Battery Rodgers
| Battery Rodgers | |
|---|---|
| Alexandria, Virginia | |
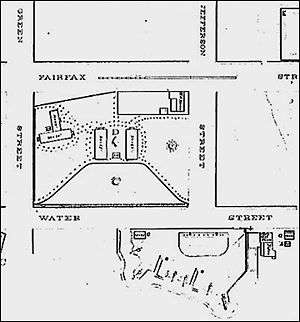 The layout of Battery Rodgers as it existed during the Civil War. Gun emplacements can be seen at the center bottom of the picture, while the remainder of the battery complex is located in the center. | |
 Battery Rodgers | |
| Coordinates | 38°47′43″N 77°02′36″W / 38.795167°N 77.0433°W |
| Site information | |
| Condition | demolished |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1863 |
| In use | 1863-1865 |
| Materials | earth |
Battery Rodgers was a gun emplacement that composed a portion of the American Civil War defenses of the American capital city of Washington, D.C.
Construction
Built in 1863, Battery Rodgers was constructed with the ability to interdict sea traffic sailing up the Potomac River to Washington. From its position on a 28-foot high cliff overlooking Battery Cove, it was positioned with a clear view of fire and was ably suited to guarding the southern Potomac River and Accotink Road (Fort Hunt Rd.) approaches to Washington. The battery was named for George W. Rodgers, a captain in the Union Navy who was killed during an attack on Fort Wagner.[1]
It was 185 feet long with sides of 60 and 80 feet.[2] During the war, the battery mounted one 6.4 inch (100 pounder) Parrott rifle and one 15-inch Rodman gun, one of the largest guns in the world at that time. The guns were supplied by two adjacent powder magazines, and the battery complex included a hospital, barracks, mess hall, and prison. It was garrisoned by 6 commissioned officers, 1 ordnance sergeant, and 256 men. Following the conclusion of the war, the Battery was disbanded and its guns were removed to other locations in Washington. The land on which the battery rested was sold soon afterward, due in no small part to its location in the center of Alexandria, Virginia.
Today, no portion of the battery still stands, but it is memorialized by a small marker in Alexandria, at the intersection of South Lee Street and Green Street and the corner of Jones Point Park. The Rodman gun used at the battery was moved across the Potomac to Fort Foote, and can still be seen there today.
 View of Battery Rodgers with 8-inch (200-pdr) Parrott rifle in front and 15-inch Rodman gun behind.
View of Battery Rodgers with 8-inch (200-pdr) Parrott rifle in front and 15-inch Rodman gun behind. A 15-inch Rodman gun in Battery Rodgers.
A 15-inch Rodman gun in Battery Rodgers. Another view of Battery Rodgers showing the 8-inch (200-pdr) Parrott rifle and the 15-inch Rodman gun.
Another view of Battery Rodgers showing the 8-inch (200-pdr) Parrott rifle and the 15-inch Rodman gun. One of the dug-in ammunition magazines at Battery Rodgers.
One of the dug-in ammunition magazines at Battery Rodgers. The site of Battery Rodgers in 2009
The site of Battery Rodgers in 2009
Notes
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Battery Rodgers. |
References
- "Out of the Attic: Battery Rodgers". The Alexandria Times. Alexandria, VA. 3 June 2010.
- Cooling III, Benjamin Franklin; Owen II, Walton H. (6 October 2009). Mr. Lincoln's Forts: A Guide to the Civil War Defenses of Washington. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6307-1.
- Howe, A.P. (1891). "Report from Headquarters, Inspector of Artillery, May 17, 1864". The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies, Series I. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office. XXXVI (II): 883–897. Retrieved 2007-11-25.
External links
Coordinates: 38°47.71′N 77°2.598′W / 38.79517°N 77.043300°W