Australian megafauna

Australian megafauna comprises a number of large animal species in Australia, often defined as species with body mass estimates of greater than 45 kg (100 lb)[1] or equal to or greater than 130% of the body mass of their closest living relatives. Many of these species became extinct during the Pleistocene (16,100±100 – 50,000 years BC).[2]
There are similarities between prehistoric Australian megafauna and some mythical creatures from the Aboriginal dreamtime.[3]
Causes of extinction
The cause of the extinction is an active, contentious and factionalised field of research where politics and ideology often takes precedence over scientific evidence, especially when it comes to the possible implications regarding Aboriginal people (who appear to be responsible for the extinctions).[4] It is hypothesised that with the arrival of early Australian Aboriginals (around 70,000~65,000 years ago), hunting and the use of fire to manage their environment may have contributed to the extinction of the megafauna.[5] Increased aridity during peak glaciation (about 18,000 years ago) may have also contributed, but most of the megafauna were already extinct by this time.
New evidence based on accurate optically stimulated luminescence and uranium-thorium dating of megafaunal remains suggests that humans were the ultimate cause of the extinction of megafauna in Australia.[6][7] The dates derived show that all forms of megafauna on the Australian mainland became extinct in the same rapid timeframe — approximately 46,000 years ago[1] — the period when the earliest humans first arrived in Australia (around 70,000~65,000 years ago).[5] Analysis of oxygen and carbon isotopes from teeth of megafauna indicate the regional climates at the time of extinction were similar to arid regional climates of today and that the megafauna were well adapted to arid climates.[6] The dates derived have been interpreted as suggesting that the main mechanism for extinction was human burning of a landscape that was then much less fire-adapted; oxygen and carbon isotopes of teeth indicate sudden, drastic, non-climate-related changes in vegetation and in the diet of surviving marsupial species. However, early Australian Aborigines appear to have rapidly eliminated the megafauna of Tasmania about 41,000 years ago (following formation of a land bridge to Australia about 43,000 years ago as Ice Age sea levels declined) without using fire to modify the environment there,[8][9][10] implying that at least in this case hunting was the most important factor. It has also been suggested that the vegetational changes that occurred on the mainland were a consequence, rather than a cause, of the elimination of the megafauna.[8] This idea is supported by sediment cores from Lynch's Crater in Queensland, which indicate that fire increased in the local ecosystem about a century after the disappearance of megafaunal browsers, leading to a subsequent transition to fire-tolerant sclerophyll vegetation.[11][12][13]
Chemical analysis of fragments of eggshells of Genyornis newtoni, a flightless bird that became extinct in Australia, from over 200 sites, revealed scorch marks consistent with cooking in human-made fires, presumably the first direct evidence of human contribution to the extinction of a species of the Australian megafauna.[14] This was later contested by another study that noted the too small dimensions (126 x 97 mm, roughly like the emu eggs, while the moa eggs were about 240 mm) for the Genyornis supposed eggs, and rather, attributed them to another extinct, but much smaller bird. The real time that saw Genyornis vanish is still an open question, but this was believed as one of the best documented megafauna extinction in Australia[15]
"Imperceptive overkill"; a scenario where anthropogenic pressures take place; slowly and gradually wiping the megafauna out; has been suggested.[16]
On the other hand, there is also compelling evidence to suggest that (contrary to other conclusions) the megafauna lived alongside humans for several thousand years.[17][18] The question of; if (and how) the megafauna died before the arrival of humans is still debated; with some authors maintaining that only a minority of such fauna remained by the time the first humans settled on the mainland.[19] One of the most important advocates of human role, Tim Flannery, author of the book Future Eaters, was also heavily criticized for his conclusions [20][21]
Living Australian megafauna
The term "megafauna" is usually applied to large animals (over 100 kg (220 lb)). In Australia, however, megafauna were never as large as those found on other continents, and so a more lenient criterion of over 40 kg (88 lb) is often applied[22]
Mammals

- The red kangaroo (Macropus rufus) grows up to 1.8 m (6 ft) tall and weighs up to 85 kg (187 lb). Females grow up to 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh up to 35 kg (77 lb). Tails on both males and females can be up to 1 m (3 ft 3 in) long.
