BCCIP
BRCA2 and CDKN1A-interacting protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCCIP gene.[5][6][7]
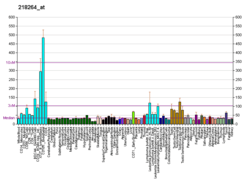
This gene product was isolated on the basis of its interaction with BRCA2 and p21 proteins. It is an evolutionarily conserved nuclear protein with multiple interacting domains. The N-terminal half shares moderate homology with regions of calmodulin and M-calpain, suggesting that it may also bind calcium. Functional studies indicate that this protein may be an important cofactor for BRCA2 in tumor suppression, and a modulator of CDK2 kinase activity via p21. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.[7]
Interactions
BCCIP has been shown to interact with BRCA2,[5] P21,[6] and PTPmu (PTPRM)[8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000107949 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030983 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 Liu J, Yuan Y, Huan J, Shen Z (Apr 2001). "Inhibition of breast and brain cancer cell growth by BCCIPalpha, an evolutionarily conserved nuclear protein that interacts with BRCA2". Oncogene. 20 (3): 336–45. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204098. PMID 11313963.
- 1 2 Ono T, Kitaura H, Ugai H, Murata T, Yokoyama KK, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (Oct 2000). "TOK-1, a novel p21Cip1-binding protein that cooperatively enhances p21-dependent inhibitory activity toward CDK2 kinase". J Biol Chem. 275 (40): 31145–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003031200. PMID 10878006.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: BCCIP BRCA2 and CDKN1A interacting protein".
- ↑ Phillips-Mason PJ, Mourton T, Major DL, Brady-Kalnay SM (2008). "BCCIP associates with the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPmu". J Cell Biochem. 105 (4): 1059–72. doi:10.1002/jcb.21907. PMC 2758318. PMID 18773424.
External links
- Human BCCIP genome location and BCCIP gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Coleman RA, Rao P, Fogelsong RJ, Bardes ES (1992). "2-Bromopalmitoyl-CoA and 2-bromopalmitate: promiscuous inhibitors of membrane-bound enzymes". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1125 (2): 203–9. doi:10.1016/0005-2760(92)90046-X. PMID 1571364.
- Machackova E, Damborsky J, Valik D, Foretova L (2002). "Novel germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in breast and breast/ovarian cancer families from the Czech Republic". Hum. Mutat. 18 (6): 545. doi:10.1002/humu.1232. PMID 11748848.
- Armakolas A, Ladopoulou A, Konstantopoulou I, et al. (2002). "BRCA2 gene mutations in Greek patients with familial breast cancer". Hum. Mutat. 19 (1): 81–2. doi:10.1002/humu.9003. PMID 11754111.
- Robson M, Scheuer L, Nafa K, et al. (2002). "Unique de novo mutation of BRCA2 in a woman with early onset breast cancer". J. Med. Genet. 39 (2): 126–8. doi:10.1136/jmg.39.2.126. PMC 1735025. PMID 11836363.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Meng X, Liu J, Shen Z (2003). "Genomic structure of the human BCCIP gene and its expression in cancer". Gene. 302 (1–2): 139–46. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)01098-3. PMID 12527204.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Meng X, Liu J, Shen Z (2004). "Inhibition of G1 to S cell cycle progression by BCCIP beta". Cell Cycle. 3 (3): 343–8. doi:10.4161/cc.3.3.672. PMID 14726710.
- Deloukas P, Earthrowl ME, Grafham DV, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 10". Nature. 429 (6990): 375–81. doi:10.1038/nature02462. PMID 15164054.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, et al. (2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Meng X, Lu H, Shen Z (2007). "BCCIP functions through p53 to regulate the expression of p21Waf1/Cip1". Cell Cycle. 3 (11): 1457–62. doi:10.4161/cc.3.11.1213. PMID 15539944.
- Lu H, Guo X, Meng X, et al. (2005). "The BRCA2-interacting protein BCCIP functions in RAD51 and BRCA2 focus formation and homologous recombinational repair". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (5): 1949–57. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.5.1949-1957.2005. PMC 549367. PMID 15713648.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Meng X, Yue J, Liu Z, Shen Z (2007). "Abrogation of the transactivation activity of p53 by BCCIP down-regulation". J. Biol. Chem. 282 (3): 1570–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607520200. PMC 2679999. PMID 17135243.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.