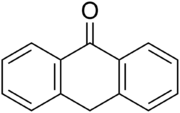
Anthrone
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
10H-Anthracen-9-one | |
| Other names
Carbothrone; anthranone; 9-oxoanthracene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.813 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H10O | |
| Molar mass | 194.23 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to light yellow needles |
| Density | Solid |
| Melting point | 155 to 158 °C (311 to 316 °F; 428 to 431 K) |
| Boiling point | 721 °C (1,330 °F; 994 K) |
| Insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Anthrone is a tricyclic aromatic ketone. It is used for a popular cellulose assay and in the colorometric determination of carbohydrates.[1] The anthrones are used in pharmacy as laxative. They stimulate the motion of the colon and are reduce water reabsorption. Anthrones can be extracted from a number of plant species, including Rhamnus frangula, Aloe ferox, Rheum officinale and Cassia senna.
Synthesis
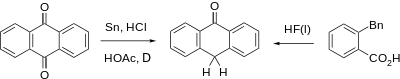
Anthrone can be prepared from anthraquinone by reduction with tin, glacial acetic acid and hydrochloric acid, or cyclization of o-benzylbenzoic acid with liquid Hydrogen fluoride.
- Use: Perlapine by Beckmann rearrangement.
References
- ↑ Trevelyan, W. E.; Forrest, RS; Harrison, JS (1952). "Determination of Yeast Carbohydrates with the Anthrone Reagent". Nature. 170 (4328): 626–627. doi:10.1038/170626a0. PMID 13002392.
- ↑ "ANTHRONE". Organic Syntheses. 8: 8. 1928. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.008.0008.
- ↑ Fieser, Louis F.; Hershberg, E. B. (May 1939). "Inter- and Intramolecular Acylations with Hydrogen Fluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 61 (5): 1272–1281. doi:10.1021/ja01874a079.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.