Applesoft BASIC
| Original author(s) | Marc McDonald and Ric Weiland |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1977 |
| Stable release |
Applesoft II
/ 1978 |
| Operating system | Apple II series |
| Type | Microsoft BASIC |
Applesoft BASIC is a dialect of Microsoft BASIC, developed by Marc McDonald and Ric Weiland, supplied with the Apple II series of computers. It supersedes Integer BASIC and is the BASIC in ROM in all Apple II series computers after the original Apple II model. It is also referred to as FP BASIC (from "floating point") because of the Apple DOS command used to invoke it, instead of INT for Integer BASIC.
Applesoft BASIC was supplied by Microsoft and its name is derived from the names of both Apple and Microsoft. Apple employees, including Randy Wigginton, adapted Microsoft's interpreter for the Apple II and added several features. The first version of Applesoft was released in 1977 on cassette tape and lacked proper support for high-resolution graphics. Applesoft II, which was made available on cassette and disk and in the ROM of the Apple II Plus and subsequent models, was released in 1978. It is this latter version, which has some syntax differences and support for the Apple II high-resolution graphics modes, that is usually synonymous with the term "Applesoft."
History
When Steve Wozniak wrote Integer BASIC for the Apple II, he did not implement support for floating point math because he was primarily interested in writing games, a task for which integers alone were sufficient.[1] In 1976, Microsoft had developed Microsoft BASIC, a BASIC interpreter for the MOS Technology 6502, but at the time there was no production computer that used it. Upon learning that Apple had a 6502 machine, Microsoft asked if the company were interested in licensing BASIC, but Steve Jobs replied that Apple already had one.
The Apple II was unveiled to the public at the West Coast Computer Faire in April 1977 and became available for sale in June. One of the most common customer complaints about the computer was BASIC's lack of floating-point capability. Integer BASIC is limited to whole numbers between −32768 and 32767 and caused problems for users attempting to write business applications with it. Steve Wozniak had never added floating point capabilities to Integer BASIC as he did not consider them necessary for gaming and educational software, the two primary tasks he envisioned for the Apple II. As Wozniak—the only person who understood Integer BASIC well enough to add floating point features—was busy with the Disk II drive and controller and with Apple DOS, Apple turned to Microsoft. Making things more problematic was that the rival Commodore PET personal computer had a floating point-capable BASIC interpreter from the beginning. The Applesoft license also saved Microsoft from near-bankruptcy when they licensed BASIC to Commodore for the PET in an agreement that proved unexpectedly costly for them.
Apple reportedly obtained an eight-year license for Applesoft BASIC from Microsoft for a flat fee of $31,000, renewing it in 1985 through an arrangement that gave Microsoft the rights and source code for Apple's Macintosh version of BASIC.[2] Applesoft was designed to be backwards-compatible with Integer BASIC and uses the core of Microsoft's 6502 BASIC implementation, which includes using the GET command for detecting key presses and not requiring any spaces on program lines. While Applesoft BASIC is slower than Integer BASIC, it has many features that the older BASIC lacks:
- Atomic strings: A string is no longer an array of characters (as in Integer BASIC and C); it is instead a garbage-collected object (as in Scheme and Java). This allows for string arrays;
DIM A$(10)resulted in a vector of eleven string variables numbered 0–10. - Multidimensional arrays (numbers or strings)
- Single-precision floating point variables with an 8-bit exponent and a 31-bit significand and improved math capabilities, including trigonometry and logarithmic functions
- Commands for high-resolution graphics
DATAstatements, withREADandRESTOREcommands, for representing numerical and string values in quantityCHR$,STR$, andVALfunctions for converting between string and numeric types (both languages did have theASCfunction)- User-defined functions: simple one-line functions written in BASIC, with a single parameter
- Error-trapping, allowing BASIC programs to handle unexpected errors by means of a subroutine written in BASIC
Conversely, Applesoft lacked the MOD (remainder) operator that had been present in Integer BASIC.
Adapting BASIC for the Apple II was a tedious job as Apple received a source listing for Microsoft 6502 BASIC which proved to be extremely buggy and also required the addition of Integer BASIC commands. Since Apple had no 6502 assembler on hand, the development team was forced to send the source code over the phone lines to Call Computer, an outfit that offered compiler services. This was an extremely tedious, slow process and after Call Computer lost the source code due to an equipment malfunction, one of the programmers, Cliff Huston, used his own IMSAI 8080 computer to cross assemble the BASIC source.[3]
Applesoft is similar to Commodore's BASIC 2.0 aside from features inherited from Integer BASIC. There are a few minor differences such as Applesoft's lack of bitwise operators; otherwise most BASIC programs that do not utilize hardware-dependent features will run on both BASICs.
As with Commodore BASIC, Applesoft handles numeric variables as 40-bit floating point, thus each variable requires five bytes of memory, and the programmer may also designate variables as integer by following them with a percent sign, in which case they use two bytes and are limited to a range of -32767 to 32768, however BASIC internally converts them back to floating point, which slows down program execution and each percent sign also takes an additional byte, so in practice this feature is only useful for reducing the memory usage of large array variables.
