''alpha''-Naphthoflavone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
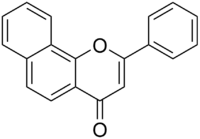
| IUPAC name
2-phenylbenzo[h]chromen-4-one | |
| Other names
7,8-Benzoflavone, ANF,2-phenylbenzo[h]chromen-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.156 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 272.30 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
alpha-Naphthoflavone, also known as 7,8-benzoflavone and 2-phenyl-benzo(h)chromen-4-one, is a synthetic[1][2] flavone derivative. It can be prepared from 2-naphthol and cinnamaldehyde.[3]
alpha-Naphthoflavone is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme aromatase, the enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen.[1][2] alpha-Naphthoflavone has been shown to cause abnormal testicular development in young chickens.[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 Campbell, Deborah R.; Kurzer, Mindy S. (1993). "Flavonoid inhibition of aromatase enzyme activity in human preadipocytes". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 46 (3): 381–388. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(93)90228-O. PMID 9831487.
- 1 2 Kellis JT Jr; Vickery LE (1984). "Inhibition of human estrogen synthetase (aromatase) by flavones". Science. 225 (4666): 1032–1034. doi:10.1126/science.6474163. PMID 6474163.
- ↑ Harvey, Ronald G.; Hahn, Jung Tai; Bukowska, Maria; Jackson, Henry (1990). "A new chromone and flavone synthesis and its utilization for the synthesis of potentially antitumorigenic polycyclic chromones and flavones". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 55 (25): 6161. doi:10.1021/jo00312a023.
- ↑ Trefil, P.; Micakova, A.; Stiborova, M.; Poplstein, M.; Brillard, J.P.; Hodek, P. (2004). "Effects of alpha-naphthoflavone on body growth and gonad development in chickens (Gallus domesticus)". Czech Journal of Animal Science - UZPI. 49 (6): 231–238.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.