor of bucket milking before the milk pipeline became more popular.
Purpose and Usage
(Expanded topic section from Dairy farming article.)
As barns began to increase in size from perhaps 6 to 12 cows to 30 or 40 cows, the bucket milker became a very laborious milking system. As the barn length increased, the farmer had to walk an increasing distance from the cow to the milk bulk tank to dump the collected milk. An early vacuum milk-transport system known as the Step-Saver was developed to save the farmer the trouble of carrying the heavy steel buckets of milk all the way back to the storage tank in the milkhouse. The system used a very long vacuum hose coiled around a receiver cart, and connected to a vacuum-breaker device in the milkhouse.
Following milking each cow, the bucket milker would be dumped into the receiver cart. A foot pedal on the base of the cart lifted the cover, which kept contaminating dust and debris out of the cart, and allowed the farmer to hold the heavy bucket milker with both hands while pouring. A diffuser plate in the top of the cart prevented milk from splashing out while rapidly pouring the milk, and a large filter disk under the diffuser removed any debris from the milk.
Milk collected in a chamber below the filter, and was slowly sucked through the long hose to the milkhouse. When empty, a large float ball in the bottom of the cart would settle down over the drain hole to seal the line and retain system vacuum. When milk was poured into the cart, the ball would float up, unsealing the drain.
An automatic vacuum breaker in the milkhouse cyclically pulled milk from the cart into a glass jar using system vacuum, followed by a release of vacuum to atmospheric pressure, allowing the milk to flow into the bulk tank by gravity flow. When the float level in the jar dropped to setpoint, system vacuum was reapplied to restart the process. Check valves on the vacuum breaker milk hose prevented milk from flowing backwards to the cart when the jar vacuum was released.
As the farmer milked the cows in series, the cart would be rolled further down the center aisle, the long milk hose unwrapped from the cart, and hung on open hooks along the ceiling of the aisle.
Wisconsin legislative code references
Use of the step saver and similar non-pipeline milk transfer systems is described in the legislative code of the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade, and Consumer Protection (DATCP).[1]
- ATCP 60.10 Milking and milk handling systems.
- (4) NON−PIPELINE SYSTEMS. If milk from milking animals is initially collected in a portable transfer receptacle and pumped to the milkhouse through a flexible tube, rather than being pumped directly to the milkhouse through a permanently mounted pipeline, the transfer receptacle and tube system shall comply with the following requirements:
- (a) The portable transfer receptacle shall be constructed of stainless steel or an equally corrosion resistant metal, and shall have an overlapping self−closing cover. The receptacle shall be supported off the floor on a cart or mobile structure which can be easily cleaned.
- (b) The tube used to transfer milk from the portable transfer receptacle to the milkhouse shall consist of a single length of transparent tubing material. The milk transfer tube shall be supported off the floor at all times. The interior milk contact surface of the transfer tube shall be mechanically cleaned, sanitized and dried after each use. The opening through which the milk transfer tube enters the milkhouse shall be kept closed when the tube is not in use. A milk transfer tube shall not be left suspended in a milking barn or parlor between uses, but shall be stored in the milkhouse.
Electromechanical pipeline washing
The Bender Machine Works also developed some of the first automated "wash-in-place" milk pipeline systems, which is generally constructed similar to an automatic dishwasher with automated fill, drain, soap dispensing, and various wash cycles. They continue to manufacture these washing systems today.
Patents
Step saver related
Releaser and other wash equipment
- Dairy Equipment Cleaner, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 2829657, Publication Date: 04/08/1958
- Dairy Equipment, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 2897828, Publication Date: 08/04/1959
- Milk line cleansing system, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 2987065, Publication Date: 06/06/1961
- Dairy Equipment, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3052190, Publication Date: 11/04/1962
- Dairy Equipment for pulsating milk or cleansing liquid in a fluid handling system, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3116714, Publication Date: 01/07/1964
- Apparatus for washing milk conducting lines, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3119399, Publication Date: 01/28/1964
- Fluid handling apparatus for milk pipeline washing system, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3139107, Publication Date: 06/30/1964
- Milker lids cleaning apparatus, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3173434, Publication Date: 03/16/1965
- Washer - Releaser for Dairy Equipment, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3186428, Publication Date: 06/01/1965
- Milk line releaser and washer apparatus, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3191576, Publication Date: 06/29/1965
- Fluid conveying apparatus, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3273514, Publication Date: 11/20/1966
- Milk line equipment, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3310061, Publication Date: 03/21/1967
- Fluid accumulator for milk line equipment, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3322100, Publication Date: 05/30/1967
- Fluid conveying apparatus, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3352248, Publication Date: 11/14/1967
- Fluid conveying apparatus having two-piece slide valve, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3412758, Publication Date: 11/26/1968
- Dump valve for fluid conveying apparatus, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3424098, Publication Date: 01/28/1969
- Portable, automatic washing unit for tanks, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3448742, Publication Date: 06/10/1969
- Automatic washing unit for storage tank or the like, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3583412, Publication Date: 06/08/1971
- Fluid line releaser and washer, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3658441, Publication Date: 04/25/1972
- Solenoid operated, two-way diverter valve for fluid line washing apparatus, Lloyd F. Bender, United States Patent 3670744, Publication Date: 06/20/1972
- Apparatus for automatically mixing a cleaning solution for automatic cleaning equipment for dairies or the like, Inventor: Rolyn A. Schmid, Assignee: Bender Machine Works, Inc., United States Patent 3921652, Publication Date: 11/25/1975
- Apparatus for automatically mixing and circulating cleaning solutions through dairy equipment, Inventor: Rolyn A. Schmid, Assignee: Bender Machine Works, Inc., United States Patent 4015618, Publication Date: 04/05/1977
- Mobile milk unit and system, Inventors: Lloyd F. Bender, Rolyn A. Schmid, Assignee: Bender Machine Works, Inc., United States Patent 4034711, Publication Date: 07/12/1977