Like with other implementations of Microsoft BASIC, Applesoft does not require any spaces on a program line and if the user types them, they are discarded by the interpreter during the process of tokenizing program lines, whereas Commodore BASIC did not delete spaces. LISTing programs will however still display spaces for readability purposes.
The INPUT statement in Applesoft BASIC does not display a question mark with its prompt like most other Microsoft BASIC implementations, and the PRINT statement does not add a leading space in front of numbers.
Coleco claimed that its Adam home computer's SmartBASIC was source-code compatible with Applesoft.[4] Microsoft licensed a BASIC compatible with Applesoft to VTech for its Laser 128 clone.[5]
Features and limitations
Through several early models of the Apple II, Applesoft BASIC did not support the use of lowercase letters in programs, except in strings. (Thus, Applesoft can display lowercase letters, but cannot recognize them as part of a program; thus, PRINT is a valid command but print and Print are unrecognizable and result in a syntax error.)
Applesoft lacks several commands and functions common to most of the non-6502 Microsoft BASIC interpreters, such as:
INSTR(search for a substring in a given string)PRINT USING(formatting numbers in printed output)INKEY$(check for a keypress without stopping the program) although a PEEK location did provide this functionality.LPRINT(output printed content to a printer instead of the screen)
Applesoft, like Integer BASIC before it, does not come with any built-in commands for dealing with files or disks, other than a feature to save programs to, and load programs from, cassette tape. The Apple II disk operating system, known simply as DOS, augments the language to provide such abilities.
Unlike in Integer BASIC, Applesoft BASIC variable names are significant only to two letters; they can be made longer, but only the first two letters are used. For instance, "LOW" and "LOSS" are treated as the same variable, and attempting to assign a value to "LOSS" overwrites any value assigned to "LOW". Furthermore, because the language used tokenization, a programmer has to avoid using any consecutive letters that are also Applesoft commands or operations (one cannot use the name "SCORE" for a variable because it interprets the OR as a Boolean operator, thus rendering it SC OR E, nor can one use "BACKGROUND" because the command "GR" invokes the low-resolution graphics mode, in this case creating a syntax error).
Sound and graphics
There is no sound support–aside from a PEEK command that can be used to click the speaker. One can also PRINT an ASCII bell character to sound the system alert beep. The language is not fast enough to produce more than a baritone buzz from repeated clicks.
Vector-based shape tables can be used to draw objects, but are slow in comparison to routines that draw bitmaps directly. No provision existed for mixing text and graphics, except for the limited "hardware split screen" of the Apple II (four lines of text at the bottom of the screen).
Extensions
Applesoft BASIC can be extended by two means: the ampersand (&) command and the USR() function. These are two features that called machine-language routines stored in memory. Routines that need to be fast or require direct access to arbitrary functions or data in memory can thus be called from a higher-level interpreted BASIC program. The USR() function takes one numerical argument, and can be programmed to derive and return a calculated function value, to be used in a numerical expression. "&" was effectively a shorthand for CALL, with an address that would be predefined.
Bugs
A deficiency in Applesoft's error-trapping with ONERR means that the system stack would not be reset if an error-handling routine did not invoke RESUME, potentially leading to a crash. Error-handling that does not employ RESUME can avoid the problem with a CALL -3288 or (equivalent) 62248 before exiting the routine.[6]
Performance
Whereas Wozniak originally referred to his Integer BASIC as "Game BASIC" (having written it so he could write a Breakout clone for his new computer),[1] few action games were written in Applesoft BASIC.
The use of "real" (floating-point) numbers for all math operations degraded performance. Although a % can be placed after a variable to mark it as integer, its value is merely converted back into single-precision, slowing down program execution and wasting memory (as each "%" required one extra byte of memory). The integer variable type on Microsoft 6502 BASIC was really only designed for arrays because each element would take two bytes (versus, in the case of Applesoft, five for floating-point).
Applesoft BASIC programs are stored as a linked list of lines; a GOTO or GOSUB takes linear time. Large programs were often written with the most-used subroutines at the top of the program to reduce the processing time for GOSUB calls.
Sample code
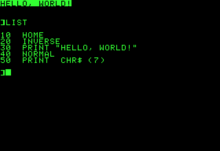
Hello World in Applesoft BASIC can be entered as the following:
10TEXT:HOME
20?"HELLO WORLD"
Multiple commands can be included on the same line of code if separated by a colon (:). The ? can be used in Applesoft BASIC (and almost all versions of Microsoft BASIC) as a shortcut for "PRINT", though spelling out the word is not only acceptable but canonical—Applesoft converted "?" in entered programs to the same token as "PRINT" (thus no memory is actually saved by using "?"), thus either appears as "PRINT" when a program is listed. The program above appears in a LIST command as:
10 TEXT : HOME
20 PRINT "HELLO WORLD"
When Applesoft II BASIC was initially released in mid-1978, it came on cassette tape and could be loaded into memory via the Apple II's machine language monitor. When the enhanced Apple II+ replaced the original II in 1979, Applesoft was now included in ROM and automatically started on power-up if no bootable floppy disk was present. Conversely, Integer BASIC was now removed from ROM and turned into an executable file on the DOS 3.3 disk.
