Wireless ad hoc network
A wireless ad hoc network[1] (WANET) or MANET (Mobile ad hoc network) is a decentralised type of wireless network.[2][3] The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks.[4] Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity and the routing algorithm in use.[5]
In the Windows operating system, ad-hoc is a communication mode (setting) that allows computers to directly communicate with each other without a router.
Wireless mobile ad hoc networks are self-configuring, dynamic networks in which nodes are free to move. Wireless networks lack the complexities of infrastructure setup and administration, enabling devices to create and join networks "on the fly" – anywhere, anytime.[6]
History on packet radio
The earliest wireless data network is called "packet radio" network, and was sponsored by Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in the early 1970s. Bolt, Beranek and Newman Technologies (BBN) and SRI International designed, built, and experimented with these earliest systems. Experimenters included Robert Kahn,[7] Jerry Burchfiel, and Ray Tomlinson.[8] Similar experiments took place in the amateur radio community with the x25 protocol. These early packet radio systems predated the Internet, and indeed were part of the motivation of the original Internet Protocol suite. Later DARPA experiments included the Survivable Radio Network (SURAN) project,[9] which took place in the 1980s. Another third wave of academic and research activity started in the mid-1990s with the advent of inexpensive 802.11 radio cards for personal computers. Current wireless ad-hoc networks are designed primarily for military utility.[10] Problems with packet radios are: (1) bulky elements, (2) slow data rate, (3) unable to maintain links if mobility is high. The project did not proceed much further until the early 1990s when wireless ad hoc networks are born.
Early work on MANET
In the early 1990s, Charles Perkins from SUN Microsystems USA, and Chai Keong Toh from Cambridge University separately started to work on a different Internet, that of a wireless ad hoc network. Perkins was working on the dynamic addressing issues. Toh worked on a new routing protocol, which was known as ABR – associativity-based routing.[11] Perkins eventually proposed DSDV – Destination Sequence Distance Vector routing, which was based on distributed distance vector routing. Toh's proposal was an on-demand based routing, i.e. routes are discovered on-the-fly in real-time as and when needed. ABR[12] was submitted to IETF as RFCs. ABR was implemented successfully into Linux OS on Lucent WaveLAN 802.11a enabled laptops and a practical ad hoc mobile network was therefore proven[2][13][14] to be possible in 1999. Another routing protocol known as AODV was subsequently introduced and later proven and implemented in 2005.[15] In 2007, David Johnson and Dave Maltz proposed DSR – Dynamic Source Routing.[16]
Applications
The decentralized nature of wireless ad-hoc networks makes them suitable for a variety of applications where central nodes can't be relied on and may improve the scalability of networks compared to wireless managed networks, though theoretical and practical limits to the overall capacity of such networks have been identified. Minimal configuration and quick deployment make ad hoc networks suitable for emergency situations like natural disasters or military conflicts. The presence of dynamic and adaptive routing protocols enables ad hoc networks to be formed quickly. Wireless ad-hoc networks can be further classified by their applications:
Mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs)
A mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a continuously self-configuring, self-organizing, infrastructure-less[17] network of mobile devices connected without wires. It is sometimes known as "on-the-fly" networks or "spontaneous networks".[18]
Vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs)
VANETs are used for communication between vehicles and roadside equipment. Intelligent vehicular ad hoc networks (InVANETs) are a kind of artificial intelligence that helps vehicles to behave in intelligent manners during vehicle-to-vehicle collisions, accidents. Vehicles are using radio waves to communicate with each other, creating communication networks instantly on-the-fly while vehicles are moving on the roads.