- Eastern grey kangaroos (Macropus giganteus). Although a male typically weighs around 66 kg (145 lb) and stand almost 2 m (6 ft 7 in) tall, the scientific name Macropus giganteus (gigantic large-foot) is misleading, as the red kangaroo living in the semi-arid inland is larger.
- The antilopine kangaroo (Macropus antilopinus), sometimes called the antilopine wallaroo or the antilopine wallaby, is a species of macropod found in northern Australia at Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, the Top End of the Northern Territory, and the Kimberley region of Western Australia. can weigh as much as 47 kg (104 lb) and grow over 1 m (3 ft 3 in) long.
- Common wombats (Vombatus ursinus) can reach 40 kg (88 lb). They thrive in Eastern Australia and Tasmania, preferring temperate forests and highland regions.
Birds

- The emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
- The southern cassowary (Casuarius casuarius)
Reptiles

- Goanna, being predatory lizards, are often quite large or bulky, with sharp teeth and claws. The largest goanna is the perentie (Varanus giganteus), which can grow over 2 m (6 ft 7 in) in length. Not all goannas are gargantuan though: pygmy goannas may be smaller than a man's arm.
- A healthy adult male saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) is typically 4.8–7 m (15 ft 9 in–23 ft 0 in) long and weighs around 770 kg (1,700 lb)), with many being much larger than this.[2] The female is much smaller, with typical body lengths of 2.5–3 m (8 ft 2 in–9 ft 10 in). An 8.5 m (28 ft) saltwater crocodile was reportedly shot on the Norman River of Queensland in 1957; a cast was made of it and is on display as a popular tourist attraction. However, due to the lack of solid evidence (other than the plaster) and the length of time since the crocodile was caught, it is not considered "official"..
- Freshwater crocodile (Crocodylus johnsoni) The freshwater crocodile is a relatively small crocodilian. Males can grow to 2.3–3 m (7 ft 7 in–9 ft 10 in) long, while females reach a maximum size of 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in). Males commonly weigh around 40 kg (88 lb), with large specimens up to 53 kg (120 lb) or more, against the female weight of 20 kg (44 lb). In areas such as Lake Argyle and Katherine Gorge there exist a handful of confirmed 4 m (13 ft) individuals.
Extinct Australian megafauna
The following is an incomplete list of extinct Australian megafauna (monotremes, marsupials, birds and reptiles) in the format:
- Latin name, (common name, period alive), and a brief description.
Monotremes
Monotremes are arranged by size with the largest at the top.
- Zaglossus hacketti was a sheep-sized echidna uncovered in Mammoth Cave in Western Australia, and is the largest monotreme so far uncovered.
- Obdurodon dicksoni was a platypus up to 60 cm (2 ft) in total length, fossils of which were found at Riversleigh.
- Megalibgwilia ramsayi was a large, long-beaked echidna with powerful forelimbs for digging.
Marsupials
Marsupials are arranged by size, with the largest at the top.
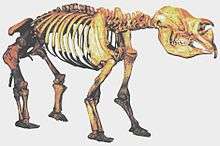
1,000–3,000 kilograms (2,200–6,610 lb)[23]
- Diprotodon optatum is not only the largest species of diprotodontid, but also the largest marsupial that ever existed. Approximately 3 m (10 ft) long and 2 m (7 ft) high at the shoulder and weighing up to 2,780 kg (6,130 lb), it resembled a giant wombat. It is the only marsupial known, living or extinct, to have conducted seasonal migration.[24]
- Zygomaturus trilobus was a smaller (bullock-sized, about 2 m (7 ft) long by 1 m (3 ft) high) diprotodontid that may have had a short trunk. It appears to have lived in wetlands, using two fork-like incisors to shovel up reeds and sedges for food.