Early evolution
The original Applesoft, stored in RAM as documented in its Reference Manual of November 1977, has smaller interpreter code than the later Applesoft II, occupying 8½ kb of memory,[8] instead of the 10 kb used by the later Applesoft II. Consequently, it lacks a number of command features developed for the later, mainstream version:
- All commands supporting Apple's "high resolution" graphics (9 total)
- Error-trapping with ONERR...GOTO and RESUME
- Machine-routine shorthand call "&"
- Screen-clearing HOME (a call to a system ROM routine)
- Text-output control NORMAL, INVERSE, FLASH and SPEED=
- The print-space function SPC() is listed among reserved words in the manual, but is not otherwise documented (the TAB() print-function is documented)
- Cassette tape storage of numerical arrays: STORE and RECALL
- Device response: WAIT
as well as several the later version would have, that had already been present in Apple's Integer BASIC:
- Program-line deletion: DEL
- Machine-routine access: CALL
- Peripheral device access: IN# and PR# (although IN without "#" is listed among reserved words)
- Memory range control: HIMEM: and LOMEM:
- Execution tracking for debugging: TRACE and NOTRACE
- Screen-positioning: HTAB and VTAB
- Subroutine aborting POP
- Functions PDL() to read the analog controllers, and SCRN() to read the low-resolution graphics screen (both accessing system ROM routines)
In addition, its low-resolution graphics commands have different names from their Integer BASIC/Applesoft II counterparts. All command names are of the form PLTx such that GR, COLOR=, PLOT, HLIN and VLIN are called PLTG, PLTC, PLTP, PLTH, and PLTV, respectively. The command for returning to text mode, known as TEXT in other versions, is simply TEX, and carries the proviso that it has to be the last statement in a program line.
Applesoft BASIC 1.x was closer to Microsoft's original 6502 BASIC code than the later Applesoft II; it retained the Memory Size? prompt and displayed a Microsoft copyright notice. To maintain consistency with Integer BASIC, the "Ok" prompt from Microsoft's code was replaced by a ] character. Applesoft 1.x also prompted the user if he wished to disable the LET and REM statements in exchange for lo-res graphics functions.
The USR() function is also defined differently, serving as a stand-in for the absent CALL command. Its argument is not for passing a numerical value to the machine-language routine, but is instead the call-address of the routine itself; there is no "hook" to pre-define the address. All of several examples in the manual use the function only to access "system monitor ROM" routines, or short user-routines to manipulate the ROM routines. No mention is made of any code to calculate the value returned by the function itself; the function is always shown being assigned to "dummy" variables, which, without action to set a value by user-code, just receive a meaningless value handed back to them. Even accessed ROM routines that return values (in examples, those that provide the service of PDL() and SCRN() functions) merely have their values stored, by user-routines, in locations that are separately PEEKed in a subsequent statement.
Unlike in Integer BASIC and Applesoft II, the Boolean operators AND, OR and NOT perform bitwise operations on 16-bit integer values. If they are given values outside that range, an error results.
The terms OUT and PLT (and the aforementioned IN) appear in the list of reserved words, but are not explained anywhere in the manual.
See also
- ALF's Formula Transfer Link, speed enhancement for Applesoft BASIC
- Chinese BASIC, a Chinese-localized version of Applesoft BASIC
- Apple III BASICs from Apple and Microsoft
References
- 1 2 Wozniak, Steve (2014-05-01). "How Steve Wozniak Wrote BASIC for the Original Apple From Scratch". Gizmodo. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ Herzfeld, Andy "MacBasic – The Sad Story of MacBasic". http://www.folklore.org/StoryView.py?project=Macintosh&story=MacBasic.txt . Folklore.org. 2014 February 12
- ↑ "History of the Apple II - Chapter 16 - Languages". Retrieved July 6, 2016.
- ↑ Coleco Presents The Adam Computer System. YouTube. 2016-05-03 [1983-09-28]. Event occurs at 31:55.
Everybody who knows Applesoft BASIC will also know Adam SmartBASIC. All the same commands, all the same controls for this BASIC, this interpreter, are available. In fact, we're going to show you a program which uses Applesoft graphic commands ... executed through Adam. ... As far as we're concerned, when we're in BASIC, and we're not PEEKing or POKEing ... anything below the BASIC interpreter, we are source-code compatible.
- ↑ Grevstad, Eric (December 1986). "Laser 128 / An Affordable Compatible". inCider. p. 58. Retrieved 2017-04-24.
- ↑ Applesoft BASIC Programmer's Reference Manual (for IIe only), Apple Computer, Inc., 1982
- ↑ This article includes text from Everything2, licensed under GFDL.
- ↑ Applesoft Extended Precision Floating Point Basic Language Reference Manual, Apple Computer, Inc., November 1977