Smart phone ad hoc networks (SPANs)
A SPAN leverages existing hardware (primarily Wi-Fi and Bluetooth) and software (protocols) in commercially available smartphones to create peer-to-peer networks without relying on cellular carrier networks, wireless access points, or traditional network infrastructure. Most recently, Apple's iPhone with version 7.0 iOS and higher have been enabled with multi-peer ad hoc mesh networking capability,[19] in iPhones, allowing millions of smart phones to create ad hoc networks without relying on cellular communications. It has been claimed that this is going to "change the world".[20]
Wireless mesh networks
Mesh networks take their name from the topology of the resultant network. In a fully connected mesh, each node is connected to every other node, forming a "mesh". A partial mesh, by contrast, has a topology in which some nodes are not connected to others, although this term is seldom in use. Wireless ad hoc networks can take the form of a mesh networks or others. A wireless ad hoc network does not have fixed topology, and its connectivity among nodes is totally dependent on the behavior of the devices, their mobility patterns, distance with each other, etc. Hence, wireless mesh networks are a particular type of wireless ad hoc networks, with special emphasis on the resultant network topology. While some wireless mesh networks (particularly those within a home) have relatively infrequent mobility and thus infrequent link breaks, other more mobile mesh networks require frequent routing adjustments to account for lost links. Google Home, Google Wi-Fi, and Google OnHub all support Wi-Fi mesh (i.e., Wi-Fi ad hoc) networking.[21] Apple's AirPort allows the formation of wireless mesh networks at home, connecting various Wi-Fi devices together and providing good wireless coverage and connectivity at home.[22]
Army tactical MANETs
Army has been in need of "on-the-move" communications for a long time. Ad hoc mobile communications[23] come in well to fulfill this need, especially its infrastructureless nature, fast deployment and operation. Military MANETs are used by military units with emphasis on rapid deployment, infrastructureless, all-wireless networks (no fixed radio towers), robustness (link breaks are no problem), security, range, and instant operation. MANETs can be used in army "hopping" mines,[24] in platoons where soldiers communicate in foreign terrains, giving them superiority in the battlefield. Tactical MANETs can be formed automatically during the mission and the network "disappears" when the mission is over or decommissioned. It is sometimes called "on-the-fly" wireless tactical network.
Air Force UAV Ad hoc networks
Unmanned aerial vehicle, is an aircraft with no pilot on board. UAVs can be remotely controlled (i.e., flown by a pilot at a ground control station) or can fly autonomously based on pre-programmed flight plans. Civilian usage of UAV include modeling 3D terrains, package delivery (Amazon), etc.[25]
UAVs have also been used by US Air Force[26] for data collection and situation sensing, without risking the pilot in a foreign unfriendly environment. With wireless ad hoc network technology embedded into the UAVs, multiple UAVs can communicate with each other and work as a team, collaboratively to complete a task and mission. If a UAV is destroyed by an enemy, its data can be quickly offloaded wirelessly to other neighboring UAVs. The UAV ad hoc communication network is also sometimes referred to UAV instant sky network.
Navy ad hoc networks
Navy ships traditionally use satellite communications and other maritime radios to communicate with each other or with ground station back on land. However, such communications are restricted by delays and limited bandwidth. Wireless ad hoc networks enable ship-area-networks to be formed while at sea, enabling high speed wireless communications among ships, enhancing their sharing of imaging and multimedia data, and better co-ordination in battlefield operations.[27] Some defense companies (such as Rockwell Collins and Rohde & Schwartz) have produced products that enhance ship-to-ship and ship-to-shore communications.[28]
Wireless sensor networks
Sensors are useful devices that collect information related to a specific parameter, such as noise, temperature, humidity, pressure, etc. Sensors are increasingly connected via wireless to allow large scale collection of sensor data. With a large sample of sensor data, analytics processing can be used to make sense out of these data. The connectivity of wireless sensor networks rely on the principles behind wireless ad hoc networks, since sensors can now be deploy without any fixed radio towers, and they can now form networks on-the-fly. "Smart Dust" was one of the early projects done at U C Berkeley, where tiny radios were used to interconnect smart dust.[29] More recently, mobile wireless sensor networks (MWSNs) have also become an area of academic interest.
Ad hoc home smart lighting
ZigBee is a low power form of wireless ad hoc networks that is now finding their way in home automation. Its low power consumption, robustness and extended range inherent in mesh networking can deliver several advantages for smart lighting in homes and in offices. The control includes adjusting dimmable lights, color lights, and color or scene. The networks allow a set or subset of lights to be controlled over a smart phone or via a computer.[30] The home automation market is tipped to exceed $16 billion by 2019.
