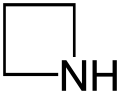
Azetidine
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Azetidine | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Azetane | |||
| Other names
Azacyclobutane Trimethylene imine 1,3-Propylenimine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 102384 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.240 | ||
| EC Number | 207-963-8 | ||
| 986 | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H7N | |||
| Molar mass | 57.09 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Clear slight brown liquid | ||
| Density | 0.847 g/cm3 at 25 °C | ||
| Boiling point | 61 to 62 °C (142 to 144 °F; 334 to 335 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 11.25 (pKa of conjugate acid in water),[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  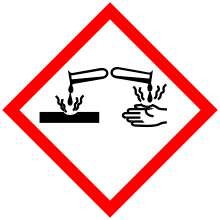 | ||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| H225, H314 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Azetidine is a saturated heterocyclic organic compound containing three carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. It is a liquid at room temperature with a strong odor of ammonia and is strongly basic compared to most secondary amines. Azetidines do not occur as frequently in nature and have been studied far less than closely related chemical compounds such as pyrrolidine and β-lactam.
Natural occurrence
Azetidine and its derivatives are relatively rare structural motifs in natural products. Notably, they are a key component of mugineic acids and penaresidins. Perhaps the most abundant azetidine containing natural product is azetidine-2-carboxylic acid, a non-proteinogenic homolog of proline.
See also
- Azete, the unsaturated analog
References
- ↑ Bansal, R.K. "Heterocyclic Chemistry" 3rd Ed. 1999, p. 96
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.