BES-5
| BES-5 reactor | |
|---|---|
 BES-5 type reactor | |
| Generation | Experimental |
| Reactor concept | RTG |
| Status | ~29 units in earth orbit |
| Main parameters of the reactor core | |
| Fuel (fissile material) | 235U |
| Fuel state | 37 solid cylinders |
| Neutron energy spectrum | Fast |
| Primary control method |
six rods, BC 2 with LiH inserts |
| Neutron Reflector | Beryllium |
| Primary coolant | NaK |
| Reactor usage | |
| Primary use | US-A satellites |
| Power (thermal) | 100 kW |
| Power (electric) | 1.3–5 kW |
BES-5, also known as Bouk or Buk (Russian: бук, lit. 'beech'), was a Soviet thermoelectric generator that was used to power 31 satellites in the US-A (RORSAT) project. The heat source was a Uranium 235 fast fission nuclear reactor (FNR).
Background
Spacecraft nuclear reactors are typically fast reactors for reasons of space and weight. Moderator materials add bulk and mass which is not desirable in a spacecraft. Fast reactors require more highly enriched fuel than the typical 5% enrichment of moderated reactors, the BES-5 uses 95% enrichment Uranium. Note that some of the U-238 (which is fertile and not fissile) will be converted to Pu-239 during operation, and this is taken into consideration during the design and while estimating the power output and design life expectancy.
Reactor design
The design of the BES-5 FNR is such that a sub-critical assembly exists into which a rod of fissile material is inserted. Feedback and monitoring of the power level will keep the reactor delayed critical and not prompt critical, which can be done by a mechanical control system.
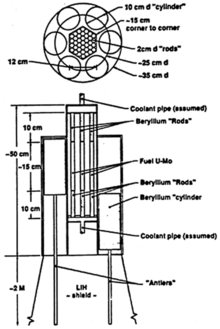
The fuel core of the reactor was 0.24 m in diameter, 0.67 m long and weighed, as an assembly, 53 kg,[1] [2] and contained 31–44 kg of enriched uranium. The entire reactor, including the radiation shielding, weighed 385 kg.
The uranium fuel was more than 90% enriched U235 [3] and generated 3 kW of electrical power[4] created by thermoelectric conversion of 100 kW of thermal output.
Use in space
The BES-5 reactor was used in more than 31 satellite missions to power the radar units of the US-A surveillance satellites. The reactor was designed to be boosted to a high orbit at the end of its operational life, to prevent the radioactive fuel from re-entering earth's atmosphere.
There were, however, several mishaps related to failures in the ejection system, most notably Kosmos 954, which burned up over Canada. Kosmos 1402 also re-entered the atmosphere, but burned up over the Atlantic ocean, away from populated areas. Kosmos 1900 failed to reach its disposal orbit, and remains in low earth orbit.
See also
References
- ↑ Special illustrated presentation by the delegation of the Russian Federation at the XXXIII session of the scientific and technical subcommittee of COPOUS on collisions of nuclear power sources with space debris, Vienna, February 16, 1996
- ↑ http://www.svengrahn.pp.se/trackind/RORSAT/RORSAT.html
- ↑ G.M. Gryaznov, V.S. Nikolayev, V.I. Serbin, V.M. Tyugin, "Radiation safety of the space nuclear power systems and its realization on the satellite Cosmos-1900", Chapter 45 of the book Space Nuclear Power Systems 1989, Orbit Book Company, Malabar, Florida 1992,
- ↑ A.V Zrodnikov, V.Y Poupko, G.M. Gryaznov, "Experimental detection of neutron gas pressure on the control rods of a nuclear reactor under microgravity conditions", Proceedings of 11 th symposium on space nuclear power and propulsion, January 9–13, 1994, Albuquerque, American Institute of Physics, new York, 1994.