Ad hoc street light networks
Wireless ad hoc smart street light networks are beginning to evolve. The concept is to use wireless control of city street lights for better energy efficiency, as part of a smart city architectural feature.[31] Multiple street lights form a wireless ad hoc network. A single gateway device can control up to 500 street lights. Using the gateway device, one can turn individual lights ON, OFF or dim them, as well as find out which individual light is faulty and in need of maintenance.[32]
Ad hoc networked of robots
Robots are mechanical systems that drive automation and perform chores that would seem difficult for man. Efforts have been made to co-ordinate and control a group of robots to undertake collaborative work to complete a task. Centralized control is often based on a "star" approach, where robots take turns to talk to the controller station. However, with wireless ad hoc networks, robots can form a communication network on-the-fly, i.e., robots can now "talk" to each other and collaborate in a distributed fashion.[33] With a network of robots, the robots can communicate among themselves, share local information, and distributively decide how to resolve a task in the most effective and efficient way.[34]
Disaster rescue ad hoc network
Another civilian use of wireless ad hoc network is public safety. At times of disasters (floods, storms, earthquakes, fires, etc.), a quick and instant wireless communication network is necessary. Especially at times of earthquakes when radio towers had collapsed or were destroyed, wireless ad hoc networks can be formed independently. Firemen and rescue workers can use ad hoc networks to communicate and rescue those injured. Commercial radios with such capability are available on the market.[35][36]
Hospital ad hoc network
Wireless ad hoc networks allow sensors, videos, instruments, and other devices to be deployed and interconnected wirelessly for clinic and hospital patient monitoring, doctor and nurses alert notification, and also making senses of such data quickly at fusion points, so that lives can be saved.[37][38]
Challenges
Several books[3][39] and works have revealed the technical and research challenges[40][41] facing wireless ad hoc networks or MANETs. The advantages and challenges (cons) can be briefly summarized below:
Advantages
- Highly performing network.
- No expensive infrastructure must be installed
- Use of unlicensed frequency spectrum
- Quick distribution of information around sender
- No single point of failure.
Cons
- All network entities may be mobile ⇒ very dynamic topology
- Network functions must have high degree of adaptability
- No central entities ⇒ operation in completely distributed manner.
Radios for ad hoc
Wireless ad hoc networks can operate over different types of radios. They can be UHF (300 – 3000 MHz), SHF (3 – 30 GHz), and EHF (30 – 300 GHz). Wi-Fi ad hoc uses the unlicensed ISM 2.4 GHz radios. They can also be used on 5.8 GHz radios.
Next generation Wi-Fi known as 802.11ax provides low delay, high capacity (up to 10Gbit/s) and low packet loss rate, offering 12 streams – 8 streams at 5 GHz and 4 streams at 2.4 GHz. IEEE 802.11ax uses 8x8 MU-MIMO, OFDMA, and 80 MHz channels. Hence, 802.11ax has the ability to form high capacity Wi-Fi ad hoc networks.
At 60 GHz, there is another form of Wi-Fi known as WiGi – wireless gigabit. This has the ability to offer up to 7Gbit/s throughput. Currently, WiGi is targeted to work with 5G cellular networks.[42]
The higher the frequency, such as those of 300 GHz, absorption of the signal will be more predominant. Army tactical radios usually employ a variety of UHF and SHF radios, including those of VHF to provide a variety of communication modes. At the 800, 900, 1200, 1800 MHz range, cellular radios are predominant. Some cellular radios use ad hoc communications to extend cellular range to areas and devices not reachable by the cellular base station.
Protocol stack
The challenges[3][43] affecting MANETs span from various layers of the OSI protocol stack. The media access layer (MAC) has to be improved to resolve collisions and hidden terminal problems. The network layer routing protocol has to be improved to resolve dynamically changing network topologies and broken routes. The transport layer protocol has to be improved to handle lost or broken connections. The session layer protocol has to deal with discovery of servers and services.
A major limitation with mobile nodes is that they have high mobility, causing links to be frequently broken and reestablished. Moreover, the bandwidth of a wireless channel is also limited, and nodes operate on limited battery power, which will eventually be exhausted. Therefore, the design of a mobile ad hoc network is highly challenging, but this technology has high prospects to be able to manage communication protocols of the future.
The cross-layer design deviates from the traditional network design approach in which each layer of the stack would be made to operate independently. The modified transmission power will help that node to dynamically vary its propagation range at the physical layer. This is because the propagation distance is always directly proportional to transmission power. This information is passed from the physical layer to the network layer so that it can take optimal decisions in routing protocols. A major advantage of this protocol is that it allows access of information between physical layer and top layers (MAC and network layer).
Some elements of the software stack were developed to allow code updates in situ, i.e., with the nodes embedded in their physical environment and without needing to bring the nodes back into the lab facility.[44] Such software updating relied on epidemic mode of dissemination of information and had to be done both efficiently (few network transmissions) and fast.
