Anacaona
| Anacaona | |
|---|---|
 Anacaona | |
| Born |
1474 Yaguana, Jaragua, present-day Léogâne, Haiti |
| Died |
c. 1503 Hispaniola |
| Spouse | Caonabo |
| Occupation | Cacica |
Anacaona (from Taíno anacaona, meaning 'golden flower'; from ana, meaning 'flower', and caona, meaning 'gold, golden'; 1474-1503) was a Taíno cacica (chief), born into a family of chiefs, and sister of Bohechío, chief of Jaragua. Her husband was Caonabo, chief of the nearby territory of Maguana (located in present-day Dominican Republic). Her brother and her husband were two of the five highest caciques who ruled the island of Kiskeya (Spanish: Quisqueya, now called Hispaniola) when the Spaniards colonized it in 1492. She was celebrated as a composer of ballads and narrative poems, called areítos.
Life
Anacaona was born in Yaguana, the capital of Jaragua (present day Léogâne, Haiti)[1], where her brother Bohechío was chieftain in 1474. During Christopher Columbus's visit in late 1496, Anacaona and Bohechío appeared as equal negotiators. On that occasion, described by Bartolomé de las Casas in Historia de las Indias, Columbus successfully negotiated for tribute of food and cotton to be paid by the natives to the Spanish under his command.
The visit is described as having taken place in a friendly atmosphere. Several months later, Columbus arrived with a caravel to collect a part of the tribute. Anacaona and Bohechío had sailed briefly aboard the caravel, near today's Léogâne in the Gulf of Gonâve as his guests. At first relations between natives and Conquistadors were cordial, the natives realizing too late their lands were actually being stolen and their subjects enslaved.

Anacaona's high status was probably strengthened by elements of matrilineal descent in the Taíno society, as described by Peter Martyr d'Anghiera. Taíno caciques usually passed inheritance to the eldest children of their sisters. If their sisters had no children, then they chose among the children of their brothers, and when there were none, they fell back upon one of their own.
Anacaona had one child, named Higuemota, whose dates of birth and death are lost to history.
Arrest and death
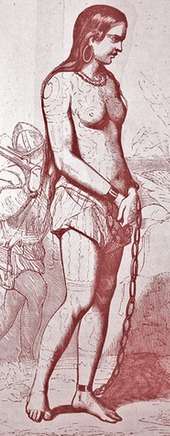

Anacaona became chief of Jaragua after her brother's death. Her husband Caonabo, suspected of having organized a recent attack on La Navidad (a Spanish settlement on north-western Hispaniola), was captured by Alonso de Ojeda and shipped to Spain, dying in a shipwreck during the journey — as many other Taíno leaders died on Spanish ships away from their native lands. The Taínos, being ill-treated by the conquerors, revolted and made a long war against them.
In 1503 during a meeting of 80 caciques, including Anacaona, the Spanish Governor Nicolás de Ovando ordered the meeting house to be set on fire to burn them alive,[2][3] similar to what centuries later occurred to Rigoberta Menchú's family in Guatemala. Cacica Anacaona and her Taíno noblemen were arrested — all accused of conspiracy for resisting occupation and executed.
Prior to her execution, Anacaona was offered clemency if she would give herself as concubine to one of the Spaniards, which was common in the era. Standing with her fellow Taínos in solidarity, the Caribbean indigenous female leader (cacica) chose execution over colluding with her Spanish enemy, her refusal cementing her legend. Anacaona remained rebellious and independent until her violent public death.
Because Anacaona refused the sexual offer of the Spanish intruders while others were shot, Anacaona was executed by hanging. She was only 29 years old.
Legacy
Her immortalization in the intertwining histories of Haiti and the Dominican Republic has resulted in the use of her name for various places in both countries. Many in Haiti claim her as a significant icon in early Haitian history and a primordial founder of their country.
Renowned Haitian American author Edwidge Danticat wrote an award-winning novel, from The Royal Diaries series, Anacaona: Golden Flower, Haiti, 1490, in dedication to the fallen chief, and a more recent novel has appeared about Anacaona, "Ayiti's Taíno Queen/Anacaona, La Reine Taíno d'Ayiti" by Maryse N. Roumain, PhD. She is immortalized in music by Haitian folk singers Ansy and Yole Dérose in "Anacaona", as well as by Puerto Rican salsa composer Tite Curet Alonso in his song "Anacaona" and in Irka Mateo's "Anacaona". Cheo Feliciano's first track of his first solo album, "Cheo", is "Anacaona".
See also
- Chiefdoms of Hispaniola
- Enriquillo
- Anti-Colonialism
- Female Native American leaders
Notes
- ↑ Hall, Michael R. (2012). Historical Dictionary of Haiti. Scarecrow Press. p. 158. ISBN 9780810878105.
- ↑ Floyd, Troy (1973). The Columbus Dynasty in the Caribbean, 1492-1526. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. pp. 61–63.
- ↑ Casas, Bartolomé de las (2007-01-09). A Brief Account of the Destruction of the Indies – via Project Gutenberg.
References
- Bartolomé de las Casas: A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies.
- Peter Martyr d'Anghiera: De Orbe Novo.
- Samuel M. Wilson: Hispaniola - Caribbean Chiefdoms in the Age of Columbus. The University of Alabama Press, 1990. ISBN 0-8173-0462-2.
Attribution
