Baekje language
| Buyeo-Baekje | |
|---|---|
| Puyo-Paekche | |
| Native to | Paekche |
| Region | Korea |
| Era | 5th–7th centuries[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
xpp |
xpp | |
| Glottolog | None |
| Han-Baekje | |
|---|---|
| Han-Paekche | |
| Native to | Paekche |
| Region | Korea |
| Era | 5th–7th centuries |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
pkc |
pkc | |
| Glottolog |
paek1234[8] |
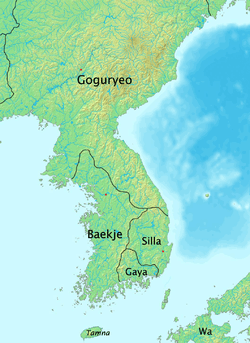 Baekje at its height in 375. | |
The language of the ancient kingdom of Baekje (18 BCE – 660 CE), one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, was a Koreanic language, related to Goguryeo language and Silla language.[9] Chinese records suggest that the Baekje language was same to the Goguryeo language (which is same to the Buyeo language) and mutually intelligible to the Silla language.
梁書 列傳 百濟 : 今言語服章略與高驪同, 行不張拱, 拜不申足則異
(Book of Liang : Baekje language is roughly same to Goguryeo.)
梁書 列傳 新羅 : 語言待百濟而後通焉
(Book of Liang : Silla language has to be translated by Baekje so that they can communicate with China.)
See also
References
- ↑ Buyeo-Baekje at MultiTree on the Linguist List
- ↑ "Han-Paekche ('Han' referring to the apparently autochthonous non-Puyo-Koguryoic languages; Korean is a Han language)"
- ↑ "The World's Major Languages": Edition 2. Bernard Comrie (2017), Routledge
- ↑ "International Encyclopedia of Linguistics" (Volume 1) William J. Frawley (2003), Oxford University Press
- ↑ "Voice and Articulation", Kenneth C. Crannell (2011), Wadsworth Company
- ↑ "Studies on the phonological system of Korean", Kim Wan-jin (1981), Ilchogak
- ↑ "Community languages: a handbook", Barbara M. Horvath, Paul Vaughan (1991), Multilingual Matters Ltd
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Paekche". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Bellwood, Peter (2013). The Global Prehistory of Human Migration. Malden: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781118970591.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.