- Palorchestes azael (the marsupial tapir) was a diprotodontoid similar in size to Zygomaturus. It had long claws and a longish trunk. It lived during the Pleistocene.[3]
- Nototherium was a diprotodontoid relative of the larger Diprotodon.
100–1,000 kilograms (220–2,200 lb)
- Euowenia grata
- Euryzygoma dunense
- Phascolonus gigas
- Ramsayia magna
- Procoptodon goliah (the giant short-faced kangaroo) is the largest kangaroo to have ever lived. It grew 2–3 metres (7–10 feet) tall, and weighed up to 230 kg (510 lb).
- Procoptodon rapha, P. pusio and P. texasensis
- Protemnodon a form of giant wallaby with 4 species.[25]
- Palorchestes parvus
- Macropus pearsoni and M. ferragus
- Thylacoleo carnifex (the marsupial lion) was the largest meat-eating mammal to have ever lived in prehistoric Australia, and was of comparable size to female placental-mammal lions and tigers
10–100 kilograms (22–220 lb)
- Simosthenurus pales
- Sthenurus tindalei and S. atlas
- Phascolarctos stirtoni was a koala similar to the modern form, but one third larger.
- Phascolomys medius
- Lasiorhinus angustidens
- Thylacinus cynocephalus (the thylacine or Tasmanian tiger)
- Congruus congruus a wallaby from Naracoorte.
- Troposodon minor
- Sthenurus oreas
- Simosthenurus occidentalis (another sthenurine) was about as tall as a modern eastern grey kangaroo, but much more robust. It is one of the nine species of leaf-eating kangaroos identified in fossils found in the Naracoorte Caves National Park.
 Zygomaturus trilobus
Zygomaturus trilobus - Simothenurus brownei
- Propleopus oscillans (the carnivorous kangaroo), from the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, was a large (about 70 kg (150 lb) rat-kangaroo with large shearing and stout grinding teeth that indicate it may have been an opportunistic carnivore able to eat insects, vertebrates (possibly carrion), fruits, and soft leaves. Grew to about 1.5–3 m (5–10 ft) in height.
- Simothenurus maddocki
- Sthenurus andersoni
- Thylacoleo carnifex, (the marsupial lion), was the size of a leopard, and had a cat-like skull with large slicing pre-molars. It had a retractable thumb-claw and massive forelimbs. It was almost certainly carnivorous and a tree-dweller.
- Vombatus hacketti
- Macropus thor
- Macropus piltonensis
- Macropus rama
- Simothenurus gilli
- Warrendja wakefieldi a wombat from Naracoorte.
- Sarcophilus harrisii laniarius was a large form of the Tasmanian devil.
Birds
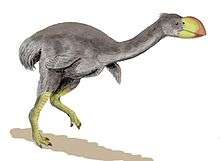
- Family Dromornithidae: this group of birds was more closely related to fowl than modern ratites.
- Dromornis stirtoni, (Stirton's thunder bird, Miocene epoch) was a flightless bird 3 m (10 ft) tall that weighed about 500 kg (1,100 lb). It is one of the largest birds so far discovered. It inhabited subtropical open woodlands and may have been carnivorous. It was heavier than the moa and taller than Aepyornis.
- Bullockornis planei (the "demon duck of doom") was another huge member of the Dromornithidae. It was up to 2.5 m (8 ft) tall and weighed up to 250 kg (550 lb); it was probably carnivorous.
- Genyornis newtoni (the mihirung) was related to Dromornis, and was about the height of an ostrich. It was the last survivor of the Dromornithidae. It had a large lower jaw and was probably omnivorous.
- Leipoa gallinacea (formerly Progura) was a giant malleefowl.