Routing
Routing[45] in wireless ad hoc networks or MANETs generally falls into three categories, namely: (a) proactive routing, (b) reacting routing, and (c) hybrid routing.
Proactive routing
This type of protocols maintains fresh lists of destinations and their routes by periodically distributing routing tables throughout the network. The main disadvantages of such algorithms are:
- Respective amount of data for maintenance.
- Slow reaction on restructuring and failures.
Example: Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR)
Distance vector routing
As in a fix net nodes maintain routing tables. Distance-vector protocols are based on calculating the direction and distance to any link in a network. "Direction" usually means the next hop address and the exit interface. "Distance" is a measure of the cost to reach a certain node. The least cost route between any two nodes is the route with minimum distance. Each node maintains a vector (table) of minimum distance to every node. The cost of reaching a destination is calculated using various route metrics. RIP uses the hop count of the destination whereas IGRP takes into account other information such as node delay and available bandwidth.
Reactive routing
This type of protocol finds a route based on user and traffic demand by flooding the network with Route Request or Discovery packets. The main disadvantages of such algorithms are:
- High latency time in route finding.
- Excessive flooding can lead to network clogging.[46]
However, clustering can be used to limit flooding. The latency incurred during route discovery is not significant compared to periodic route update exchanges by all nodes in the network.
Example: Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Routing (AODV)
Flooding
Is a simple routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on. Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as Usenet and peer-to-peer file sharing and as part of some routing protocols, including OSPF, DVMRP, and those used in wireless ad hoc networks.
Hybrid routing
This type of protocol combines the advantages of proactive and reactive routing. The routing is initially established with some proactively prospected routes and then serves the demand from additionally activated nodes through reactive flooding. The choice of one or the other method requires predetermination for typical cases. The main disadvantages of such algorithms are:
- Advantage depends on number of other nodes activated.
- Reaction to traffic demand depends on gradient of traffic volume.[47]
Example: Zone Routing Protocol (ZRP)
Position-based routing
Position-based routing methods use information on the exact locations of the nodes. This information is obtained for example via a GPS receiver. Based on the exact location the best path between source and destination nodes can be determined.
Example: "Location-Aided Routing in mobile ad hoc networks" (LAR)
Technical requirements for implementation
An ad hoc network is made up of multiple "nodes" connected by "links."
Links are influenced by the node's resources (e.g., transmitter power, computing power and memory) and behavioral properties (e.g., reliability), as well as link properties (e.g. length-of-link and signal loss, interference and noise). Since links can be connected or disconnected at any time, a functioning network must be able to cope with this dynamic restructuring, preferably in a way that is timely, efficient, reliable, robust, and scalable.
The network must allow any two nodes to communicate by relaying the information via other nodes. A "path" is a series of links that connects two nodes. Various routing methods use one or two paths between any two nodes; flooding methods use all or most of the available paths.[48]
Medium-access control
In most wireless ad hoc networks, the nodes compete for access to shared wireless medium, often resulting in collisions (interference).[49] Collisions can be handled using centralized scheduling or distributed contention access protocols.[49] Using cooperative wireless communications improves immunity to interference by having the destination node combine self-interference and other-node interference to improve decoding of the desired signals.
Software reprogramming
Large-scale ad hoc wireless networks may be deployed for long periods of time. During this time the requirements from the network or the environment in which the nodes are deployed may change. This can require modifying the application executing on the sensor nodes, or providing the application with a different set of parameters. It may be very difficult to manually reprogram the nodes because of the scale (possibly hundreds of nodes) and the embedded nature of the deployment, since the nodes may be located in places that are difficult to access physically. Therefore, the most relevant form of reprogramming is remote multihop reprogramming using the wireless medium which reprograms the nodes as they are embedded in their sensing environment. Specialized protocols have been developed for the embedded nodes which minimize the energy consumption of the process as well as reaching the entire network with high probability in as short a time as possible.[44][50]
Mathematical models
The traditional model is the random geometric graph. Early work included simulating ad hoc mobile networks on sparse and densely connected topologies. Nodes are firstly scattered in a constrained physical space randomly. Each node then has a predefined fixed cell size (radio range). A node is said to be connected to another node if this neighbor is within its radio range. Nodes are then moved (migrated away) based on a random model, using random walk or brownian motion. Different mobility and number of nodes present yield different route length and hence different number of multi-hops.
