Aramaic Inscription of Laghman
| Aramaic inscription of Laghman | |
|---|---|
 Aramaic inscription of Laghman | |
| Material | Natural stone. |
| Writing | Aramaic |
| Created | circa 260 BCE |
| Period/culture | 3rd Century BCE |
| Discovered | 34°35′05″N 70°11′00″E / 34.5846°N 70.1834°ECoordinates: 34°35′05″N 70°11′00″E / 34.5846°N 70.1834°E |
| Place | Laghman Province, Afghanistan |
| Present location | Laghman Province, Afghanistan |


The Aramaic inscription of Laghman, also called the Laghman II inscription, is an inscription on a slab of natural rock in the area of Laghmân, Afghanistan, written in Aramaic by the Indian emperor Ashoka about 260 BCE, and often categorized as one of Minor Rock Edicts of Ashoka.[1][2] This inscription was published in 1970 by André Dupont-Sommer. Since Aramaic was an official language of the Achaemenid Empire, and reverted to being just its vernacular tongue in 320 BCE with the conquests of Alexander the Great, it seems that this inscription was addressed directly to the populations of this ancient empire still present in northwestern India, or to border populations for whom Aramaic remained the language used in everyday life.[3]
Epigraphical context
The discovery of this inscription follows that of several other inscriptions in Aramaic or Greek (individually, or both languages together), written by Asoka. The most famous are the Kandahar Bilingual Inscription, written in Greek and Aramaic, or the Greek Edicts of Ashoka, also found in Kandahar. Previously, in 1915, Sir John Marshall had discovered the Aramaic Inscription of Taxila, and in 1932 another inscription in Aramaic was discovered in the Laghman Valley in Pul-i-Darunteh, also called "Laghman I", the Aramaic inscription of Pul-i-Darunteh, then in 1963 an "Indo-Aramaic" inscription alternating Indian Prakrit and the Aramaic language, but using only Aramaic characters, with the Aramaic parts translating the Indian parts transcribed in the Aramaic alphabet, was also discovered in Kandahar: the Aramaic Inscription of Kandahar.[3]
The inscription
The text of the Aramaic Inscription of Laghman has been transliterated into the Roman alphabet and translated as follows:[3]:
BŠNT 10 | ḤZY | PRYDRŠ MLK' | RQ DḤ'
MH MṢD BRYWT KWRY
MN ŠRYRYN DWDY MH 'BD RYQ QŠTN
200 ZNH TMH TDMR ŠMH ZNH 'RH' KNPTY SHTY
GNT' YTRY 120 TRT' TNH 100 'L' 80
'M W'ŠW DYN'In the year 10, behold, the king Priyadasi expelled vanity from among prosperous men,
friends of that which is vain, friends of those who fish fish creatures.
At 200 "bows", there is over there the place called Tadmor.
This is the KNPTY road, that is to say (the road) of the Garden:
more than 120 ("bow"). At TRT', here: 100. Above: 80.Done with Wasu The Judge
— Translation by André Dupont-Sommer [3]
Interpretations
The translation is slightly incomplete but brings some valuable indications. It first mentions the propagation of moral rules, which Ashoka will call "Dharma" in his Edicts of Ashoka, consisting of the abandonment of vanity and respect for the life of the people and animals (here, urging people to give up fishing) [3][2].