Reptiles

- Varanus priscus (formerly Megalania prisca) was a giant, carnivorous goanna that might have grown to as long as 7 m (23 ft), and weighed up to 1,940 kg (4,280 lb) (Molnar, 2004). Giant goannas and humans overlapped in time in Pleistocene Australia, but there is no evidence that they directly encountered each other.[26]
- Wonambi naracoortensis was a non-venomous snake of 5–6 m (16–20 ft) in length. It was an ambush predator living at waterholes located in natural sun traps and killed its prey by constriction.
- Quinkana sp., was a terrestrial crocodile that grew from 5 m (16 ft) to possibly 7 m (23 ft) in length. It had long legs positioned underneath its body, and chased down mammals, birds and other reptiles for food. Its teeth were blade-like for cutting rather than pointed for gripping as with water dwelling crocodiles. It belonged to the mekosuchine subfamily (all now extinct). It was discovered at Bluff Downs in Queensland.
- L. dubudingala, lived during the Pliocene epoch, grew up to 10 m (33 ft) long, and is the largest Australian snake known. It hunted mammals, birds and reptiles in riparian woodlands. It is most similar to the extant olive python (Liasis olivacea).[27]
- Meiolania was a genus of huge terrestrial cryptodire turtle measuring 2.5 m (8 ft) in length, with a horned head and spiked tail.
Extinct megafauna contemporaneous with Aboriginal Australians
Monsters and large animals in Dreamtime stories have been associated with extinct megafauna.
The association was made at least as early as 1845, with colonists writing that Aboriginal people identified diprotodon bones as belonging to bunyips, and Thomas Worsnop concluding that the fear of bunyip attacks at watering holes remembered a time when diprotodon lived in marshes.[28]
In the early 1900s, John Walter Gregory outlined the Kadimakara (or Kuddimurka or Kadimerkera) story of the Diyari (similar stories being told by nearby peoples), which describes the deserts of Central Australia as having once been "fertile, well-watered plains" with giant gum-trees, and almost solid cloud cover overhead. The trees created a roof of vegetation in which lived the strange monsters called Kadimakara - which sometimes came to the ground to eat. One time, the gum-trees were destroyed, forcing the Kadimakara to remain on the earth, particularly Lake Eyre and Kalamurina, until they died.[29]
In times of drought and flood, the Diyari performed corroborees (including dances and blood sacrifices) at the bones of the Kadimakara to appease them and request that they intercede with spirits of rain and cloud. Sites of Kadimakara bones identified by Aboriginal people corresponded with megafauna fossil sites, and an Aboriginal guide identified a diprotodon jaw as belonging to the Kadimakara.[29]
Gregory speculated that the story could be a remnant from when the Diyari lived elsewhere, or when the geographical conditions of Central Australia were different. The latter possibility would indicate Aboriginal coexistence with megafauna, with Gregory saying:[29]
If, therefore, the geologist can determine whether the bones of the extinct monsters of Lake Eyre correspond to those described in the aboriginal traditions, he can throw light on several interesting problems. If the legends attribute to the extinct animals characters which they possessed, but which the natives could not have inferred from the bones, then the legends are of local origin. They would prove that man inhabited Central Australia, at the same time as the mighty diprotodon and the extinct, giant kangaroos. If, on the other hand, there is no such correspondence between the legends and the fossils, then we must regard the traditions as due to the habit of migratory peoples, of localising in new homes the incidents recorded in their folk-lore.
