Alameda Corridor
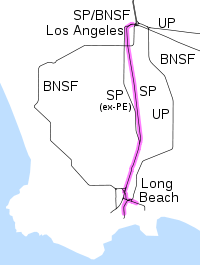
The Alameda Corridor is a 20-mile (32 km) freight rail "expressway"[1] owned by the Alameda Corridor Transportation Authority (reporting mark ATAX) that connects the national rail system near downtown Los Angeles, California, to the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach, running parallel to Alameda Street.[2] The corridor is considered one of the region's largest transportation projects in the past 20 years.[1]
Description


The project is notable for the Mid-Corridor Trench, a below-ground, triple-tracked rail line that is 10 miles (16 km) long, 33 feet (10 m) deep, and 50 feet (15 m) wide,[3] shared by the BNSF Railway and Union Pacific Railroad (UP)[1] via trackage rights. The Alameda Corridor allows trains to bypass 90 miles (140 km) of early 20th-century branch lines and the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway's historic Harbor Subdivision along a high-speed grade-separated corridor, built mainly on the alignment of a former Southern Pacific Railroad (SP) line, avoiding more than 200 street-level railroad crossings where automobiles previously had to wait for lengthy freight trains to pass.[4] Many of those same rail lines were inadequately protected with little more than “wigwag” crossing signals dating from the original construction of the lines. One important use of the corridor is to carry cargo containers to and from the ports. The corridor has a maximum speed of 40 miles per hour (64 km/h).
History
The Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles completed the purchase of SP's Alameda Corridor line for $235 million in December 1994.[5][6] The line began operation on April 15, 2002, and reached a peak of 60 train movements per day by October 2006.[7] It is credited with significantly relieving congestion on the Long Beach Freeway (I-710) and elsewhere in the region. In 2007 the line carried 17,824 trains carrying 4.7 million TEUs (20-foot equivalent units) of containers.[7]
Future development
Alameda Corridor East
The Alameda Corridor–East project, currently under construction, will grade-separate many of the crossings along UP's Alhambra Subdivision and the Los Angeles Subdivision. Many crossings, which are currently at grade, tie up traffic on north–south streets for long periods multiple times a day as long freight trains pass enroute to and from the UP yards in Vernon and Commerce. The project includes 19 grade separations and elimination of 23 grade crossings.[8]
Included as part of the Alameda Corridor–East project is the $336.9 million San Gabriel Trench, which will submerge the track between Ramona street and San Gabriel Boulevard in San Gabriel.[9] Construction began in 2012 and was completed in 2017.[10][11]
Along with federal and state funding, the project is funded in part by the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Redden, J. W.; Selig, E. T.; Zaremsbki, A. M. (February 2002). "Stiff track modulus considerations". RT&S: Railway Track & Structures. 98 (2): 25–30.
- ↑ Uranga, Rachel (October 20, 2016). "How an obscure Alameda Corridor rail agency avoided public accountability laws for years". Long Beach Press Telegram. Retrieved October 21, 2016.
- ↑ Fortner, Brian (September 2002). "The Train Lane". Civil Engineering. 72 (9): 52–61.
- ↑ Cerny, L. T. (May 2002). "Alameda corridor opens to traffic in L.A.". RT&S: Railway Track & Structures. 98 (5): 32.
- ↑ "Corridor Purchase". Alameda Corridor Transportation Authority. Retrieved 2006-03-12.
- ↑ Zamichow, Nora (September 9, 1993). "Wilson OKs Use of Eminent Domain to Create Railway Corridor: Transit: Governor urges that condemnation be used only as a last resort in talks with Southern Pacific, which wants $260 million for its route between Downtown and the Harbor area". Los Angeles Times.
- 1 2 "Corridor Statistics". Alameda Corridor Transportation Authority. Archived from the original on 2008-06-02. Retrieved 2008-07-23.
- ↑ "Alameda Corridor-East Construction Authority Project Overview".
- ↑ Ortega, Fred (2008-04-10). "State OKs funds for San Gabriel crossing". Pasadena Star News. Archived from the original on 10 February 2012.
- ↑ Aragon, Greg (December 11, 2015). "$1.6 billion Alameda Corridor-East Construction Project Gets Boost from CTC". Engineering News-Record.
- ↑ Pool, Bob (February 6, 2012). "At a planned train trench, an archaeological treasure trove". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Alameda Corridor. |