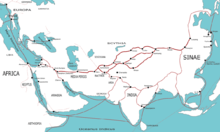
Then, according to semitologist André Dupont-Sommer, who made a detailed analysis of the script observed in multiple rock inscriptions in the Laghman valley as well as in other Aramaic inscriptions of Ashoka,[4] the inscription mentions the city of Tadmor (Tdmr in the Aramaic script in the inscription, ie Palmyra), destination of the great commercial road leading from India to the Mediterranean basin, located at a distance of 3800km. According to the reading of Dupont-Sommer, Palmyra is separated by two hundreds "bows" from Laghman. In the inscription, the word used to indicate bow is "QŠTN", and Dupont-Sommer asserted that it is an Aramaic word denoting a unit to measure a distance of 15 to 20 kilometres, which could represent a day on the road for an archer.[3] Other distances are then given, which makes it possible to interpret Laghman's inscription as a kind of information terminal on the main trade route with the West.[3][5]
Franz Altheim and Ruth Altheim-Stiehl read three hundred instead of two hundred bows; they equated it with the Vedic unit of measurement yojona, c. 12 kilometres, which would result in a number close to the actual 3800 kilometres distance between Laghman and Palmyra.[6] The linguist Helmut Humbach criticized the reading of Dupont-Sommer and considered his claims regarding the distance to have no validation.[7]
Another issue is that the Aramaic alphabet, the letters "r" and "d" share an identical character.[8] Jean de Menasce read the city's name "Trmd" and identified it with Termez on the Oxus river.[9] Linguist Franz Rosenthal also contested the reading of Dupont-Sommer and considered that the inscription refers to an estate called "Trmr".[10] Historian Bratindra Nath Mukherjee rejected the readings of both Dupont-Sommer and de Menasce; he contested the large value attributed to "bow", considering it a small unit. The historian also rejected the reading of Tdmr and Trmd as referring to a city; in the view of Mukherjee, the name, whether Tdmr or Trmd refers to the rock on which the inscription was carved itself.[9][11]
The Aramaic Inscription of Laghman is the oldest of the known Ashoka inscriptions, with the Kandahar Bilingual Inscription, both dated to the year 10 of Ashoka's reign [3] .
Another Aramaic inscription, almost identical, was discovered nearby in the Laghman Valley, and published in 1974 [12].
See also
- List of the Edicts of Ashoka
- Kandahar Bilingual Inscription
- Asoka - the Buddhist Emperor of India Chapter 4 by Vincent Arthur Smith: The Rock Edicts (this version)
Sources
- Kaizer, Ted (2017). "Trajectories of Hellenism at Tadmor-Palmyra and Dura-Europos". In Chrubasik, Boris; King, Daniel. Hellenism and the Local Communities of the Eastern Mediterranean: 400 BCE-250 CE. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-192-52819-3.
- MacDowall, David w.; Taddei, Maurizio (1978). "The Early Historic Period: Achaemenids and Greeks". In Allchin, Frank Raymond; Hammond, Norman. The Archaeology of Afghanistan from Earliest Times to the Timurid Period. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-120-50440-4.
- Mukherjee, Bratindra Nath (2000) [1984]. Studies in Aramaic Edicts of Aśoka (2 ed.). Kolkata: Indian Museum. OCLC 62327000.
- Rosenthal, Franz (1978). "The Second Laghmân Inscription". Eretz-Israel: Archaeological, Historical and Geographical Studies. Israel Exploration Society. 14: H.L. Ginsberg Volume. ISSN 0071-108X.
References
- ↑ Nakamura, Hajime (1987). Indian Buddhism: A Survey with Bibliographical Notes. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 349. ISBN 9788120802728.
- 1 2 Behrendt, Kurt A. (2004). Handbuch der Orientalistik. BRILL. p. 39. ISBN 9004135952.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 A new Aramaic inscription of Asoka found in the Laghman Valley (Afghanistan), André Dupont-Sommer Proceedings of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles-Lettres Year 1970 114-1 pp.158-173
- ↑ Script of the Laghman Valley Fig 3
- ↑ The Silk Road Encyclopedia. Seoul Selection. 2016. p. 991. ISBN 9781624120763.
- ↑ Kaizer 2017, p. 33, 34.
- ↑ MacDowall & Taddei 1978, p. 192.
- ↑ Kaizer 2017, p. 34.
- 1 2 Mukherjee 2000, p. 11.
- ↑ Rosenthal 1978, p. 99.
- ↑ Kaizer 2017, p. 33,34.
- ↑ Essenism and Buddhism, Dupont-Sommer, André, Proceedings of the sessions of the Academy of Inscriptions and Belles-Lettres Year 1980 124-4 pp.698-715 p.707