— John Walter Gregory, Dead Heart of Australia
After examining fossils, Gregory concluded that the story was a combination of the two factors but that the environment of Lake Eyre had probably not changed much since Aboriginal habitation. He concluded that while some references to Kadimakara were probably memories of the crocodiles once found in Lake Eyre, others that describe a "big, heavy land animal, with a single horn on its forehead" were probably references to diprotodon.[29]
Geologist Michael Welland describes from across Australia Dreamtime "tales of giant creatures that roamed the lush landscape until aridity came and they finally perished in the desiccated marshes of Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre", giving as examples the Kadimakara of Lake Eye as well as continent-wide stories of the Rainbow Serpent, which he says corresponds with Wonambi naracoortensis.[30]
Journalist Peter Hancock speculates in The Crococile That Wasn't that a Dreamtime story from the Perth area could be a memory of Megalania.[31]
Rock art in the Kimberley appears to depict a marsupial lion[32] and a marsupial tapir,[33] as does Arnhem land art.[34] Arnhem art also appears to depict Genyornis, a bird that is believed to have gone extinct 40,000 years ago.[35]
An Early Triassic archosauromorph found in Queensland, Kadimakara australiensis, is named after the Kadimakara.[36]
See also
References
- 1 2 Roberts, R. G.; Flannery, T. F.; Ayliffe, L. K.; Yoshida, H.; Olley, J. M.; Prideaux, G. J.; Laslett, G. M.; Baynes, A.; Smith, M. A.; Jones, R.; Smith, B. L. (2001-06-08). "New Ages for the Last Australian Megafauna: Continent-Wide Extinction About 46,000 Years Ago" (PDF). Science. 292 (5523): 1888–1892. Bibcode:2001Sci...292.1888R. doi:10.1126/science.1060264. PMID 11397939. Retrieved 2011-08-26.
- 1 2 Vanderwal and Fullager 1989 as cited in Josephine Flood (2004) Archaeology of the Dreamtime, J.B Publishing, Marleston p, 182 ISBN 1-876622-50-4
- 1 2 Mackness, B.S. (2009). "Reconstructing Palorchestes (Marsupialia: Palorchestidae) — from Giant Kangaroo to Marsupial 'Tapir'". Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales. 130: 21–36.
- ↑ Claudio Tuniz, Richard Gillespie, Cheryl Jones The Bone Readers: Atoms, Genes and the Politics of Australia's Deep Past Allen & Unwin 2009 ISBN 9781741147285 Pg 14
- 1 2 Miller, G. H. (2005). "Ecosystem Collapse in Pleistocene Australia and a Human Role in Megafaunal Extinction". Science. 309: 287–290. Bibcode:2005Sci...309..287M. doi:10.1126/science.1111288. PMID 16002615.
- 1 2 Prideaux, G. J.; Long, J. A.; Ayliffe, L. K.; Hellstrom, J. C.; Pillans, B.; Boles, W. E.; Hutchinson, M. N.; Roberts, R. G.; Cupper, M. L.; Arnold, L. J.; Devine, P. D.; Warburton, N. M. (2007-01-25). "An arid-adapted middle Pleistocene vertebrate fauna from south-central Australia". Nature. 445 (7126): 422–425. Bibcode:2007Natur.445..422P. doi:10.1038/nature05471. PMID 17251978. Retrieved 2011-08-26.
- ↑ Saltré, Frédérik; Rodríguez-Rey, Marta; Brook, Barry W.; Johnson, Christopher N; Turney, Chris S. M.; Alroy, John; Cooper, Alan; Beeton, Nicholas; Bird, Michael I.; Fordham, Damien A.; Gillespie, Richard; Herrando-Pérez, Salvador; Jacobs, Zenobia; Miller, Gifford H.; Nogués-Bravo, David; Prideaux, Gavin J.; Roberts, Richard G.; Bradshaw, Corey J. A. (2016). "Climate change not to blame for late Quaternary megafauna extinctions in Australia". Nature Communications. 7: 10511. Bibcode:2016NatCo...710511S. doi:10.1038/ncomms10511. ISSN 2041-1723.
- 1 2 Diamond, Jared (2008-08-13). "Palaeontology: The last giant kangaroo". Nature. 454 (7206): 835–836. Bibcode:2008Natur.454..835D. doi:10.1038/454835a. PMID 18704074. Retrieved 2011-05-08.
