Anegada Passage
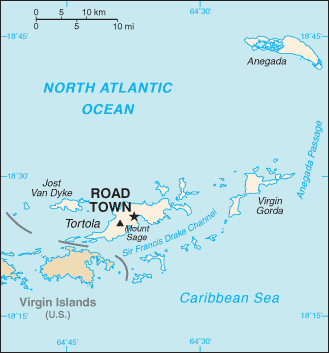
Anegada Passage is a strait in the Caribbean, at 18°22′41″N 63°50′15″W / 18.377986°N 63.837433°W. It separates the British Virgin Islands and the British ruled Sombrero Island of Anguilla, and connects the Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean. It is 2300 m deep. Because the threshold depths are 1800 and 1600 m, Atlantic deep water from 1600 m level may flow into the deep areas in the Caribbean Sea.[1]
The Anegada Passage is a key shipping lane for the Panama Canal.[2] Often called the "Oh-my-god-a Passage"[3], it is considered a difficult passage for sailors because of the winds, waves, and swells.[4]
The passage consists of multiple basins and ridges. The Anegada Trough or Virgin Islands Basin was the likely site of the 1867 Virgin Islands earthquake and subsequent tsunami.[5][6].
References
- ↑ "Anegada Passage". Encyclopedia Britanica. Retrieved 2018-08-01.
- ↑ "The World Factbook". CIA. Retrieved 2017-08-01.
- ↑ "The "Oh-my-god-a Passage"". Motivator. Retrieved 2017-08-01.
- ↑ "Anegada Passage". SV Party of Five. Retrieved 2018-08-01.
- ↑ "Significant Earthquake". NOAA. Retrieved 2018-08-01.
- ↑ "Tsunami Simulations of the 1867 Virgin Island Earthquake: Constraints on Epicenter Location and Fault Parameters". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. Retrieved 2018-08-01.