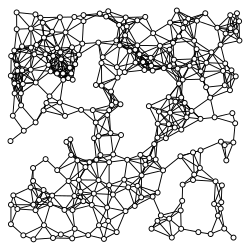
These are graphs consisting of a set of nodes placed according to a point process in some usually bounded subset of the n-dimensional plane, mutually coupled according to a boolean probability mass function of their spatial separation (see e.g. unit disk graphs). The connections between nodes may have different weights to model the difference in channel attenuations.[49] One can then study network observables (such as connectivity,[51] centrality[52] or the degree distribution[53]) from a graph-theoretic perspective. One can further study network protocols and algorithms to improve network throughput and fairness.[49]
Security
Most wireless ad hoc networks do not implement any network access control, leaving these networks vulnerable to resource consumption attacks where a malicious node injects packets into the network with the goal of depleting the resources of the nodes relaying the packets.[54]
To thwart or prevent such attacks, it was necessary to employ authentication mechanisms that ensure that only authorized nodes can inject traffic into the network.[55] Even with authentication, these networks are vulnerable to packet dropping or delaying attacks, whereby an intermediate node drops the packet or delays it, rather than promptly sending it to the next hop.
Simulation
One key problem in wireless ad hoc networks is foreseeing the variety of possible situations that can occur. As a result, modeling and simulation (M&S) using extensive parameter sweeping and what-if analysis becomes an extremely important paradigm for use in ad hoc networks. Traditional M&S tools include OPNET, and NetSim.
See also
References
- ↑ "Wireless ATM & Ad Hoc Networks, 1997, Kluwer Academic Press".
- 1 2 Chai Keong Toh Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks, Prentice Hall Publishers, 2002. ISBN 978-0-13-007817-9
- 1 2 3 C. Siva Ram Murthy and B. S. Manoj, Ad hoc Wireless Networks: Architectures and Protocols, Prentice Hall PTR, May 2004. ISBN 978-0-13-300706-0
- ↑ Morteza M. Zanjireh; Hadi Larijani (May 2015). A Survey on Centralised and Distributed Clustering Routing Algorithms for WSNs (PDF). IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference. Glasgow, Scotland. doi:10.1109/VTCSpring.2015.7145650.
- ↑ Morteza M. Zanjireh; Ali Shahrabi; Hadi Larijani (2013). ANCH: A New Clustering Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks (PDF). 27th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops. WAINA 2013. doi:10.1109/WAINA.2013.242.
- ↑ Chai Keong Toh. Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks. United States: Prentice Hall Publishers, 2002.
- ↑ "Robert ("Bob") Elliot Kahn". A.M. Turing Award. Association for Computing Machinery.
- ↑ J. Burchfiel; R. Tomlinson; M. Beeler (May 1975). Functions and structure of a packet radio station (PDF). National Computer Conference and Exhibition. pp. 245–251. doi:10.1145/1499949.1499989.
- ↑ Beyer, Dave (October 1990). "Accomplishments of the DARPA SURAN Program - IEEE Conference Publication". ieeexplore.ieee.org. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ↑ American Radio Relay League. "ARRL's VHF Digital Handbook", p 1-2, American Radio Relay League,2008
- ↑ Chai Keong Toh Associativity-Based Routing for Ad Hoc Mobile Networks, Wireless Personal Communications Journal, 1997.
- ↑ Chai Keong Toh IETF MANET DRAFT: Long-lived Ad Hoc Routing based on the Concept of Associativity
- ↑ "Experimenting with an Ad Hoc Wireless Network on Campus: Insights & Experiences", ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2001".
- ↑ ""Implementation of Ad Hoc Mobile Networks", Chapter 7 of BOOK: Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks, Prentice Hall, 2001, ISBN 0-13-007817-4".
- ↑ "AODV Implementation Design and Performance Evaluation" by Ian D. Chakeres
- ↑ The Dynamic Source Routing Protocol (DSR) for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for IPv4
- ↑ "Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks:Protocols and Systems, 2001".
- ↑ "Spontaneous Networking by Laura Feeney, IEEE Communications, 2001".
- ↑ "MultipeerConnectivity from Apple".
- ↑ "How an Underappreciated iOS 7 Feature Will Change the World by Mike Elgan".