- ↑ Turney, C. S. M.; Flannery, T. F.; Roberts, R. G.; et al. (2008-08-21). "Late-surviving megafauna in Tasmania, Australia, implicate human involvement in their extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. NAS. 105 (34): 12150–12153. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10512150T. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801360105. PMC 2527880. PMID 18719103. Retrieved 2011-05-08.
- ↑ Roberts, R.; Jacobs, Z. (October 2008). "The Lost Giants of Tasmania" (PDF). Australasian Science. 29 (9): 14–17. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-27. Retrieved 2011-08-26.
- ↑ Biello, D. (2012-03-22). "Big Kill, Not Big Chill, Finished Off Giant Kangaroos". Scientific American. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ↑ McGlone, M. (2012-03-23). "The Hunters Did It". Science. 335 (6075): 1452–1453. Bibcode:2012Sci...335.1452M. doi:10.1126/science.1220176. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ↑ Rule, S.; Brook, B. W.; Haberle, S. G.; Turney, C. S. M.; Kershaw, A. P. (2012-03-23). "The Aftermath of Megafaunal Extinction: Ecosystem Transformation in Pleistocene Australia". Science. 335 (6075): 1483–1486. Bibcode:2012Sci...335.1483R. doi:10.1126/science.1214261. PMID 22442481. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ↑ Miller, Gifford; Magee, John; Smith, Mike; Spooner, Nigel; Baynes, Alexander; Lehman, Scott; Fogel, Marilyn; - Johnston, Harvey; Williams, Doug; Clark, Peter; Florian, Christopher; Holst, Richard & DeVogel, Stephen (29 January 2016). "Human predation contributed to the extinction of the Australian megafaunal bird Genyornis newtoni ~ 47 ka". Nature Communications. Nature Publishing Group. 7 (10496). Bibcode:2016NatCo...710496M. doi:10.1038/ncomms10496. PMC 4740177. PMID 26823193. Retrieved 1 February 2016.
- ↑ Trevor H. Worthy, A case of mistaken identity for Australia’s extinct big bird -the Conversation, jan 2016
- ↑ "Humans, not climate change, wiped out Australian megafauna". phys.org. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ↑ "Aboriginal archaeological discovery in Kakadu rewrites the history of Australia". Smh.com.au. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- ↑ Olley, Jon. "Aboriginal Australians co-existed with the megafauna for at least 17,000 years". theconversation.com. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ↑ Wroe, Stephen; Field, Judith H.; Archer, Michael; Grayson, Donald K.; Price, Gilbert J.; Louys, Julien; Faith, J. Tyler; Webb, Gregory E.; Davidson, Iain; Mooney, Scott D. (28 May 2013). "Climate change frames debate over the extinction of megafauna in Sahul (Pleistocene Australia-New Guinea)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (22): 8777–8781. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110.8777W. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302698110. PMC 3670326. PMID 23650401. Retrieved 30 May 2017 – via www.pnas.org.
- ↑ "The Future Eaters - It's critics". www.abc.net.au. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ↑ "The Flannery eaters". www.smh.com.au. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ↑ Danielle Clode (2009) Prehistoric giants: the megafauna of Australia, Museum Victoria ISBN 978-0-9803813-2-0
- ↑ Flannery. T Pleistocene extinctions as cited in Josephine Flood (2004) Archaeology of the Dreamtime, J.B Publishing, Marleston p. 178 ISBN 1-876622-50-4
- ↑ Price, Gilbert J.; Ferguson, Kyle J.; Webb, Gregory E.; Feng, Yue-xing; Higgins, Pennilyn; Nguyen, Ai Duc; Zhao, Jian-xin; Joannes-Boyau, Renaud; Louys, Julien (2017-09-27). "Seasonal migration of marsupial megafauna in Pleistocene Sahul (Australia–New Guinea)". Proc. R. Soc. B. 284 (1863): 20170785. doi:10.1098/rspb.2017.0785. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 5627191. PMID 28954903.
