Atambua
| Atambua | |
|---|---|
| Town | |
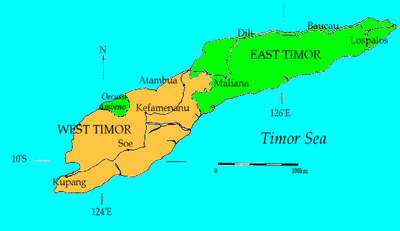 Atambua  Atambua Atambua (Lesser Sunda Islands)  Atambua Atambua (Indonesia) | |
| Coordinates: 9°6′22″S 124°53′33″E / 9.10611°S 124.89250°ECoordinates: 9°6′22″S 124°53′33″E / 9.10611°S 124.89250°E | |
| Country |
|
| Region | Lesser Sunda Islands |
| Province |
|
| Regency | Belu Regency |
| Area | |
| • Town | 32.8 km2 (12.7 sq mi) |
| • Land | 32.8 km2 (12.7 sq mi) |
| • Water | 0.0 km2 (0.0 sq mi) 0%% |
| • Metro | 32.8 km2 (12.7 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 350 m (1,150 ft) |
| Population (2015) | |
| • Town | 76.052 |
| • Metro | 76.052 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (ICST) |
| Area code | (+62) 389 |
| Climate | Aw |
| Website |
belukab |
Atambua is the regency seat of Belu Regency, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
The town stretches as far as 8.5 km from North to South and 5 km from East to West, and is located in the north of the western half of Timor Island. The town is located at an altitude of about 350 m above sea level with temperatures ranging between 23-35 degrees Celsius making this area feel quite warm.
An influx of citizens fleeing from East Timor in 1999 made Atambua a big town. It is now the second largest city in West Timor behind Kupang, also the fourth largest city in East Nusa Tenggara behind Kupang, Ende, and Maumere. Most of its citizens speak Tetun and Dawan L. Atambua is a multi-ethnic town with most of its citizens are Timor, Rote, Sabu, and Flores with some emigrants from East Timor and China. But in spite of diversity, the citizens could still live in harmony.
The town's religion is made up of over 90% of Roman Catholic, 5% of Protestant and a few more of Muslim, Hindu, and Buddha. The town is home to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Atambua. The Diocese's population is over 95% Catholic, among the highest percentages of Catholics in all of Indonesia.
A brief history
Atambua is founded by the Dutch East Indies on October 1916. The dutch moved to Atambua from Atapupu, a port village in Kakuluk Mesak. The Japan military took over Atambua in 1942-1943. They planted lots of trees, which can be seen in Hutan Jati Nenuk. After Independence, Indonesia's first president, Soekarno went to Atambua and planted more trees in the place now called Lapangan Umum. The most notably tree planted there is the banyan tree. In September 1999, more than 250,000 refugees arrived here from East Timor, after their vote for independence and the following violence. As late as 2002, there was an estimated 60,000 refugees left in camps.[1]

Media
Television
As like Belu Regency, the television in this city is limited, which are:
- TVRI (UHF 10)
- Belu TV (UHF 37)
Radio AM/FM
In this city, there are many radios, which are:
| No. | Name of Radio | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RRI Programa 1 Atambua | FM 91.5 MHz |
| 2 | RRI Programa 2 Atambua | FM 99.8 MHz |
| 3 | RRI Programa 3 | FM 99.0 MHz |
| 4 | RRI Programa 4 Atambua (SCBT*)** | FM 93.1 MHz |
| 5 | Favorit Radio | FM 98.2 MHz |
| 6 | Radio Dian Mandiri | FM 100.6 MHz |
| 7 | Misi Kalvari (Miskal) FM | FM 106.5 MHz |
*) SCBT means Saluran Citra Budaya Timor (Timor Culture Channel) **) The radio is currently turned off
Transportation Systems
The town's transport system relies mainly on minibuses, usually called bemo or mikrolet, and "motorcycle taxi" (Ojek) provide an alternative. There are only four routes in the town served by the Mikrolets that connects the inner city of Atambua. The ojeks do not have a fixed route.
Land Transportation
Inter-city buses connect Atambua with other towns in West Timor. The city and towns that can be connected are Kupang, Soe and Kefamenanu; the distance between Atambua and Kefamenanu is 87 km, between Atambua and Soe is 179 km, and between Atambua and Kupang is 289 km. Atambua is a major gateway to East Timor by land. To go to East Timor (Timor-Leste), the vehicles usually used by road to Indonesia-East Timor (Timor-Leste) Immigration checks in Motaain (Indonesia) near Batugade are mostly with Bus and Car, such as SUVs and MPVs and Motorcycles. The distance between Atambua and Motaain (Indonesia-Timor Leste borders) is 36 km.
Air Transportation
There is an airport in Atambua, A. A. Bere Tallo Airport, about 5 kilometers from the town centre. The airport's runway is 1600m long and can therefore be used by a quite big aircraft. Daily flights to the airport is used by the Susi Air plane, Wings Air plane and Trans Nusa plane. All these flights are mainly on the Atambua - Kupang route.
Water Transportation
Atambua also has two sea ports, Atapupu for cargo and oil, and Teluk Gurita for passengers (ferry port). Ferry routes are Atambua-Kalabahi (Alor), once a week.