- ↑ ""Everyone is a node: How Wi-Fi Mesh Networking Works by Jerry Hildenbrand, 2016".
- ↑ "Apple's AirPort in the age of mesh networking by Rene Ritchie, 2016".
- ↑ "Soldier Link System (SLS) using Ad hoc networks by Northrop Grumman".
- ↑ "DARPA Hopping Mines using Ad Hoc Networking Technology".
- ↑ "The future is here: Five applications of UAV technology".
- ↑ "U.S. Air Force Chief Scientist: Stealth Drones and Killer Swarms Could Be Coming Soon".
- ↑ "We connect your naval forces by Rohde & schwartz" (PDF).
- ↑ "The first fully mobile, cross-platform ad hoc IP network utilizing legacy radio systems".
- ↑ "A Study on Smart Dust Networks, Linkoping University, 2011".
- ↑ "Mesh Networking, the Critical Open Sesame for Smart Lighting Success, 2016".
- ↑ "Smart Street Lights Wireless Mesh Networks, Telensa, UK".
- ↑ "Smart Street Lights from Maven".
- ↑ "Protocols and Applications of Ad-hoc Robot Wireless Communication Networks: An Overview" (PDF).
- ↑ "Ad-hoc Wireless Network Coverage with Networked Robots that cannot Localize, 2009" (PDF).
- ↑ "GoTenna Militrary-Grade Mesh Networking" (PDF).
- ↑ "GoTenna Pro meshing radio aspires to deploy next to rescue, fire and security teams".
- ↑ "BigNurse: A Wireless Ad Hoc Network for Patient Monitoring, 2006".
- ↑ "The home health care with the ad-hoc network system, 2007".
- ↑ "Wireless ATM & Ad Hoc Networks, 1997, Kluwer Academic Press".
- ↑ "Research Challenges for Ad hoc mobile wireless networks, University of Essex, 2005".
- ↑ "An Overview of Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Applications and Challenges" (PDF).
- ↑ "Making Sense on what's happening on Wi-Fi".
- ↑ "Wireless ATM & Ad Hoc Networks, 1997, Kluwer Academic Press".
- 1 2 Panta, Rajesh Krishna; Bagchi, Saurabh; Midkiff, Samuel P. (February 2011). "Efficient Incremental Code Update for Sensor Networks". ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 7 (4): 30:1–30:32. doi:10.1145/1921621.1921624. ISSN 1550-4859.
- ↑ "A review of current routing protocols for ad hoc mobile wireless networks by EM Royer, CK Toh in IEEE Personal Communications, 1999".
- ↑ C. Perkins, E. Royer and S. Das: Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV) Routing, RFC 3561
- ↑ Roger Wattenhofer. Algorithms for Ad Hoc Networks.
- ↑ Wu S.L., Tseng Y.C., "Wireless Ad Hoc Networking, Auerbach Publications", 2007 ISBN 978-0-8493-9254-2
- 1 2 3 4 Guowang Miao; Guocong Song (2014). Energy and spectrum efficient wireless network design. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 1107039886.
- ↑ Hui, Jonathan W.; Culler, David (2004). "The Dynamic Behavior of a Data Dissemination Protocol for Network Programming at Scale". Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems. SenSys '04. New York, NY, USA: ACM: 81–94. doi:10.1145/1031495.1031506. ISBN 1581138792.
- ↑ M.D. Penrose. "Connectivity of Soft Random Geometric Graphs". The Annals of Applied Probability. 26: 986–1028. arXiv:1311.3897. doi:10.1214/15-AAP1110.
- ↑ A.P. Giles; O. Georgiou; C.P. Dettmann. "Betweenness Centrality in Dense Random Geometric Networks". 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC). arXiv:1410.8521. doi:10.1109/ICC.2015.7249352.
- ↑ M.D. Penrose (2003). "Random Geometric Graphs". Oxford University Press.
- ↑ "The Resurrecting Duckling: Security Issues for Ad-hoc Wireless Networks by Stajano and Anderson, International Workshop on Security Protocols, 1999".
- ↑ Sencun Zhu; Shouhuai Xu; Sanjeev Setia; Sushil Jajodia (2003). "LHAP: A Lightweight Hop-by-Hop Authentication Protocol For Ad-Hoc Networks" (PDF). doi:10.1109/ICDCSW.2003.1203642.