- ↑ Helgen, K.M.; Wells, R.T.; Kear, B.P.; Gerdtz, W.R.; Flannery, T.F. (2006). "Ecological and evolutionary significance of sizes of giant extinct kangaroos". Australian Journal of Zoology. 54: 293–303. doi:10.1071/ZO05077.
- ↑ Price, Gilbert J.; Louys, Julien; Cramb, Jonathan; Feng Yue-xing; Zhao Jian-xin; Hocknull, Scott A.; Webb, Gregory E.; Nguyen Ai Duc; Joannes-Boyau, Renaud (2015-10-01). "Temporal overlap of humans and giant lizards (Varanidae; Squamata) in Pleistocene Australia". Quaternary Science Reviews. 125: 98–105. Bibcode:2015QSRv..125...98P. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.08.013.
- ↑ Scanlon, JD; Mackness, BS. (2001). "A new giant python from the Pliocene Bluff Downs Local Fauna of northeastern Queensland". Alcheringa. 25: 425–437. doi:10.1080/03115510108619232.
- ↑ Holden, Robert; Holden, Nicholas (2001). Bunyips: Australia's Folklore of Fear. National Library Australia. pp. 87–91. ISBN 9780642107329.
- 1 2 3 4 Gregory, J. W. (John Walter) (1906). The dead heart of Australia. University of California Libraries. London : J. Murray. pp. 3–7, 74, 224, 230–235.
- ↑ Welland, Michael (September 2017). "So the land is actually like a big book, you know?" (PDF). Global Land Outlook: 9–10.
- ↑ "WA history author goes digital". PerthNow. 2012-09-11. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
- ↑ Akerman, Kim. "An ancient rock painting of a marsupial lion, Thylacoleo carnifex,from the Kimberley, Western Australia".
- ↑ "More Megafaunal Depictions in Bradshaw Rock Art" (PDF).
- ↑ Murray, Peter; Chaloupka, George (October 1984). "The Dreamtime animals: extinct megafauna in Arnhem Land rock art". Archaeology in Oceania. 19 (3): 105–116. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4453.1984.tb00089.x. ISSN 0728-4896.
- ↑ "Megafauna cave painting could be 40,000 years old". ABC News. 2010-05-31. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
- ↑ Ezcurra, Martín D. (2016-04-28). "The phylogenetic relationships of basal archosauromorphs, with an emphasis on the systematics of proterosuchian archosauriforms". PeerJ. 4: e1778. doi:10.7717/peerj.1778. ISSN 2167-8359.
- Field, J. H.; Dodson, J. (1999). "Late Pleistocene megafauna and archaeology from Cuddie Springs, south-eastern Australia". Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society. 65: 1–27.
- Field, J. H.; Boles, W. E. (1998). "Genyornis newtoni and Dromaius novaehollandiae at 30,000 b.p. in central northern New South Wales". Alcheringa. 22 (2): 177–188. doi:10.1080/03115519808619199.
- Long, J.A., Archer, M. Flannery, T.F. & Hand, S. 2003. Prehistoric Mammals of Australia and New Guinea −100 Million Years of Evolution. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. 242pp.
- Molnar, R. 2004. Dragons in the Dust: The Paleobiology of the Giant Lizard Megalania. Indiana University Press. Page: 127.
- Murray, P. F.; Megirian, D. (1998). "The skull of dromornithid birds: anatomical evidence for their relationship to Anseriformes (Dromornithidae, Anseriformes)". Records of the South Australian Museum. 31: 51–97.
- Wroe, S.; Field, J.; Fullagar, R. (2002). "Lost giants". Nature Australia. 27 (5): 54–61.
- Prideaux, Gavin J; Roberts, Richard G.; Megirian, Dirk; Westaway, Kira E.; Hellstrom, John C.; Olley, John M. (2007). "Mammalian responses to Pleistocene climate change in southeastern Australia" (PDF). Geology. 35 (1): 33–36. Bibcode:2007Geo....35...33P. doi:10.1130/G23070A.1.